Search Results
Results for: 'homeworkclinic.com%20Homework%20Clinic%20HWC%20active%20processes%20passive%20processes%20Vesicular%20transport%20Active%20transport%20Simple%20diffusion%20Facilitated%20diffusion%20Osmosis%20concentration%20gradient%20bilayer'
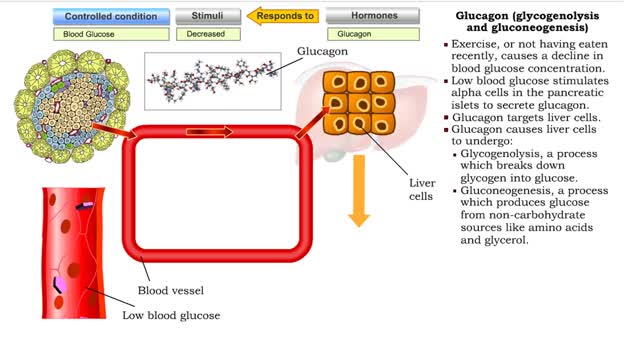
Glucagon (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 6519
• Exercise, or not having eaten recently, causes a decline in blood glucose concentration. • Low blood glucose stimulates alpha cells in the pancreatic islets to secrete glucagon. • Glucagon targets liver cells. • Glucagon causes liver cells to undergo: • Glycogenolysis, a proce...
By: HWC, Views: 6914
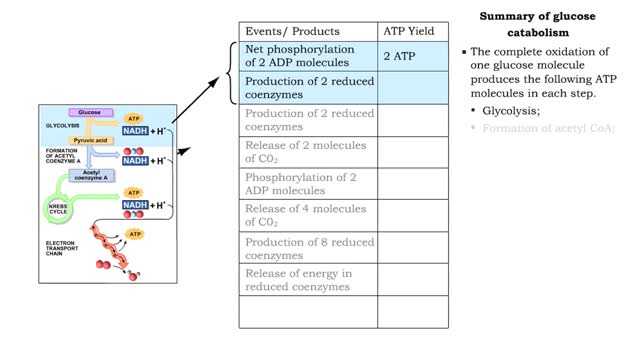
■ The complete oxidation of one glucose molecule produces the following ATP molecules in each step. • Glycolysis; • Formation of acetyl CoA; • Krebs cycle; • Electron transport chain. ■ In addition, glucose catabolism produces six CO2 molecules and water.
Cavernous Sinus Larynx Middle Ear Orbit: Granulesm Animation
By: HWC, Views: 6149
The cavernous sinuses are located within the middle cranial fossa, on either side of the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone (which contains the pituitary gland). The cavernous sinuses, a rich plexuses of veins that surround the internal carotid arteries, lie lateral to the pituitary fossa. Ant...
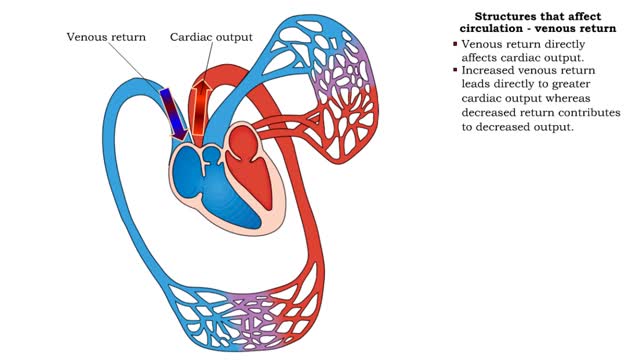
Structures that affect circulation - venous return
By: HWC, Views: 6465
• Venous return directly affects cardiac output. • Increased venous return leads directly to greater cardiac output whereas decreased return contributes to decreased output. • Venous return depends on: • Blood volume regulation by the kidneys. • Venous tone. • Skeletal muscl...
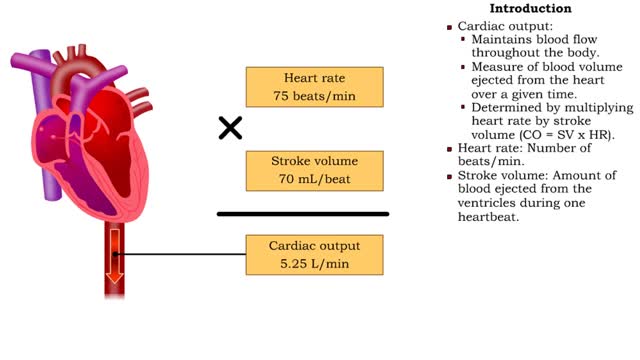
By: HWC, Views: 6468
• Cardiac output: • Maintains blood flow throughout the body. • Measure of blood volume ejected from the heart over a given time. • Determined by multiplying heart rate by stroke volume (CO = SV x HR). • Heart rate: Number of beats/min. • Stroke volume: Amount of blood eject...
Simple Diffusion - Ion transport
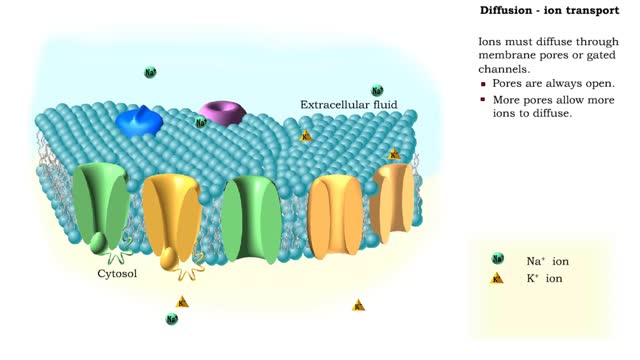
By: HWC, Views: 6714
In the process of diffusion, a substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until its concentration becomes equal throughout a space. Ions must diffuse through membrane pores or gated channels. Pores are always open. More pores allow more ions...
Simple Diffusion - gases and nonpolar compounds transport
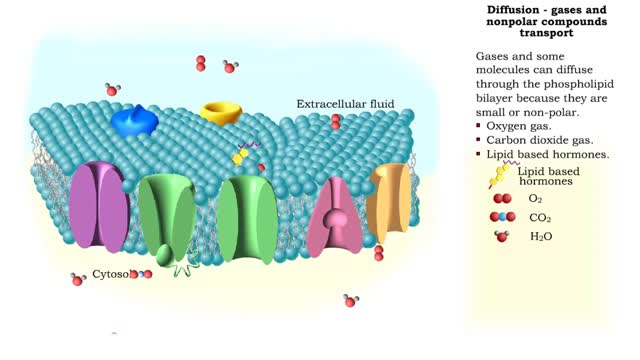
By: HWC, Views: 6980
Gases and some molecules can diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer because they are small or non-polar. Oxygen gas. Carbon dioxide gas. Lipid based hormones. Plasma membranes are selectively permeable: The lipid bilayer is always permeable to small, nonpolar, uncharged molecules ...
Bacteriophage (Virus) - Mice Experiment
By: HWC, Views: 6389
Also known as phages, these viruses can be found everywhere bacteria exist including, in the soil, deep within the earth's crust, inside plants and animals, and even in the oceans. Bacteriophages (phages) are viruses of bacteria that can kill and lyse the bacteria they infect. ... The lethalit...
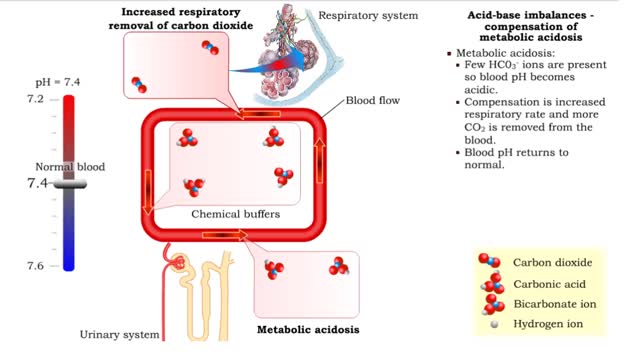
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 6926
1. Metabolic acidosis: • Few HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased respiratory rate and more CO2 is removed from the blood. • Blood pH returns to normal. 2. Metabolic alkalosis: • Many HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes alkaline...
Advertisement