Search Results
Results for: 'passive transport'
By: HWC, Views: 11940
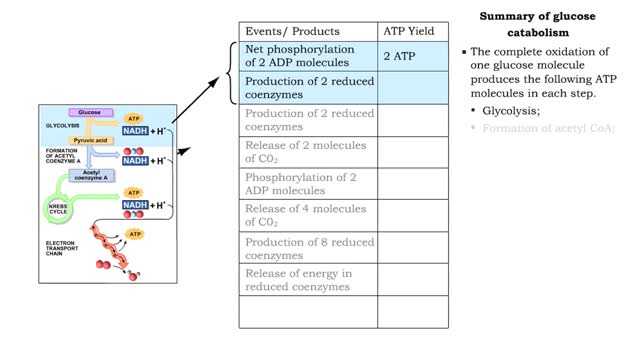
■ The complete oxidation of one glucose molecule produces the following ATP molecules in each step. • Glycolysis; • Formation of acetyl CoA; • Krebs cycle; • Electron transport chain. ■ In addition, glucose catabolism produces six CO2 molecules and water.
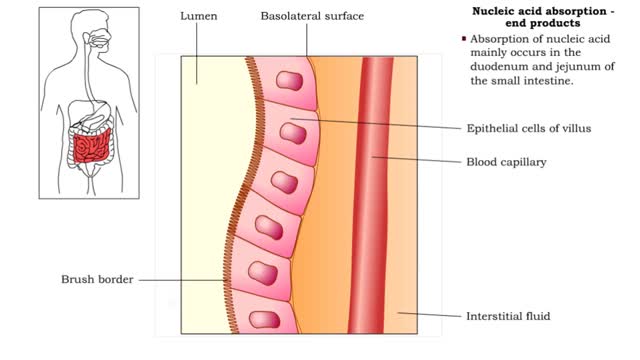
Nucleic acid digestion - brush border enzymes, end products & transport mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 11528
• Further digestion occurs at the microvilli (brush border) of the epithelial cells of the villi in the small intestine. • Two brush border enzymes complete nucleic acid digestion: • Phosphatases, which catalyze the cleavage of a phosphate to form a nucleoside (nitrogenous base and pent...
By: Administrator, Views: 15118
How smoking triggers asthma attacks and respiratory issues. Secondhand smoke is smoke from burning tobacco products, such as cigarettes, cigars, or pipes. Secondhand smoke also is smoke that has been exhaled, or breathed out, by the person smoking. Tobacco smoke contains more than 7,000 ...
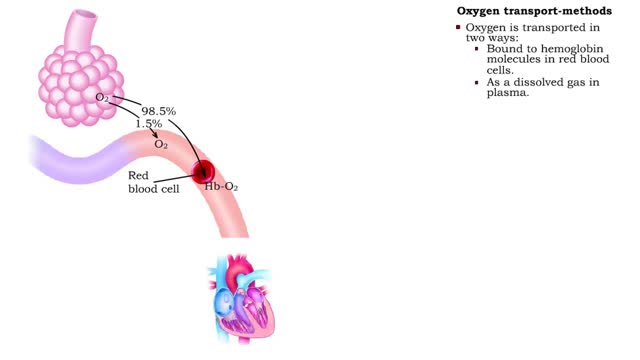
Oxygen transport - methods and oxyhemoglobin
By: HWC, Views: 11556
• The blood is the medium used for gas transport throughout the body. • Oxygen is only available in the lungs. Because the partial pressure of oxygen is higher in the alveoli than in the blood, oxygen diffuses into the blood and is transported to systemic cells. • At the tissues the par...
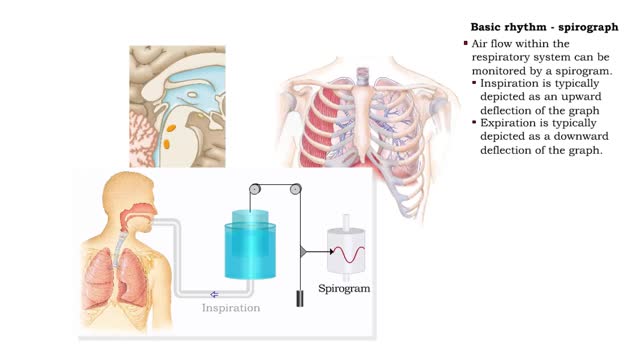
Basic rhythm - control centers in medulla oblongata, spirograph and normal tidal cycle
By: HWC, Views: 11565
• Normal ventilation is rhythmic and involves continuous cycles of inspiration and expiration. • Various regions of the brain closely regulate this rhythmic pattern of ventilation. • The rhythmicity area in the medulla regulates the basic rhythm of ventilation. • The medullary rhy...
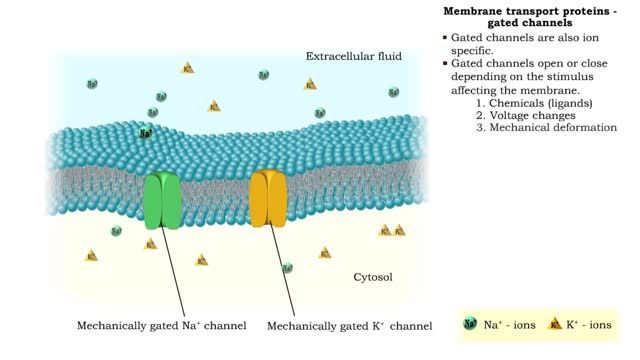
Membrane transport proteins - pores, gated channels and pumps
By: HWC, Views: 11828
• a Three different types of membrane ion transport proteins are required to produce and carry electrical signals: • Pores • Gated channels • Na+/ K+ pump • Pores are always open and allow the diffusion of Na+ and K+ ions across the membrane, down their concentration gradients...
By: HWC, Views: 12503
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
Labor and Delivery - Placenta Delivery
By: Administrator, Views: 534
Placental expulsion (also called afterbirth) occurs when the placenta comes out of the birth canal after childbirth. The period from just after the baby is expelled until just after the placenta is expelled is called the third stage of labor. The third stage of labor can be managed actively wi...
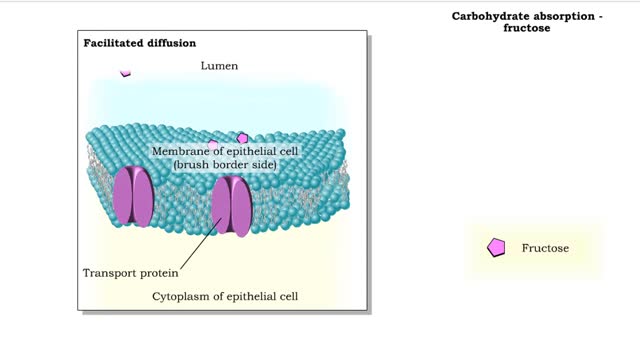
Carbohydrate digestion (brush border enzymes, end products) & Carb absorption (fructose, galactose)
By: HWC, Views: 11616
• Carbohydrate digestion concludes in microvilli of the small intestine, in brush border epithelial cells. Carbohydrate digestion -brush border enzymes • Four brush-border enzymes are involved: • Alpha-dextrinase breaks down alpha-dextrin chains by removing glucose units. • Sucras...
Advertisement