Search Results
Results for: 'membrane transport'
Phases of an Action Potential - Resting Potential, Threshold, Rising, Falling, & Recovery Phases
By: HWC, Views: 10749
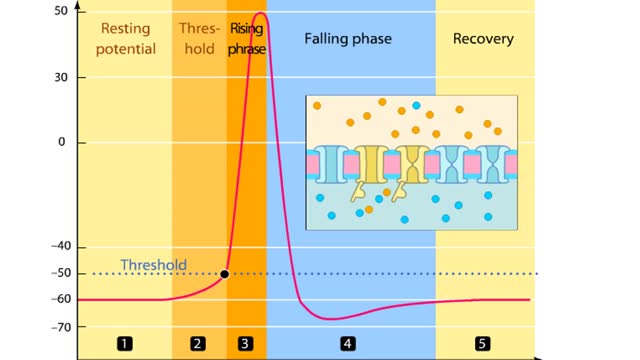
In this tutorial, we will review the phases of an action potential measured from a small area of a neuron's membrane. The action potential can be divided into five phases: the resting potential, threshold, the rising phase, the falling phase, and the recovery phase. When the neuron is at rest,...
Action potentials - electrical characteristics and generation
By: HWC, Views: 11173
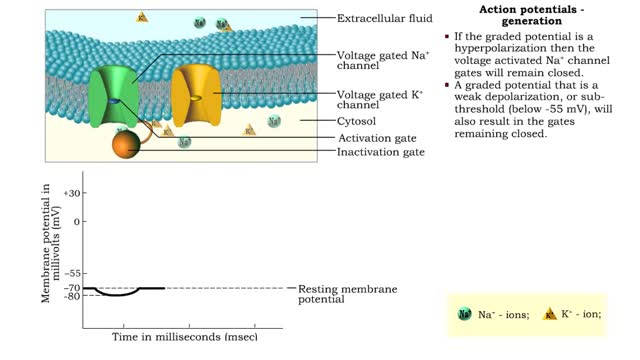
• An action potential is the nervous impulse or signal for long distance communication. Each action potential is generated at the cell's trigger zone. • Action potentials are considered an all-or-nothing phenomena because they are either generated or not. • The generation of an action...
Second Messengers in the Inositol-lipid Signaling Pathway
By: HWC, Views: 10479
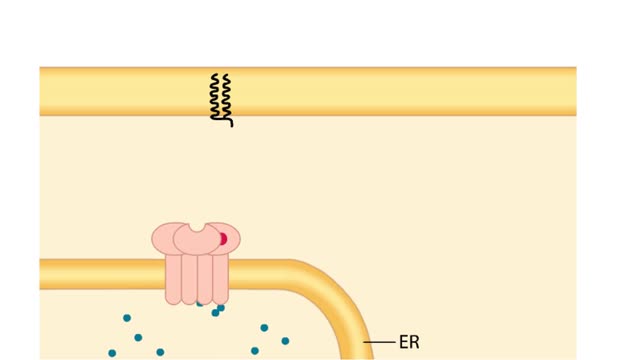
Extracellular signals produce specific responses in target cells through the action of intracellular second messengers. Here, we focus on three second messengers, IP3, DAG, and Ca2+, all involved in the inositol-lipid signaling pathway. A hormone-receptor signal on the cell surface leads to the a...
What are the Parts of a Plant Cell?
By: HWC, Views: 10374
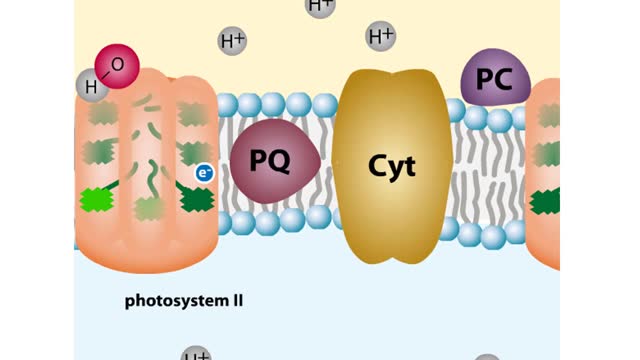
Every chloroplast in a plant cell is packed with stacks of flattened sacs called thylakoids. The thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll, as well as most of the other components required for the light reactions of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll-containing structures within the membranes are c...
By: HWC, Views: 11431
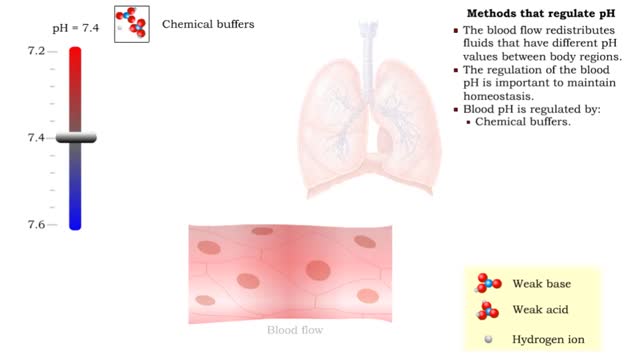
• The blood flow redistributes fluids that have different pH values between body regions. • The regulation of the blood pH is important to maintain homeostasis. • Blood pH is regulated by: • Chemical buffers. • The respiratory system. • The urinary system. • All thes...
Neurotransmission at chemical synapses & Excitory and inhibitory potentials
By: HWC, Views: 11290
• A series of events occur at chemical synapses in order to communicate with the adjacent cell. • The action potential arrives at the presynaptic membrane. • The depolarization phase of the action potential opens voltage gated Ca+ channels. • increased inflow of Ca+' into the cyto...
Acid-base imbalances - metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11435
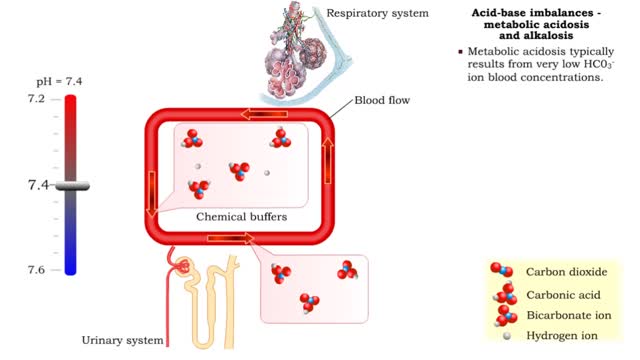
• Metabolic acidosis typically results from very low HCO3- ion blood concentrations. • Metabolic alkalosis typically results from very high HCO3- ion blood concentrations.
Acid-base imbalances - respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11663
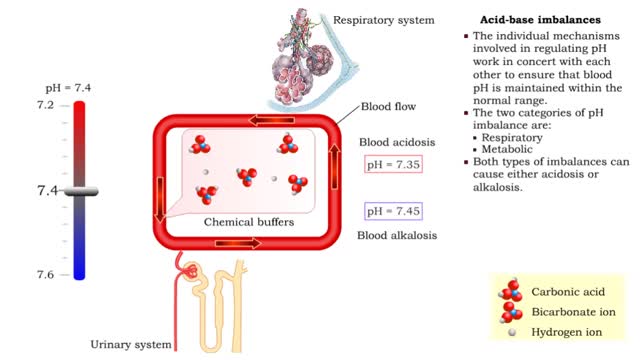
• The individual mechanisms involved in regulating pH work in concert with each other to ensure that blood pH is maintained within the normal range. • The two categories of pH imbalance are: • Respiratory • Metabolic • Both types of imbalances can cause either acidosis or alka...
Import of Dietary Glucose from Intestines to Bloodstream
By: HWC, Views: 10736
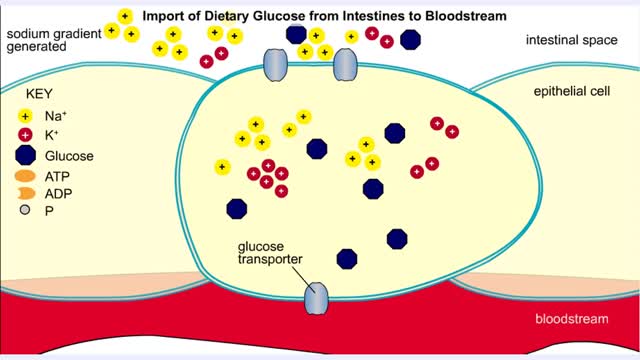
• Membranes have hydrophobic interiors. which resist the passage of hydrophilic compounds and ions. • However. transporter membrane proteins facilitate the passage of these molecules. • Passive transporters accelerate diffusion of molecules towards equilibrium (decrease a concentrat...
Advertisement