Search Results
Results for: ''
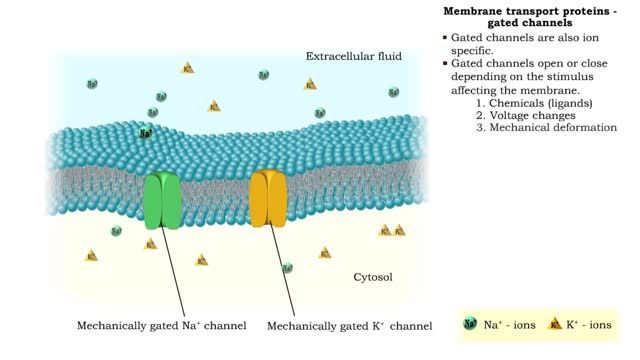
Membrane transport proteins - pores, gated channels and pumps
By: HWC, Views: 11529
• a Three different types of membrane ion transport proteins are required to produce and carry electrical signals: • Pores • Gated channels • Na+/ K+ pump • Pores are always open and allow the diffusion of Na+ and K+ ions across the membrane, down their concentration gradients...
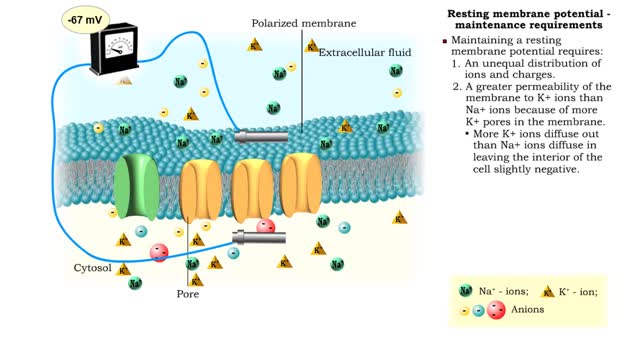
Resting membrane potential - electrical polarity and maintenance requirements
By: HWC, Views: 11057
• A resting membrane potential exists when there is a buildup of: 1. positive ions outside the membrane. 2. negative ions inside the membrane. • Membranes with opposing charges are said to be polarized. • The difference in charge applies only to the small distance across the membran...
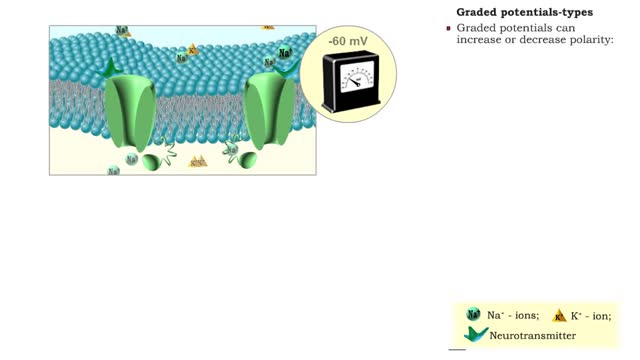
Graded potentials - electrical characteristics and types
By: HWC, Views: 11609
• A graded potential occurs when a gated channel is opened or closed, altering ion flow through the membrane. • Changes in ion and charge distributions cause voltage changes to the resting membrane potential. • The strength of the stimulus determines the number of gated channels affect...
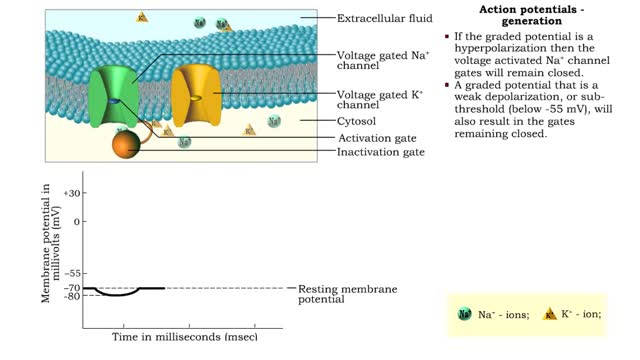
Action potentials - electrical characteristics and generation
By: HWC, Views: 11238
• An action potential is the nervous impulse or signal for long distance communication. Each action potential is generated at the cell's trigger zone. • Action potentials are considered an all-or-nothing phenomena because they are either generated or not. • The generation of an action...
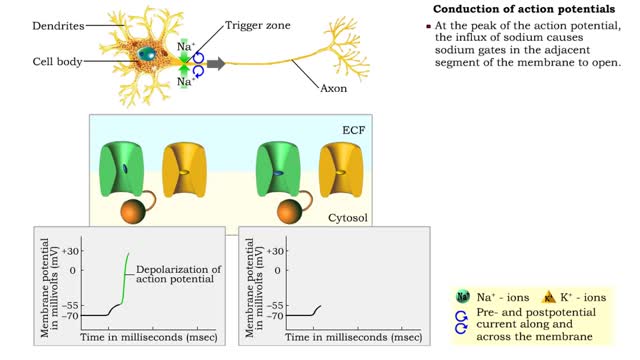
Conduction of action potentials
By: HWC, Views: 11556
• Action potentials must be rapidly conducted over long distances in order for the nervous system to communicate with other cells. • Propagation of an action potential uses processes similar to those that generate the potential at the trigger zone. • a When a graded potential reaches ...
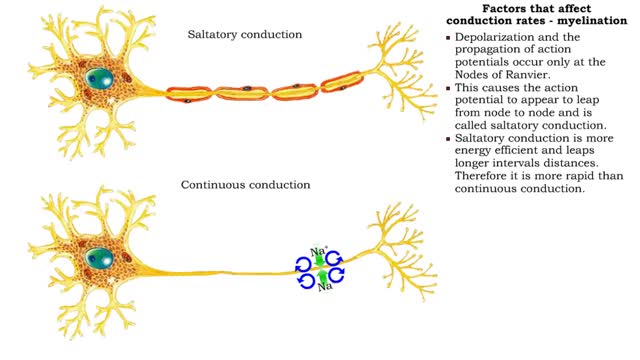
Factors that affect conduction rates (myelination, axon diameter & temperature)
By: HWC, Views: 11555
• Several factors determine the rate of conduction of action potentials: • Myelination • Axon diameter • Temperature • The step-by-step depolarization of an axon is called continuous conduction and occurs along unmyelinated axons. • Neurons in the PNS have many axons that ...
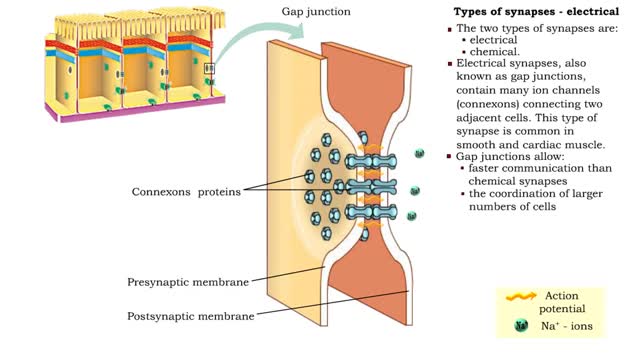
Types of synapses - electrical & chemical
By: HWC, Views: 11495
• Neurons communicate with one another or effector cells via synapses that allow information to be filtered and integrated. • The two types of synapses are: • electrical • chemical. • Electrical synapses, also known as gap junctions, contain many ion channels (connexons) conne...
Neurotransmission at chemical synapses & Excitory and inhibitory potentials
By: HWC, Views: 11356
• A series of events occur at chemical synapses in order to communicate with the adjacent cell. • The action potential arrives at the presynaptic membrane. • The depolarization phase of the action potential opens voltage gated Ca+ channels. • increased inflow of Ca+' into the cyto...
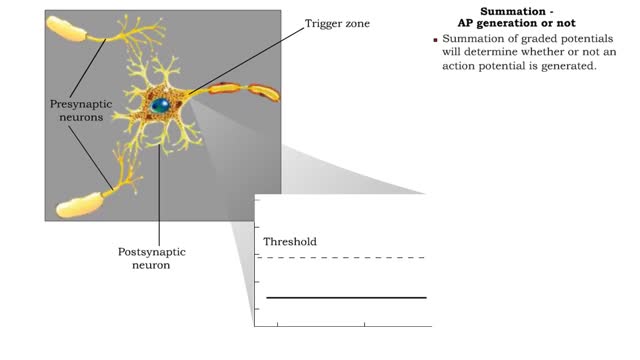
Summation - defined, spatial, temporal & AP generation or not
By: HWC, Views: 11292
If several presynaptic end bulbs release their neurotransmitter at about the same time, the combined effect may generate a nerve impulse due to summation Summation may be spatial or temporal • A typical neuron may have thousands of synapses. A corresponding number of postsynaptic membrane ...
Advertisement