Search Results
Results for: 'Energy Flow'
By: HWC, Views: 5533
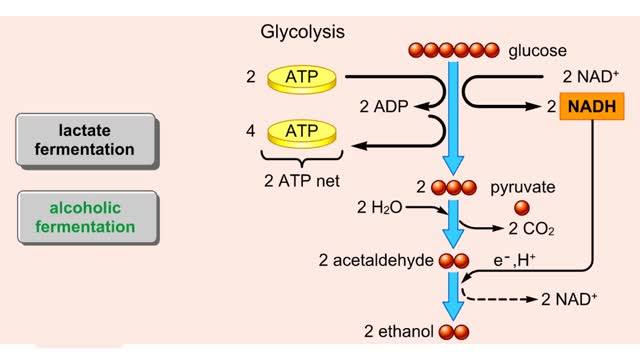
Both lactate fermentation and alcoholic fermentation begin with pyruvate formed by glycolysis. During lactate fermentation, pyruvate molecules accept electrons and hydrogen from NADH. This transfer regenerates NAD± and converts pyruvate to lactate. The net energy yield is the two ATP...
Type of Transport - Active and Passive Processes
By: HWC, Views: 11983
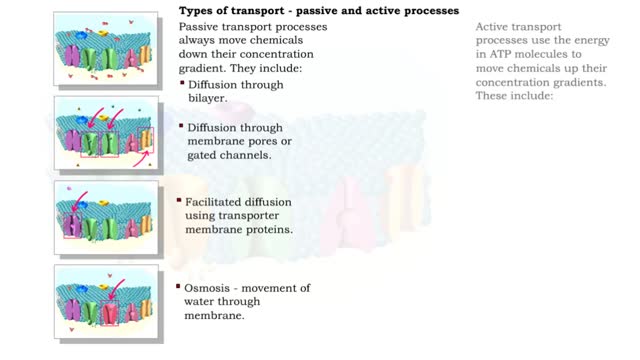
Active transport moves materials from lower to a higher concentration, while passive transport moves materials from higher to lower concentration. Active transport requires energy to proceed, while passive transport does not require the input of extra energy to occur. Transport processes that ...
The Pressure Flow Model in a Plant
By: HWC, Views: 11077
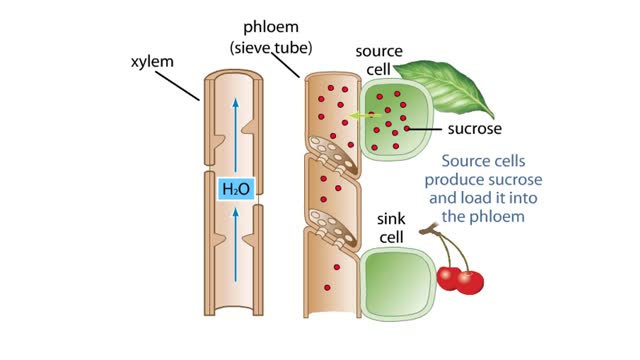
The vascular system of plants has two transport tissues, called xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem transports a variety of dissolved substances, including sugars and amino acids, throughout the plant. Water in the xylem always moves up, in the direction from th...
Blood Flow Through the Kidneys
By: Administrator, Views: 14346
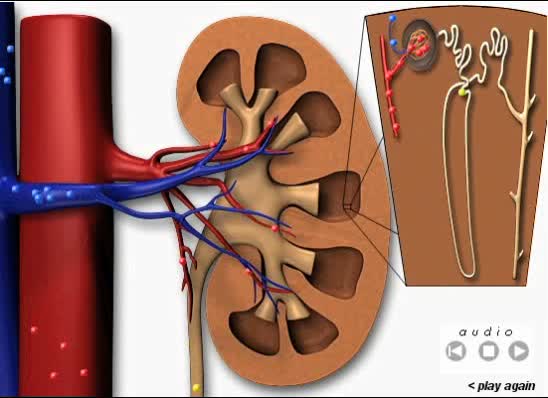
Purplish-brown, bean-shaped organs located behind abdominal cavity (retroperitoneal area) on either side of spine, between thoracic vertebrae and lumbar region.
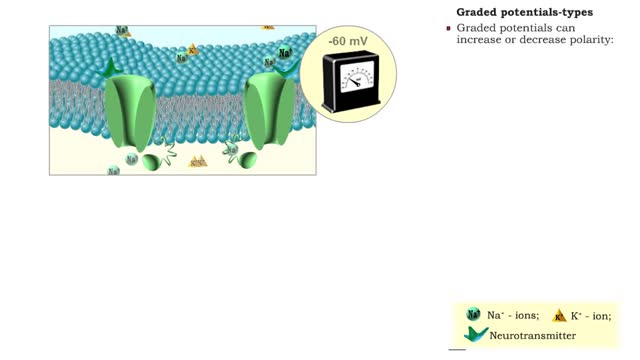
Graded potentials - electrical characteristics and types
By: HWC, Views: 11872
• A graded potential occurs when a gated channel is opened or closed, altering ion flow through the membrane. • Changes in ion and charge distributions cause voltage changes to the resting membrane potential. • The strength of the stimulus determines the number of gated channels affect...
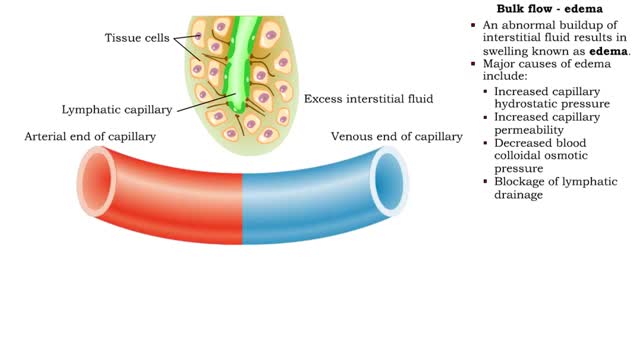
Net filtration pressure and lymph formation, edema & blood velocity
By: HWC, Views: 11484
Bulk flow -net filtration pressure and lymph formation • The net filtration pressure (NFP) is the force promoting filtration minus the force promoting reabsorption. • At the arterial end of an ideal capillary, the filtration pressures are stronger. The result: net filtration. • At t...
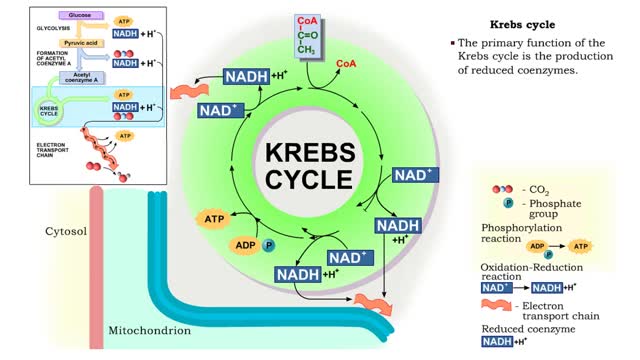
Krebs cycle : Formation of acetyl coenzyme A and Electron transport chain
By: HWC, Views: 11923
The oxidation of glucose to produce ATP is cellular respiration. Four sets of reactions are involved: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Krebs cycle reactions Electron transport chain reactions • The second pathway of glucose catabolism, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, is a transi...
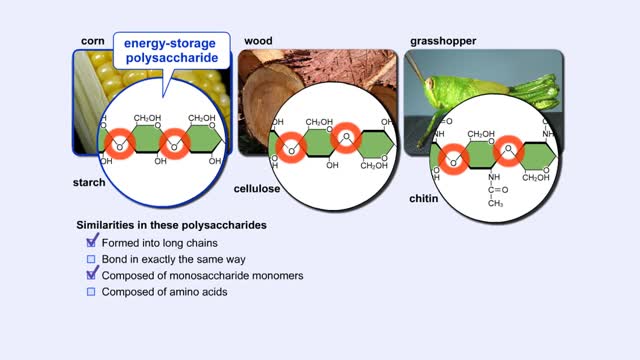
By: HWC, Views: 11274
More complex sugars are called polysaccharides (from "poly" meaning "many" and "saccharum" meaning "sugar"). Many things in nature are made of polysaccharides. Here we show one of the polysaccharides in corn, another in wood, and another in the exoskeletons of insects like grasshoppers. How are a...
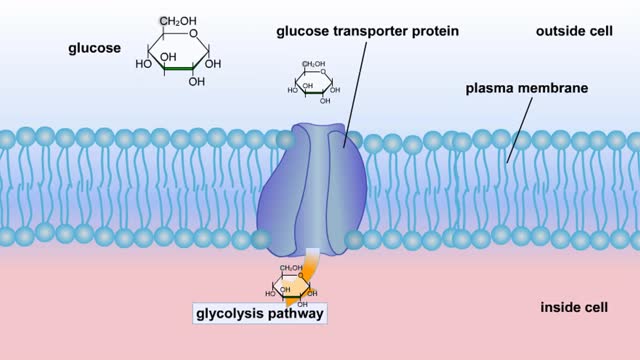
Cellular Respiration & Glucose Mobilization (Glucose transport & Phosphorylation of Glucose)
By: HWC, Views: 11415
Glucose is completely broken down into CO2 and H2O during the process of cellular respiration, which includes 3 stages: 1) glycolysis; 2) the Krebs Cycle; and 3) the electron transport chain. Glucose enters this energy yielding pathway of cellular respiration in the first stage known as...
Advertisement