Search Results
Results for: 'Heart'
By: Administrator, Views: 14644
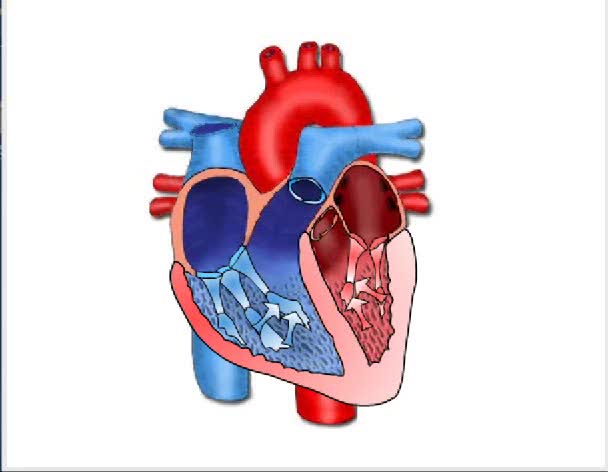
Hemodynamics is the dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms, such as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. Hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment.
Labor and Delivery - Infant Cord Apgar
By: Administrator, Views: 461
As soon as your baby is born, a delivery nurse will set one timer for one minute and another for five minutes. When each of these time periods is up, a nurse or physician will give your baby her first "tests," called Apgars. This scoring system (named after its creator, Virginia Apgar) helps t...
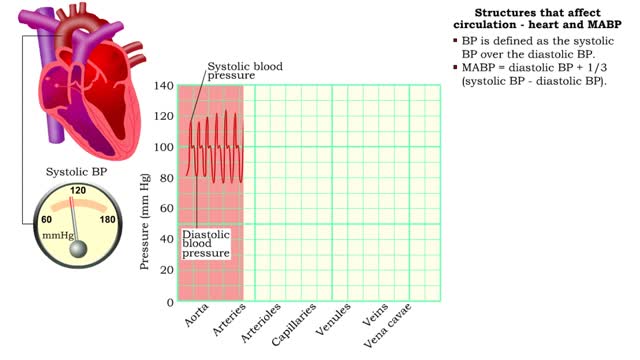
Structures that affect circulation - heart and MABP
By: HWC, Views: 10567
■ BP is defined as the systolic BP over the diastolic BP. ■ MABP = diastolic BP + 1/3 (systolic BP - diastolic BP). ■ MABP accounts for diastole lasting longer than systole; mean is not equidistant between the two pressures.
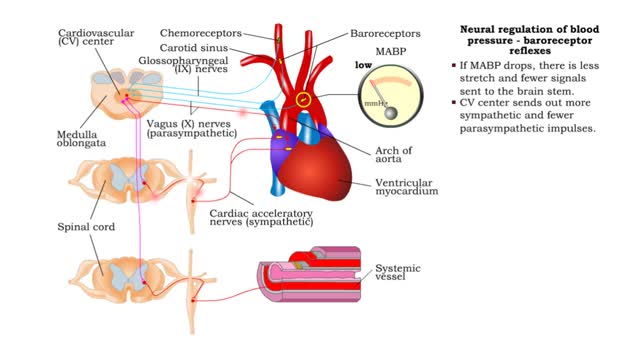
Neural regulation of blood pressure - baroreceptor and chemoreceptor reflexes
By: HWC, Views: 11400
• The nervous system regulates blood pressure with two reflex arcs: baroreceptor and chemoreceptor. ■ Baroreceptors (pressure) and chemoreceptors (chemical) are located in the carotid sinus and aortic arch. • Carotid sinus reflex helps maintain normal blood pressure in brain. • Ba...
Autonomic Nervous System Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14297
Parasympathetic Division Works to conserve energy and innervate the digestive system. When activated, it: stimulates the salivary and digestive glands. decreases the metabolic rate. slows the heart rate. reduces blood pressure. promotes the passage of material through the intestines along...
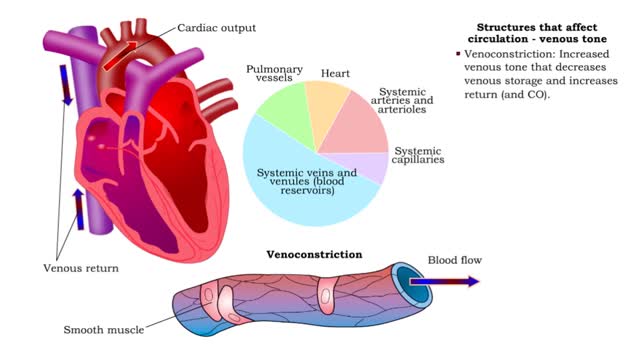
Structures that affect circulation - kidneys and blood volume and skeletal muscle pumping
By: HWC, Views: 11691
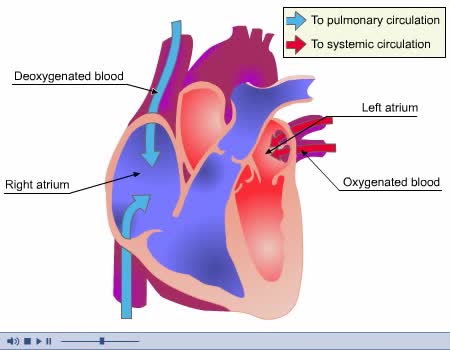
• Kidneys regulate blood volume and blood osmolarity via salt and water reabsorption. • Increased reabsorption increases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Decreased reabsorption Increases urine production, which decreases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Systemi...
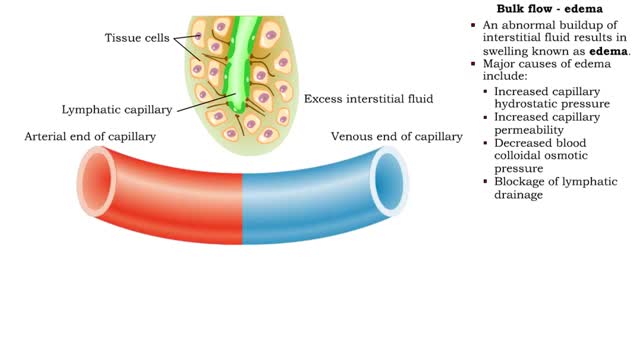
Net filtration pressure and lymph formation, edema & blood velocity
By: HWC, Views: 10885
Bulk flow -net filtration pressure and lymph formation • The net filtration pressure (NFP) is the force promoting filtration minus the force promoting reabsorption. • At the arterial end of an ideal capillary, the filtration pressures are stronger. The result: net filtration. • At t...
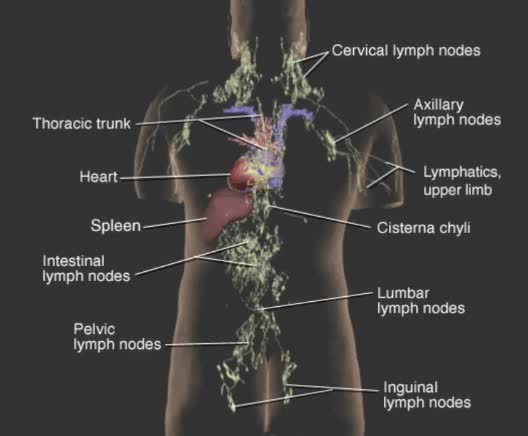
By: Administrator, Views: 578
Blood and lymph are two of the body's main fluids and are circulated through two separate but interconnected vessel systems. Blood is circulated by the action of the heart, through the circulatory system consisting largely of arteries, veins, and capillaries. Lymph does not actually circulate. ...
Advertisement