Search Results
Results for: 'Chemical Equilibrium'
Nervous pathway to the Neuromuscular (NMJ)
By: HWC, Views: 11525
• A nervous impulse, also called an action potential, starts from the brain or spinal cord to signal skeletal muscle cell contraction. Action potentials continue along a motor neuron to the muscle cell. • The signal to contract must cross a synapse - the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) - betwe...
Neural regulation of blood pressure - baroreceptor and chemoreceptor reflexes
By: HWC, Views: 11405
• The nervous system regulates blood pressure with two reflex arcs: baroreceptor and chemoreceptor. ■ Baroreceptors (pressure) and chemoreceptors (chemical) are located in the carotid sinus and aortic arch. • Carotid sinus reflex helps maintain normal blood pressure in brain. • Ba...
Hormonal feedback loop components
By: HWC, Views: 11202
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: ■ Stimulus - a change in a body condition. ■ Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after b...
By: HWC, Views: 11819
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
Bond types - Atomic structure and basis of bonds
By: HWC, Views: 11436
• Chemical bonds are fundamental to the structure and function of many types of molecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, gases, salts and water. ■ These molecules are composed of atoms that are held together by three different types of bonds. • The three types ...
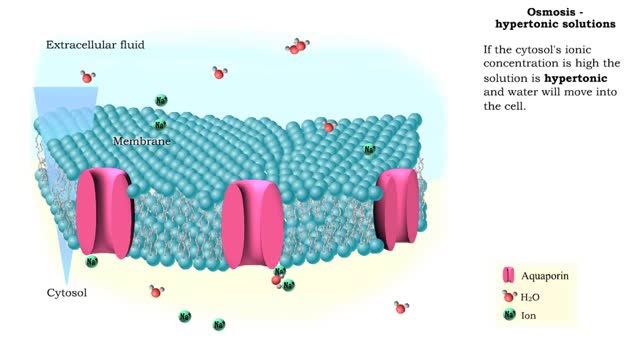
Osmosis - Isotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic Solutions
By: HWC, Views: 11136
Isotonic: Equal Water moves in and out of the cell at an equal rate. The cell remains unchanged. Hypotonic: "hypo" hippo Water moves into the cell, making it swell and get fat (like a hippo). Eventually the cell can rupture and burst (aka lyse). Hypertonic: "like a raisin" Water leaves...
Photosynthesis and Van Helmont Experiment
By: HWC, Views: 10267
All energy on Earth comes from a star, the Sun. Light must travel 160 million kilometers to reach Earth where plants capture this light energy and convert it to chemical energy in the form of sugars. This biochemical process is called PHOTOSYNTHESIS. The summary equation for photosynthesis is ...
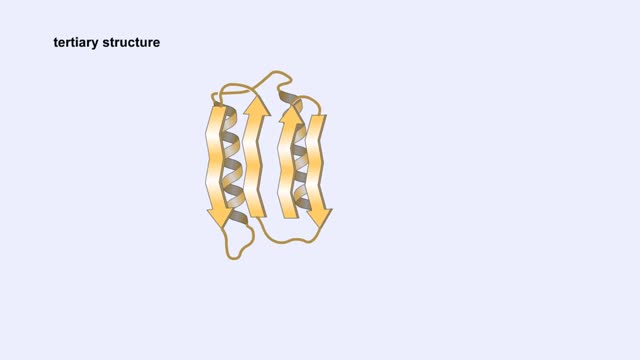
Protein Structure - Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary
By: HWC, Views: 10939
A protein's first order structure, or primary structure, begins with the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain. The 20 different amino acids can be arranged in an infinite number of sequences. For example, the hormone insulin, which regulates the uptake of glucose from the blood into ce...
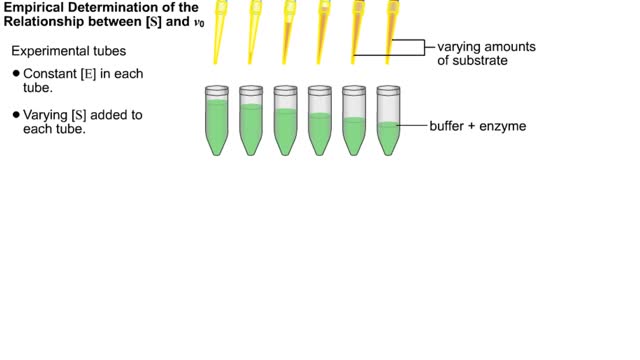
Kinetic parameters & Kinetic experiment
By: HWC, Views: 10865
Kinetics is a measure of the speed or rate of a chemical reaction. A study of kinetics allows us to determine which variables to control (temperature, reactants, catalysts) and how to vary them in order to maximize the amount of products formed and minimize the time involved. Vmax = maximum ve...
Advertisement