Search Results
Results for: 'Coronary Heart Disease'
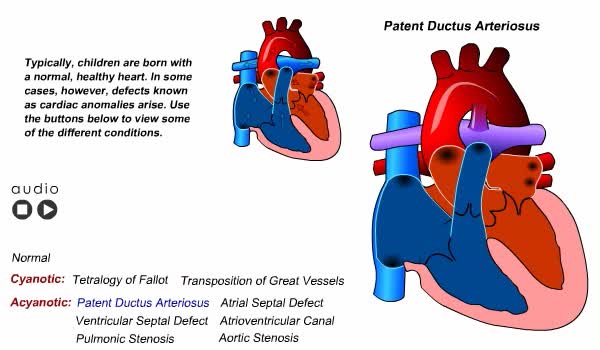
Congenital Heart Defects Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14152
Pulse, blood pressure, and respiration vary according to the child’s age. A newborn’s pulse rate is irregular and rapid, varying from 120 to 140 beats per minute. Blood pressure is low and can vary with the size of the cuff used. Average blood pressure at birth is 80/46. Respirations are ...
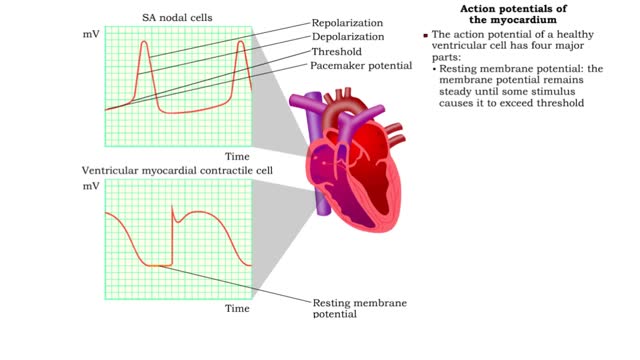
Depolarization of the SA node, Action potentials of the myocardium & ANS effects
By: HWC, Views: 10912
• A typical contractile cell in the myocardium has a resting membrane potential. • The resting membrane potential of cells in the SA node is not fixed, and is known as the pacemaker potential. • The action potential of a healthy SA nodal cell has three parts: • Pacemaker potential: ...
By: Administrator, Views: 14040
Alzheimer's disease (AD), also referred to simply as Alzheimer's, is a chronic neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and gradually worsens over time. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the d...
By: HWC, Views: 10308
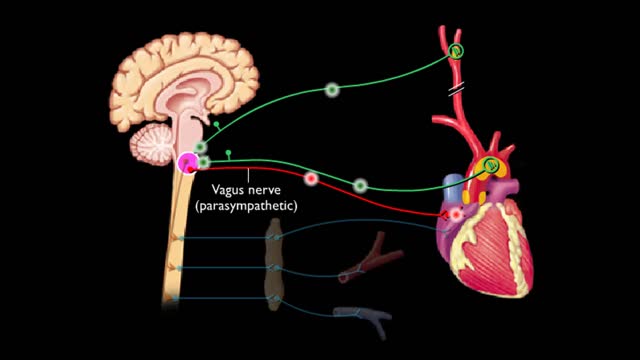
Baroreceptors located In the carotid sinus and the arch of the aorta respond to increases in blood pressure. Increased blood pressure stretches the carotid arteries and aorta causing the baroreceptors to increase their basal rate of action potential generation. Action potentials are conduct...
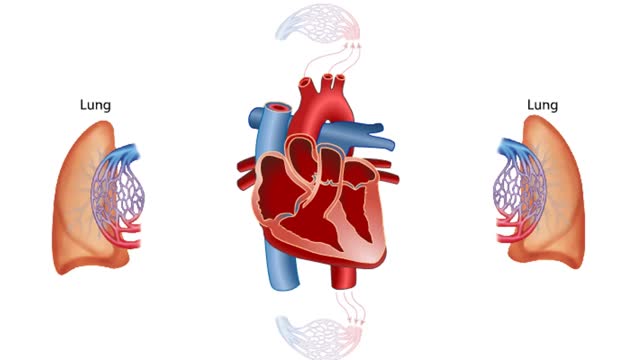
Blood Flow through the Human Heart
By: HWC, Views: 10890
The heart is the pump of the human circulatory system. The left side of the heart has two connected chambers, the left atrium and the left ventricle. The right side of the heart also has two connected chambers, the right atrium and the right ventricle. These two sides, or pumps, of the heart are ...
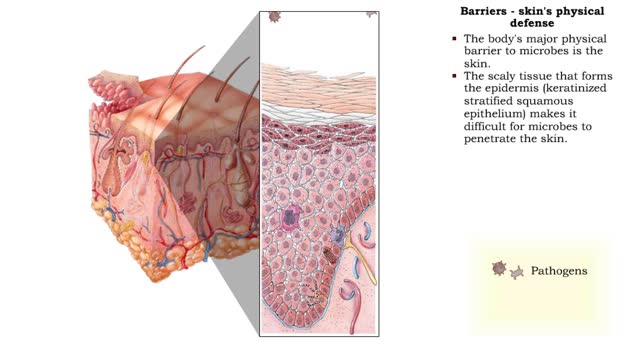
Non-specific disease resistance mechanisms & Skin's defense barriers
By: HWC, Views: 11054
• Non-specific disease resistance acts quickly to fight a wide variety of invaders. • Mechanisms include: • Barriers • Antimicrobial substances • Cellular defenses • Inflammation • Fever Barriers - types • Physical and chemical bathers prevent invasion by micro...
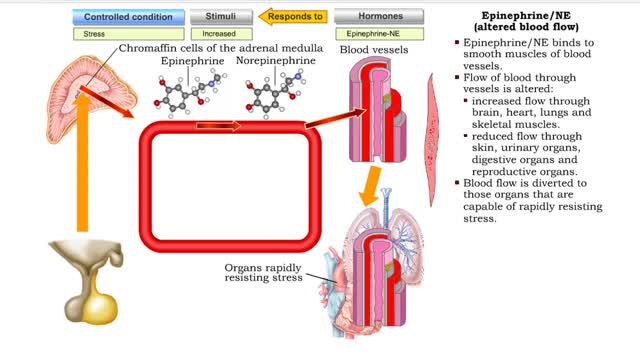
Epinephrine/NE (heart rate, altered blood flow, glycogenolysis & bronchodilation)
By: HWC, Views: 10909
• Stressors trigger increased sympathetic stimulation from the hypothalamus to the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla. • This causes the immediate release of epinephrine and norepinephrine (NE). • Epinephrine/NE binds to the cardiac muscles of the heart. • Cardiac muscle cells ...
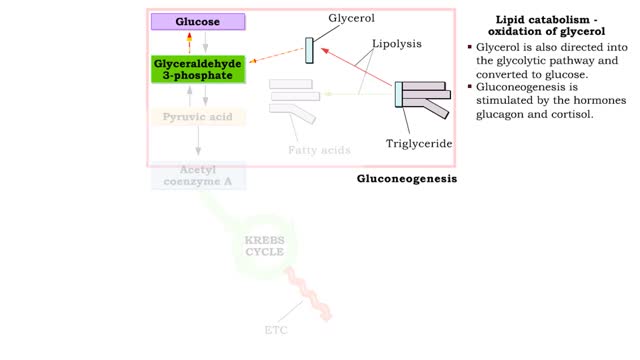
Lipid catabolism ( ketogenesis and oxidation of glycerol) and Lipid anabolism (lipogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11374
• During excessive beta oxidation, the two-carbon fatty acid fragments are converted into acidic ketone bodies. • Ketosis, the overproduction of ketone bodies, can lead to acidosis (ketoacidosis) of the blood. • After lipolysis, glycerol is converted to pyruvic acid. • Pyruvic aci...
By: Administrator, Views: 13979
Those with muscular dystrophy usually need to receive tube feedings and home nursing care. Children attend school when possible, and is able to use an adapted computer.
Advertisement