Search Results
Results for: 'Helper T cell action'
By: Administrator, Views: 14711
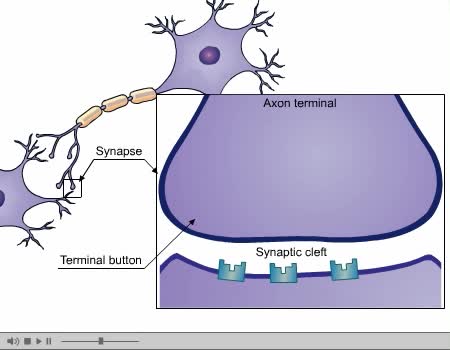
Dendrites (from Greek δένδρον déndron, "tree"), also dendrons, are branched protoplasmic extensions of a nerve cell that propagate the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body, or soma, of the neuron from which the dendrites project. Electrical stimula...
Red Blood Cells - Erythropoietin (EPO)
By: HWC, Views: 11010
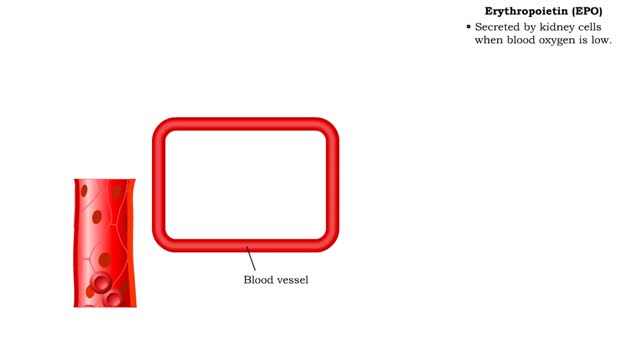
• The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone aft...
Types of synapses - electrical & chemical
By: HWC, Views: 11187
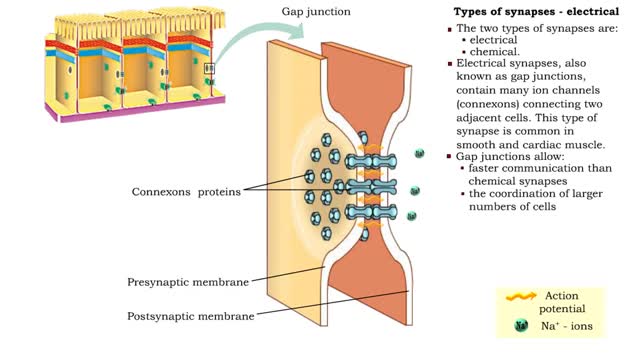
• Neurons communicate with one another or effector cells via synapses that allow information to be filtered and integrated. • The two types of synapses are: • electrical • chemical. • Electrical synapses, also known as gap junctions, contain many ion channels (connexons) conne...
By: HWC, Views: 11251
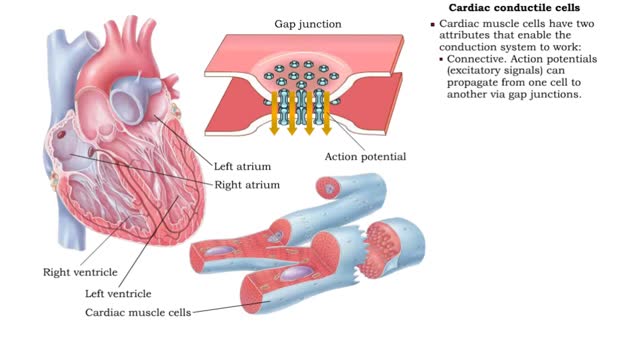
• In order for the heart to function properly, all of its cells must contract in a specific sequence. This sequence is determined by a pathway known as the conduction system. • Cardiac muscle cells have two attributes that enable the conduction system to work: • Connective. Action pot...
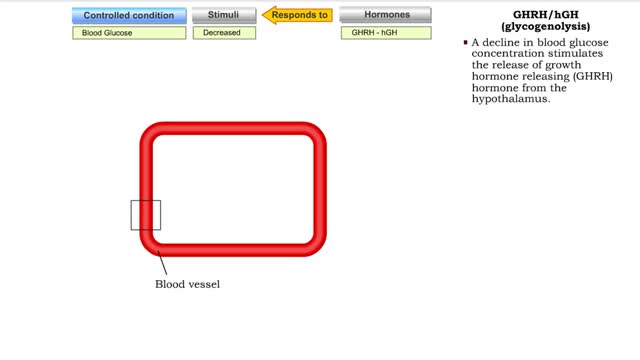
Hormonal feedback loop components & Glucagon (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 10909
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after ...
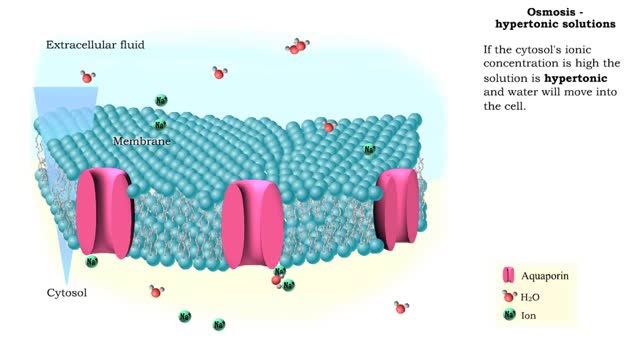
Osmosis - Isotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic Solutions
By: HWC, Views: 11197
Isotonic: Equal Water moves in and out of the cell at an equal rate. The cell remains unchanged. Hypotonic: "hypo" hippo Water moves into the cell, making it swell and get fat (like a hippo). Eventually the cell can rupture and burst (aka lyse). Hypertonic: "like a raisin" Water leaves...
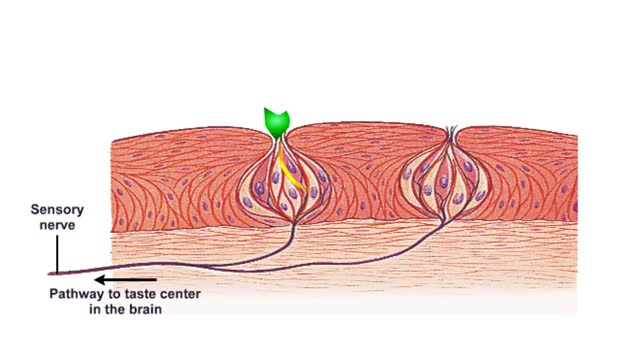
What are Taste Receptors? How Does it Work? Animation
By: HWC, Views: 7990
Do you ever wonder how you can taste the foods you eat? It all starts with taste receptors in your muscular tongue. Taste receptor neurons are found in your taste buds but you are not looking at the taste buds. The raised bumps on the surface of the tongue that you see are specialized epith...
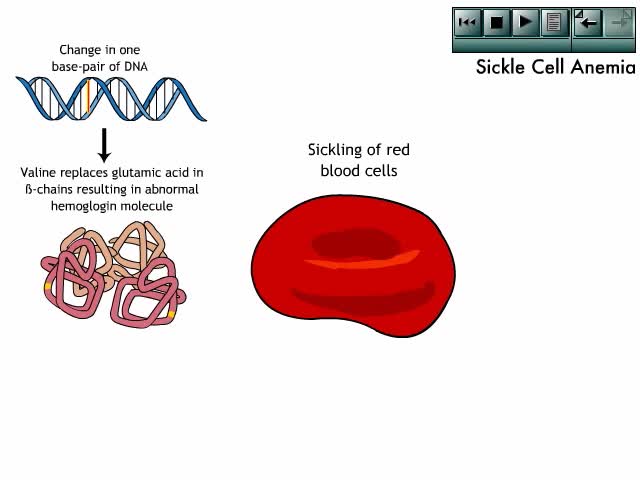
By: Administrator, Views: 14100
The clinical manifestations of sickle cell anemia result from pathologic changes to structures and systems throughout the body.
Central Nervous System Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14234
Consists of the brain and spinal cord. CNS receives impulses from throughout the body processes the information responds with an appropriate action Brain and spinal cord can be divided into: gray matter (unsheathed cell bodies and true dendrites) white matter (myelinated nerve fibers) ...
Advertisement