Search Results
Results for: 'bacterial cells'
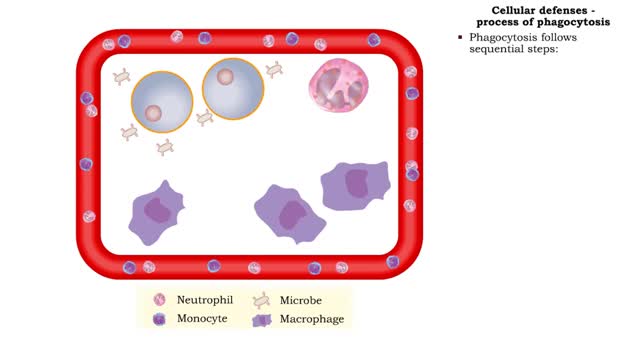
Cellular defenses (natural killer cells, phagocyte types & process of phagocytosis)
By: HWC, Views: 10288
• Lymphocytes that rapidly defend against abnormal (cancer) or virus-infected cells. • Found in blood, spleen, lymph nodes, and red bone marrow. • Lack receptors for binding with specific antigens. • Act upon cells displaying abnormal MHC antigens. • NK cells destroy cells in ...
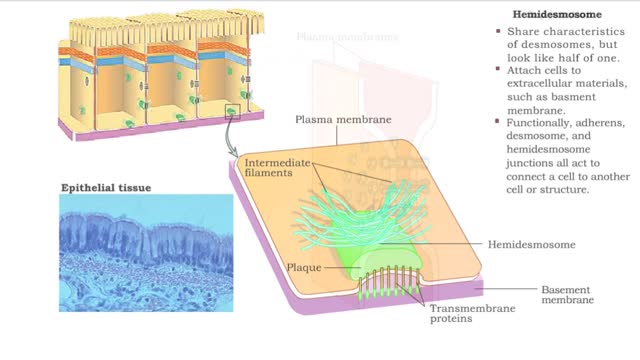
Type of Cell Junctions - Desmosome, Hemidesmosomes and Gap Junctions
By: HWC, Views: 10888
Cell Junctions: Cell junctions are found in some multi-cellular organisms. They exist of complexes and are found between cells and between cells and other structures. The junctions provide a way for cells to connect and exchange signals. What are tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions...
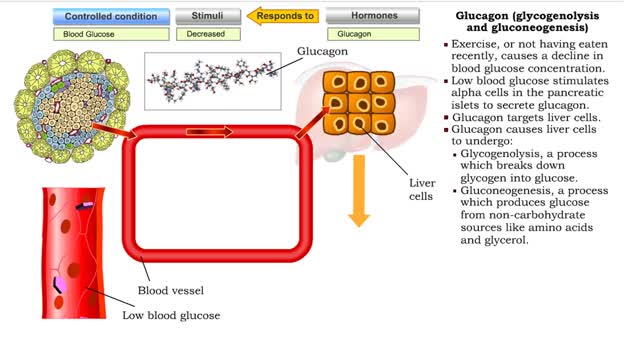
Glucagon (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 10371
• Exercise, or not having eaten recently, causes a decline in blood glucose concentration. • Low blood glucose stimulates alpha cells in the pancreatic islets to secrete glucagon. • Glucagon targets liver cells. • Glucagon causes liver cells to undergo: • Glycogenolysis, a proce...
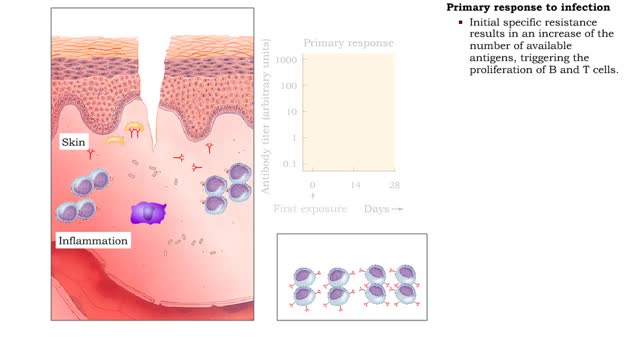
Primary and secondary response to infection
By: HWC, Views: 10392
• Pathogens enter the body by penetrating the non-specific barriers in the skin and mucus membranes. • Pathogens first encounter macrophages and natural killer cells that carry out phagocytosis and cytolysis respectively. • A pathogen's first encounter with the immune system can promo...
By: HWC, Views: 7400
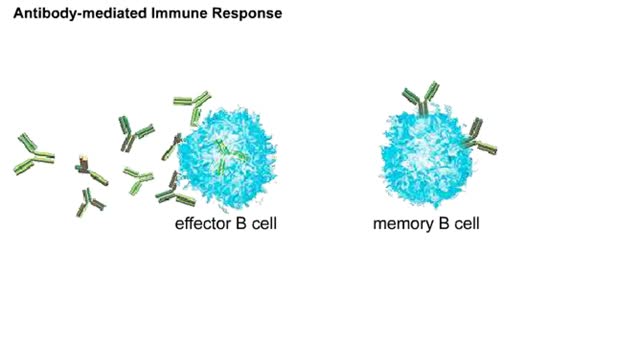
Overview of interactions in antibody-mediated and cell-mediated immunity Animation The antibody mediated immune response begins when a naive B cell encounters antigens from a pathogen, such as a bacterium. The B cell binds, processes, and displays this antigen. It is now an antigen-presenti...
Oxygen transport - methods and oxyhemoglobin
By: HWC, Views: 10385
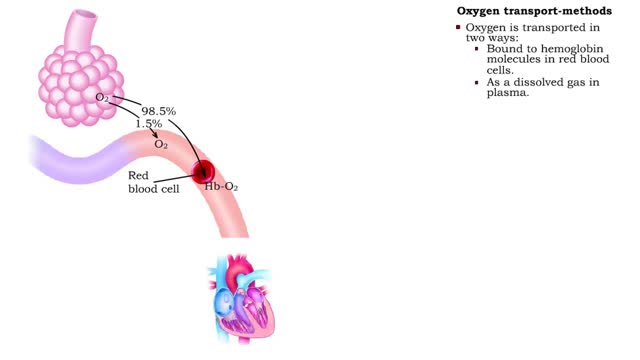
• The blood is the medium used for gas transport throughout the body. • Oxygen is only available in the lungs. Because the partial pressure of oxygen is higher in the alveoli than in the blood, oxygen diffuses into the blood and is transported to systemic cells. • At the tissues the par...
Cellular slime mold life cycle Animation
By: HWC, Views: 4826
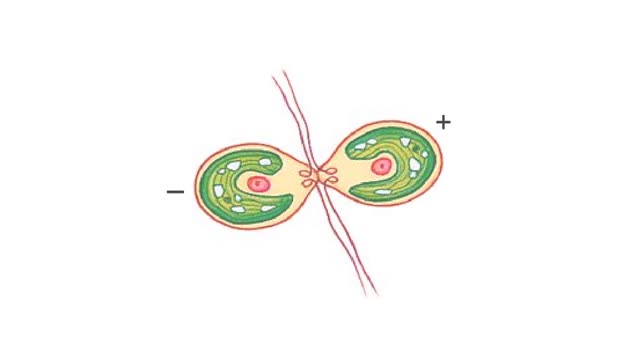
Life cycle of Dictyostelium discoideum, a cellular slime mold Animation. Amoeba-like slime mold cells live in the soil, where they feed on bacteria. The free-living cells grow and reproduce by mitosis. When food dwindles, the amoebas stream toward one another in response to a chemical...
Insulin (glucose uptake by body cells), glycogenesis and lipogenesis
By: HWC, Views: 10719
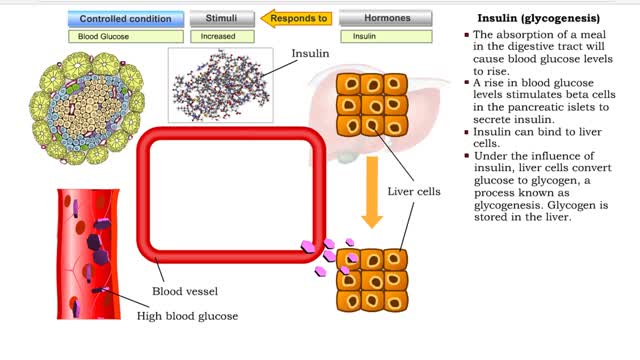
Insulin is the regulator that allows the sugar from the foods we eat (be it a piece of cake or a stick of celery) to enter our tissues and become part of the metabolic process. Insulin is made by the Islets of Langerhans, which are found in the pancreas of every person. As we previously mentio...
Introduction to Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
By: Administrator, Views: 13469
Human immunodeficiency virus gains entry into helper T cells, uses the cell DNA to replicate, interferes with normal function of the T cells, and destroys the normal cells. 1 in 10 persons with AIDS: age 50 or older. 4% of all AIDS cases: age 65 or older. AIDS’ main form of treatment: an...
Advertisement