Search Results
Results for: 'electrons'
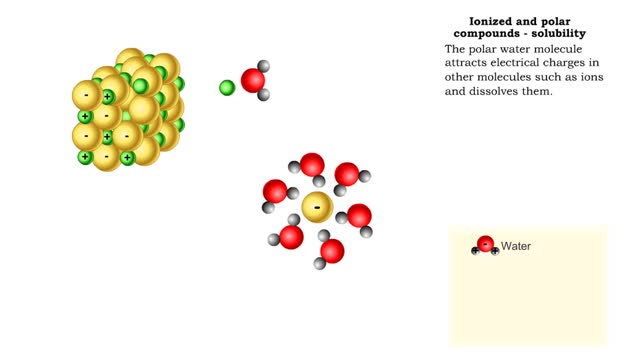
Properties of water -structure of water and polarity (Ionized and polar compounds)
By: HWC, Views: 11487
■ Water transports most of the molecules in the body. ■ The structure of a water molecule allows it to dissolve other molecules. ■ Shared electrons spend more time near the oxygen atom. ■ Oxygen end has a partial negative charge. ■ Hydrogen ends have a partial positive charge....
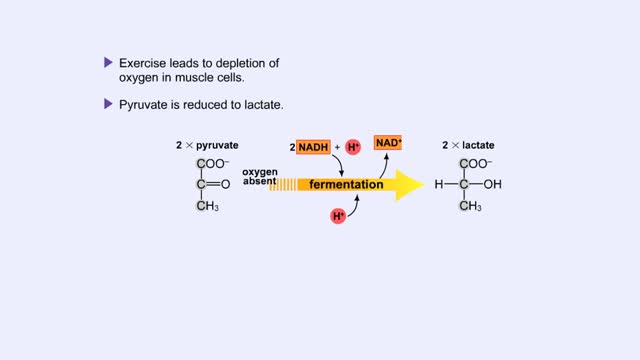
Fermentation - When Oxygen Is Absent, Pyruvate to Lactate & Pyruvate to Ethanol
By: HWC, Views: 10819
Pyruvate is the end product of glycolysis. If oxygen is present, pyruvate enters the mitochondrion where further energy yielding reactions of the Krebs cycle will take place. However, if oxygen is not present, pyruvate will enter a pathway called fermentation. This pathway regenerates NAD+ fro...
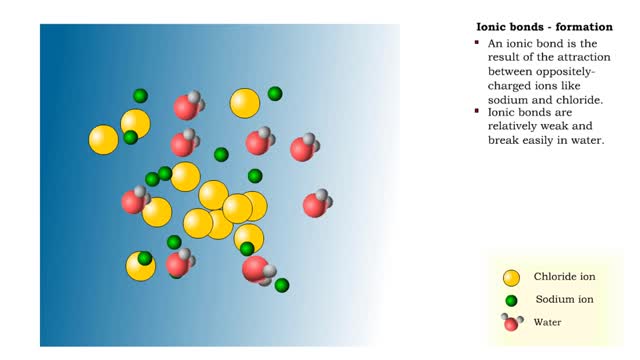
Ionic bonds - role of ions in the body
By: HWC, Views: 11633
Ions • Atoms fill up the outer orbital by transferring electrons from one atom to another. • Atoms now bear a charge and are called ions. • Sodium ion, losing an electron, has a +1 charge. • Chlorine ion, gaining an electron, has a -1 charge. Formation • An ionic bond is t...
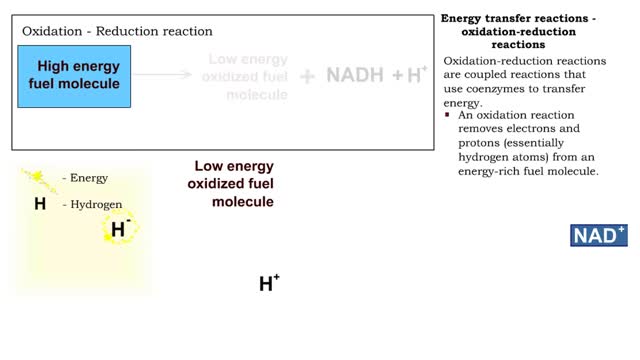
Types of energy transfer reactions: oxidation-reduction reactions and ATP generation reactions
By: HWC, Views: 11952
■ Metabolism balances anabolic and catabolic reactions. ■ Anabolism is energy transfer from ATP to simpler molecules in order to build them up into larger, more complex molecules. ■ Catabolism is breaking down larger, more complex molecules, usually to transfer energy from them in order...
Advertisement