Search Results
Results for: 'generate ATP.'
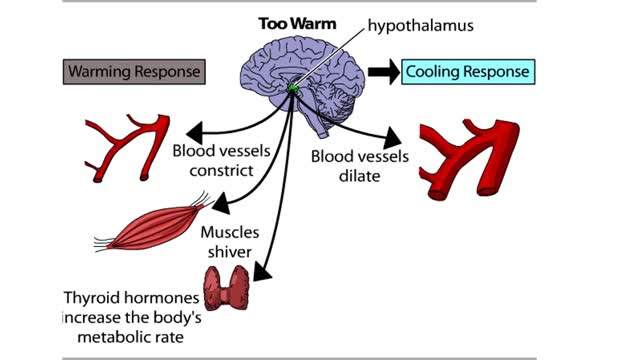
The Hypothalamus: The Body's Thermostat (Human Thermostat)
By: HWC, Views: 10784
Normal body function requires a relatively constant body temperature, which is regulated by the body's thermostat, a region of the brain called the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus generates a temperature set point for the body and appears to be the major site for the integration of temperature inf...
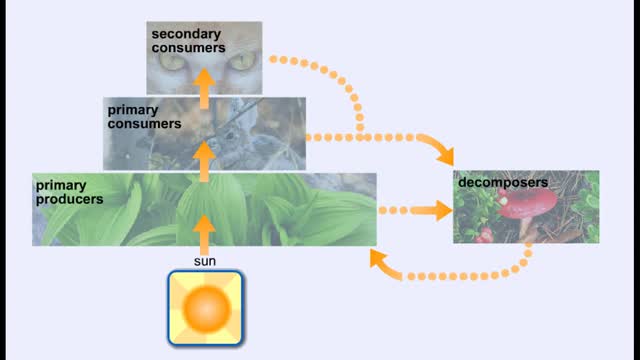
Energy Flow - Trophic Levels and Food
By: HWC, Views: 11178
All of these relationships between different species are founded on one thing: energy. Organisms get food in order to get energy, which is used by the organism for growth, maintaining health, and reproduction. We can classify the members of a community according to how they obtain food. Produc...
By: HWC, Views: 12374
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
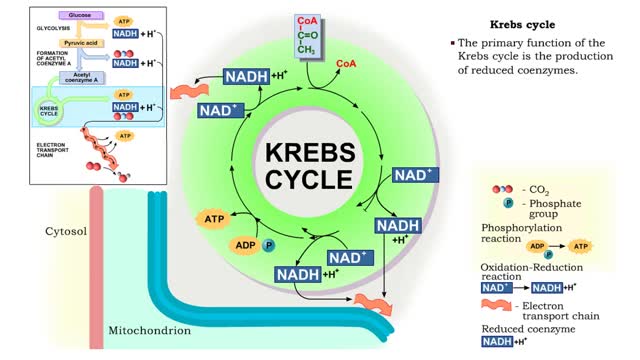
Krebs cycle : Formation of acetyl coenzyme A and Electron transport chain
By: HWC, Views: 11846
The oxidation of glucose to produce ATP is cellular respiration. Four sets of reactions are involved: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Krebs cycle reactions Electron transport chain reactions • The second pathway of glucose catabolism, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, is a transi...
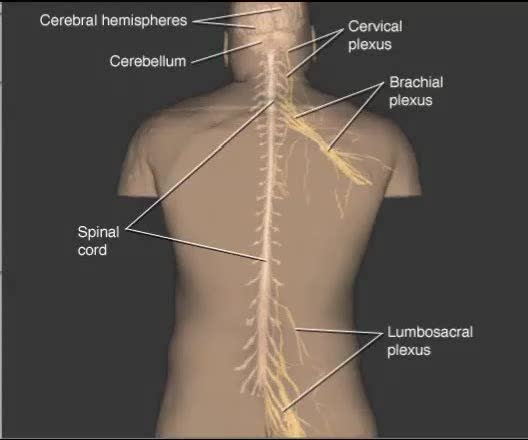
Components of the Nervous System
By: Administrator, Views: 549
The nervous system is the part of an animal that coordinates its actions by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. Nervous tissue...
Advertisement