Search Results
Results for: 'blood and systemic cell compartments'
By: Administrator, Views: 15285
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. As the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms become increasingly common. The symptoms generally come on slowly over time. Early in the disease, the most obvious are shak...
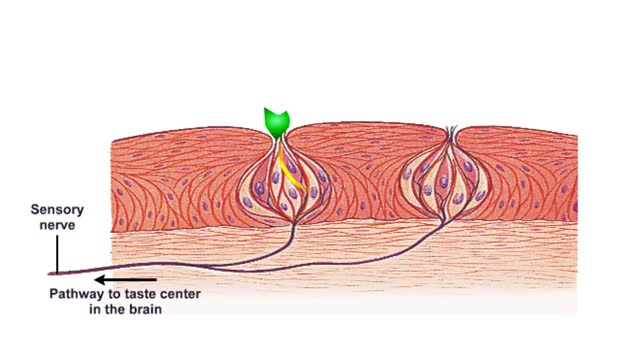
What are Taste Receptors? How Does it Work? Animation
By: HWC, Views: 7963
Do you ever wonder how you can taste the foods you eat? It all starts with taste receptors in your muscular tongue. Taste receptor neurons are found in your taste buds but you are not looking at the taste buds. The raised bumps on the surface of the tongue that you see are specialized epith...
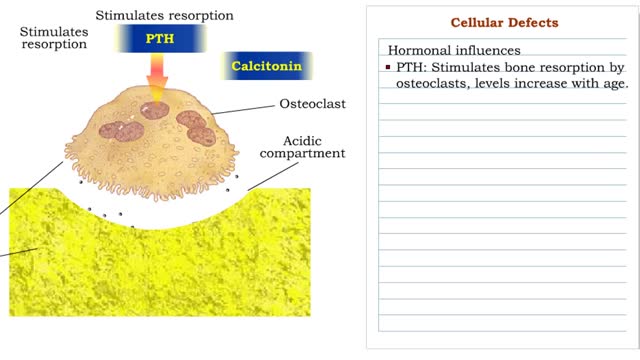
Cellular Defects - Osteoblasts, Osteoclasts and Osteocytes
By: HWC, Views: 10750
■ Metabolically active bone-building cells that secrete astroid. ■ Cover surfaces of newly formed bone and respond to growth stimuli ■ Less responsive to growth factors as the body ages. ■ Contribute to hone loss once their reproductive and biosynthetic potential lessens....
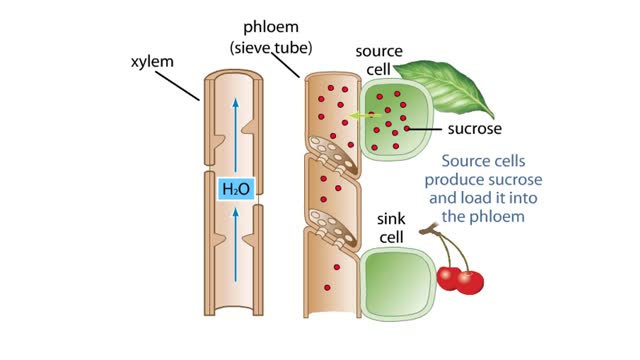
The Pressure Flow Model in a Plant
By: HWC, Views: 10457
The vascular system of plants has two transport tissues, called xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem transports a variety of dissolved substances, including sugars and amino acids, throughout the plant. Water in the xylem always moves up, in the direction from th...
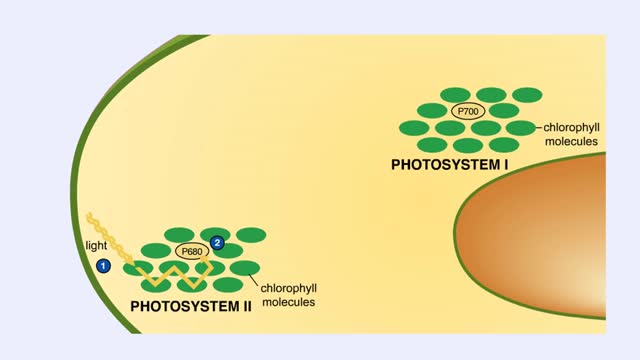
Chloroplast Structure & Light Dependent Reactions (Photosystem 1 and 2 Cyclic Electron Flow)
By: HWC, Views: 10642
The leaf is the principle photosynthetic organ of the plant. This is a cross section of a leaf. The rectangular-shaped cells are part of the photosynthetic tissue called the palisade mesophyll. Each photosynthetic cell can contain several hundred organelles known as chloroplasts. The chlorop...
Predator- prey competition and symbiosis
By: HWC, Views: 10889
Predator-prey relationships occur when one species, the predator, kills and eats an organism of another species, the prey. This graph shows the cyclical nature of predator-prey relationships, in this case among populations of Canada lynx and snowshoe rabbits. If predation is without some li...
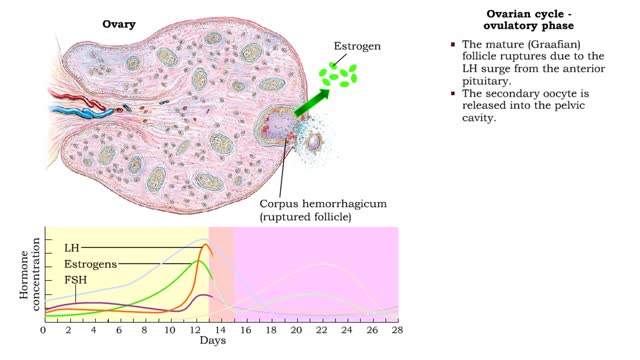
By: HWC, Views: 11435
• The ovarian cycle is a monthly sequence of events, consisting of three phases: • Preovulatory • Ovulatory • Post ovulatory Preovulatory phase • prior to ovulation: Primary follicles develop into secondary follicles. • Follicular cells surrounding the primary oocyte In...
By: Administrator, Views: 14199
Epilepsy is a group of neurological disorders characterized by epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures are episodes that can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking. These episodes can result in physical injuries, including occasionally broken bones. In ...
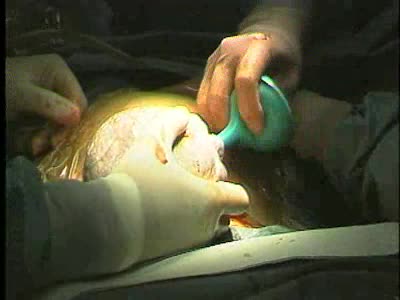
By: Administrator, Views: 461
Caesarean section, also known as C-section, or caesarean delivery, is the use of surgery to deliver babies. A caesarean section is often necessary when a vaginal delivery would put the baby or mother at risk. This may include obstructed labor, twin pregnancy, high blood pressure in the mother, br...
Advertisement