Search Results
Results for: 'Resting membrane potential'
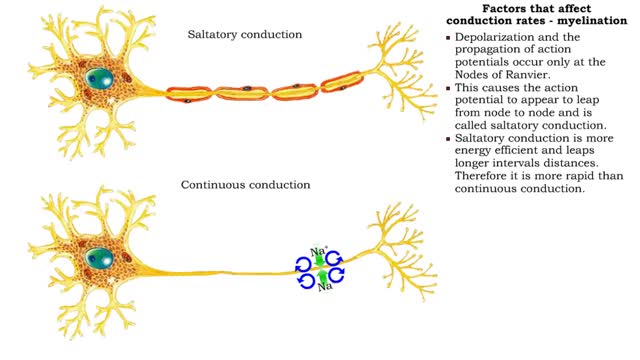
Factors that affect conduction rates (myelination, axon diameter & temperature)
By: HWC, Views: 11798
• Several factors determine the rate of conduction of action potentials: • Myelination • Axon diameter • Temperature • The step-by-step depolarization of an axon is called continuous conduction and occurs along unmyelinated axons. • Neurons in the PNS have many axons that ...
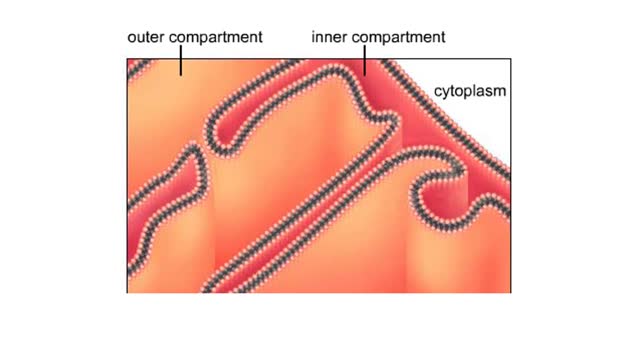
Functional zones in a mitochondrion
By: HWC, Views: 9538
A mitochondrion has a double membrane system. The outer membrane faces the cytoplasm. The inner membrane divides the organelles interior into two compartments. The enzymes that carry out the second stage reactions are in the semifluid matrix inside the inner compartment. Embedded in the ...
Olfaction. or the sense of smell
By: HWC, Views: 9129
Do you ever wonder how you can distinguish thousands of different odors? Olfaction. or the sense of smell, is used by all mammals to navigate, find food, and even find mates. We have millions of olfactory receptors for smelling in our nose. These receptor neurons bind water-soluble or volatil...
By: Administrator, Views: 15275
Dendrites (from Greek δένδρον déndron, "tree"), also dendrons, are branched protoplasmic extensions of a nerve cell that propagate the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body, or soma, of the neuron from which the dendrites project. Electrical stimula...
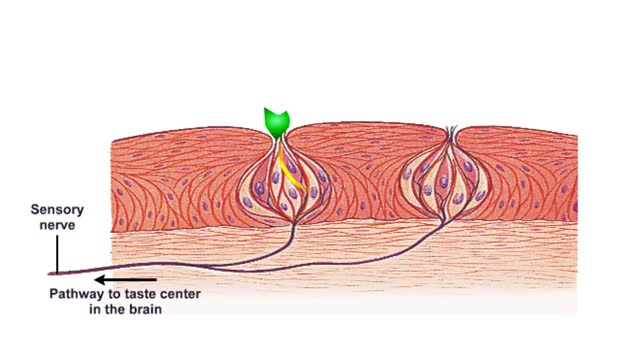
What are Taste Receptors? How Does it Work? Animation
By: HWC, Views: 8554
Do you ever wonder how you can taste the foods you eat? It all starts with taste receptors in your muscular tongue. Taste receptor neurons are found in your taste buds but you are not looking at the taste buds. The raised bumps on the surface of the tongue that you see are specialized epith...
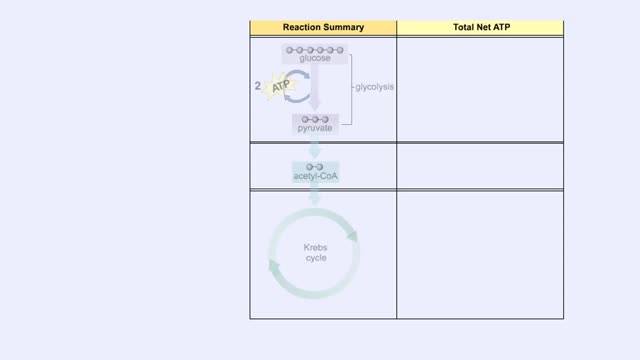
ETC Protein Complexes & Chemiosmosis (Total ATP Production and ATP Synthase)
By: HWC, Views: 11379
You will notice that FADH2 donates two electrons further downstream than NADH. This results in only two protons being pumped across the inner membrane. The final electron acceptor for these transported electrons is oxygen. Oxygen receives these electrons, plus protons from the aqueous matrix. ...
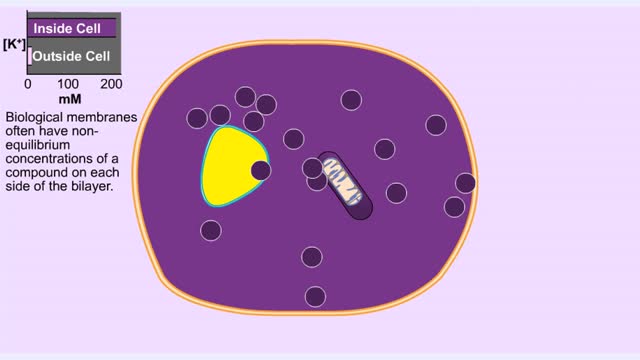
Membrane Protein and Facilitated Transport (Passive Vs Active)
By: HWC, Views: 11316
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins span the membrane, with hydrophobic amino acids interacting with the lipid bilayer and hy...
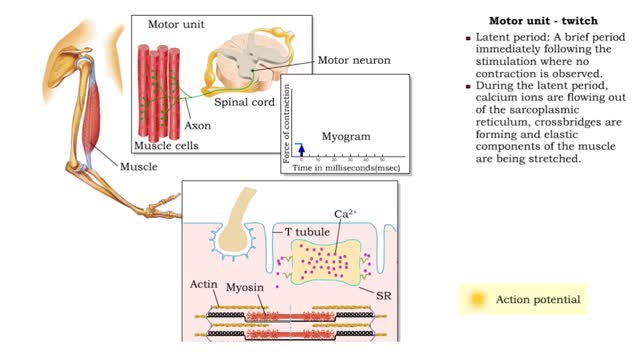
Muscle Twitch and Muscle Tension - Motor unit size and force
By: HWC, Views: 11920
• A motor unit is a group of muscle cells controlled by a single neuron. • A stimulus of sufficient intensity will cause all the cells in the motor unit to contract. • A single contraction, caused by a single action potential, is called a muscle twitch. • Latent period: A brief per...
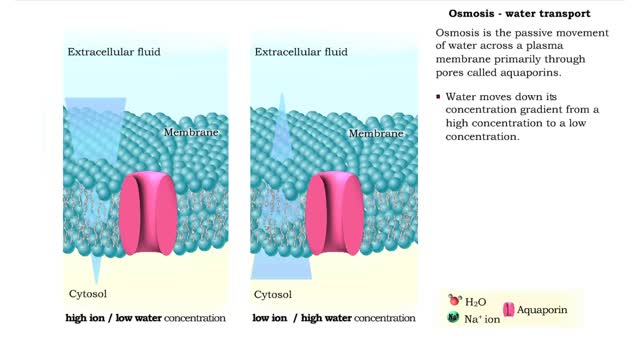
By: HWC, Views: 11844
Osmosis is the flow of water down its concentration gradient, across a semi-permeable membrane. Osmosis is an example of diffusion, which is when molecules tend to distribute themselves evenly in a space. what is a semi-permeable membrane? It is a membrane or barrier that allows some molec...
Advertisement