Search Results
Results for: 'blood flow'
By: HWC, Views: 11009
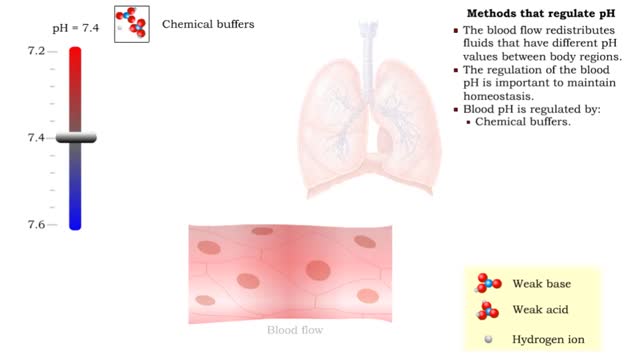
• The blood flow redistributes fluids that have different pH values between body regions. • The regulation of the blood pH is important to maintain homeostasis. • Blood pH is regulated by: • Chemical buffers. • The respiratory system. • The urinary system. • All thes...
Coronary Heart Disease Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14339
Arteriosclerotic heart disease occurs when arterial vessels are marked by thickening, hardening, and loss of elasticity in arterial walls. Course of cardiovascular disease accelerates due to: Reduced blood flow Rlevated blood lipids Defective endothelial repair
Blood Flow Through the Kidneys
By: Administrator, Views: 13642
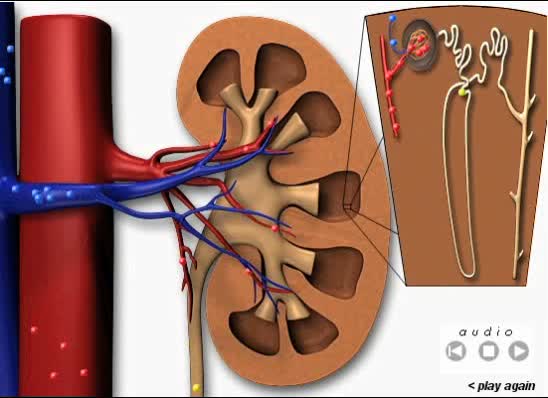
Purplish-brown, bean-shaped organs located behind abdominal cavity (retroperitoneal area) on either side of spine, between thoracic vertebrae and lumbar region.
Cortisol (protein catabolism, gluconeogenesis, vasoconstriction & anti-inflammation)
By: HWC, Views: 10627
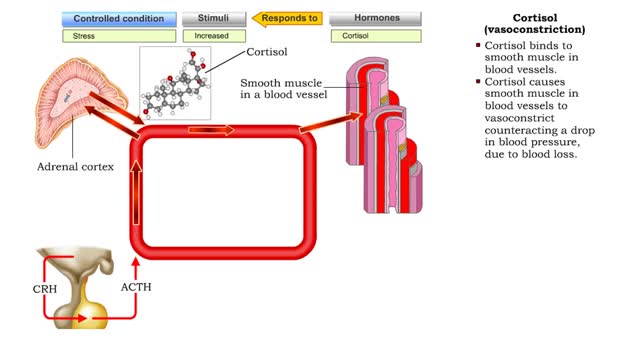
• Stressors stimulate production of hypothalamic releasing hormones, corticotropin releasing hormone, hormone (CRH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulate. • These hormones promote increased production of 1 cortisol from the zona fasciculata cells of the adrenal cortex. • Cort...
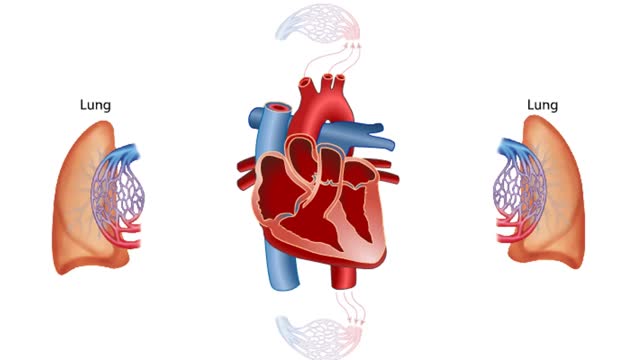
Blood Flow through the Human Heart
By: HWC, Views: 10753
The heart is the pump of the human circulatory system. The left side of the heart has two connected chambers, the left atrium and the left ventricle. The right side of the heart also has two connected chambers, the right atrium and the right ventricle. These two sides, or pumps, of the heart are ...
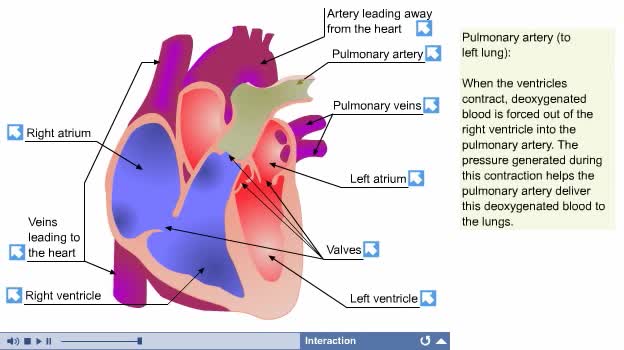
By: Administrator, Views: 13947
Circulation of blood through the chambers of the heart Septum divides heart into the right and left heart. Each side contains an upper and lower chamber: Atria, or upper chambers, receive blood. Ventricles, or lower chambers, pump blood. Valves control intake and outflow of blood in chamber...
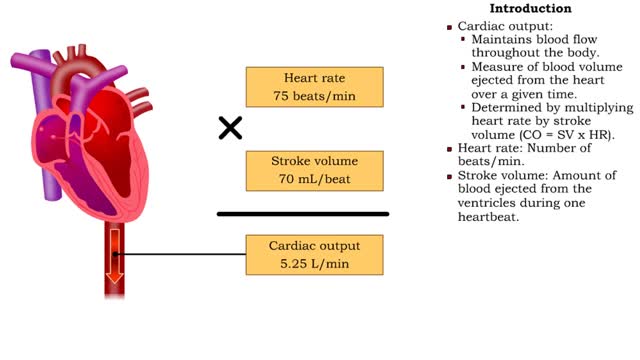
By: HWC, Views: 10657
• Cardiac output: • Maintains blood flow throughout the body. • Measure of blood volume ejected from the heart over a given time. • Determined by multiplying heart rate by stroke volume (CO = SV x HR). • Heart rate: Number of beats/min. • Stroke volume: Amount of blood eject...
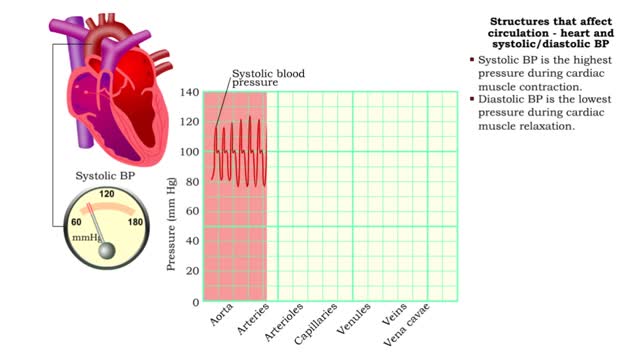
Structures that affect circulation - heart and systolic/diastolic BP
By: HWC, Views: 10835
• Heart generates blood pressure. • Arterioles produce resistance thereby regulating blood flow to tissues. • Veins store blood; kidneys regulate blood volume; both affect venous return and cardiac output. ■ Contractions of the ventricles determine blood pressure, which drives th...
By: Administrator, Views: 14327
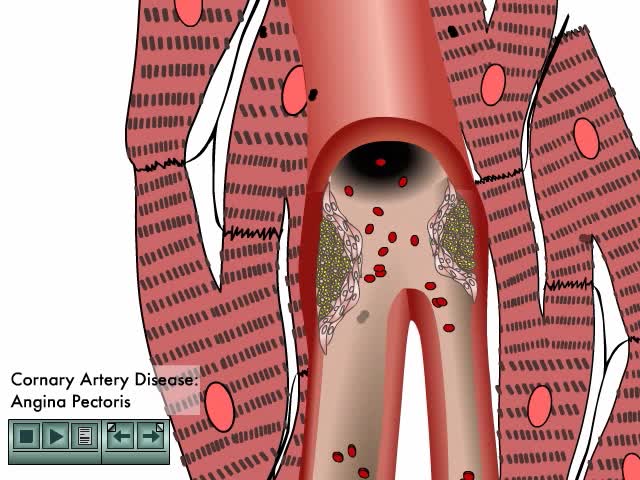
Angina is a type of chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. Angina (an-JIE-nuh or AN-juh-nuh) is a symptom of coronary artery disease. Angina, which may also be called angina pectoris, is often described as squeezing, pressure, heaviness, tightness or pain in your chest.
Advertisement