Search Results
Results for: 'plant height'
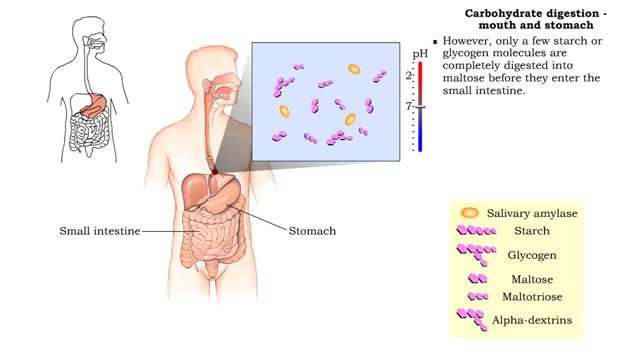
Carbohydrate digestion - mouth and stomach & pancreas and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 10842
• Digestion of complex carbohydrates (starches and glycogen) involves: • Amylases produced by the salivary glands and pancreas. • Brush-border enzymes in small intestine. • In the mouth, amylase from the parotid and submandibular salivary glands begins carbohydrate digestion. �...
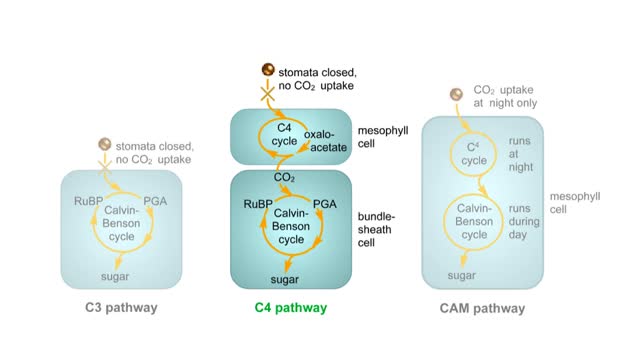
Carbon fixing adaptations Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5220
Different plants trap carbon by different pathways. Most C3 plants evolved in moist, temperate zones. On hot dry days they close their stomata to conserve water and oxygen accumulates. Under these circumstances, the enzyme rubisco uses oxygen in an inefficient reaction that competes with t...
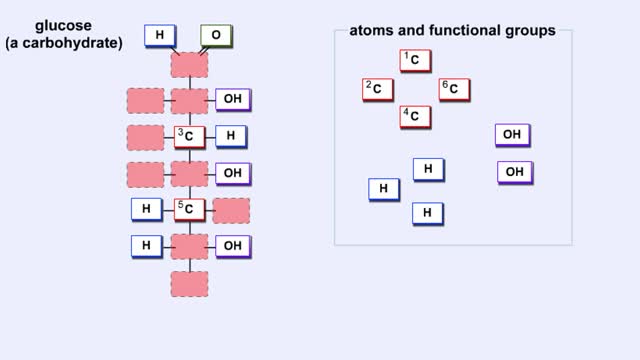
What Are Carbohydrates? Importance of Carbs & High Carb Food
By: HWC, Views: 11149
We hear a lot about carbohydrates in the news. Everybody seems to be on a low-carb diet. The news media often has stories on this diet fad, and companies are busy producing products with reduced carbohydrates. What's this fascination with carbohydrates? In a word: "Diet." The fact is that carb...
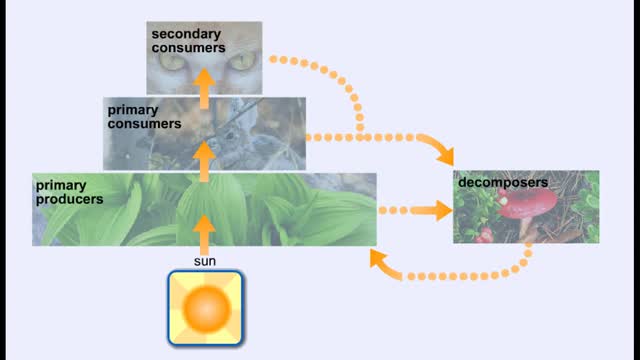
Energy Flow - Trophic Levels and Food
By: HWC, Views: 10607
All of these relationships between different species are founded on one thing: energy. Organisms get food in order to get energy, which is used by the organism for growth, maintaining health, and reproduction. We can classify the members of a community according to how they obtain food. Produc...
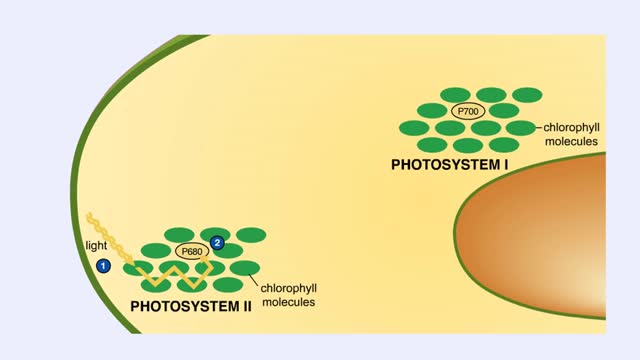
Chloroplast Structure & Light Dependent Reactions (Photosystem 1 and 2 Cyclic Electron Flow)
By: HWC, Views: 10567
The leaf is the principle photosynthetic organ of the plant. This is a cross section of a leaf. The rectangular-shaped cells are part of the photosynthetic tissue called the palisade mesophyll. Each photosynthetic cell can contain several hundred organelles known as chloroplasts. The chlorop...
Advertisement