Search Results
Results for: 'sperm formation animation'
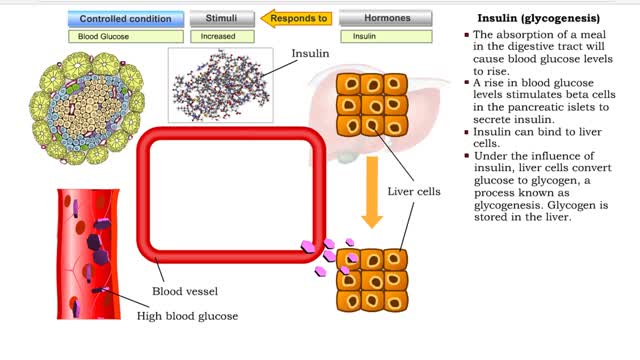
Insulin (glucose uptake by body cells), glycogenesis and lipogenesis
By: HWC, Views: 10956
Insulin is the regulator that allows the sugar from the foods we eat (be it a piece of cake or a stick of celery) to enter our tissues and become part of the metabolic process. Insulin is made by the Islets of Langerhans, which are found in the pancreas of every person. As we previously mentio...
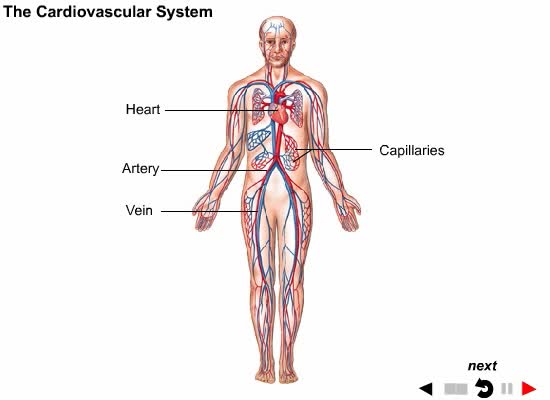
Introduction to Body Systems Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 905
Systems: A group of different organs functioning together for a common purpose.
By: Administrator, Views: 470
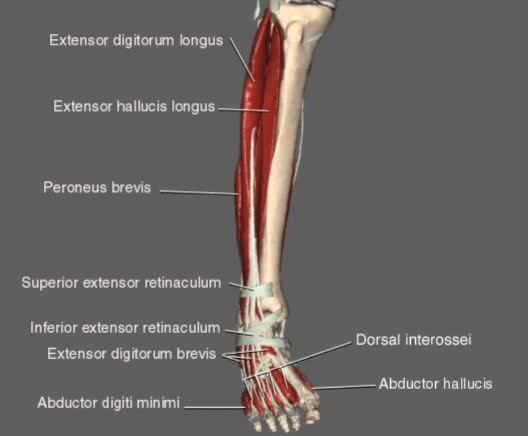
This animation shows a list of muscles found in the leg used for movement
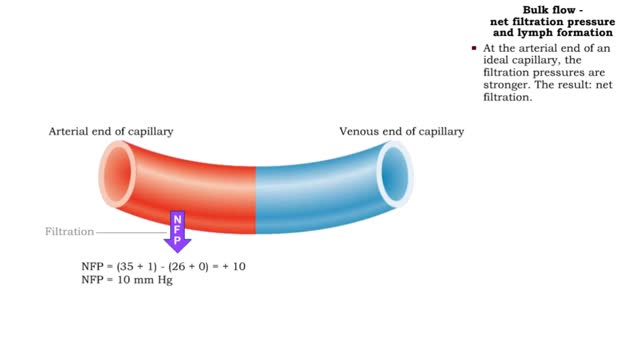
Bulk flow - Factors that influence bulk flow
By: HWC, Views: 10952
• Bulk flow helps regulate the relative volumes of blood and interstitial fluid. • Flow from blood to interstitium is called filtration. ■ Flow from interstitium to blood is called reabsorption. ■ Four factors determine the net direction of capillary exchange. ■ These factors in...
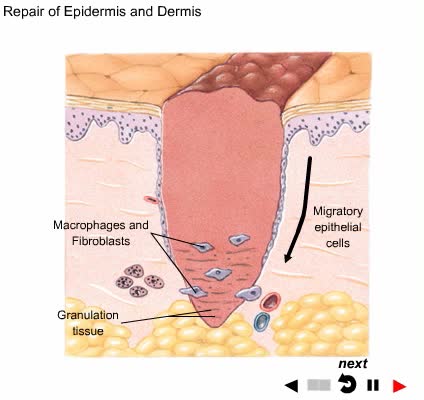
By: Administrator, Views: 13712
A wound is an injury to living tissue caused by a cut, blow, or other impact, typically one in which the skin is cut or broken.
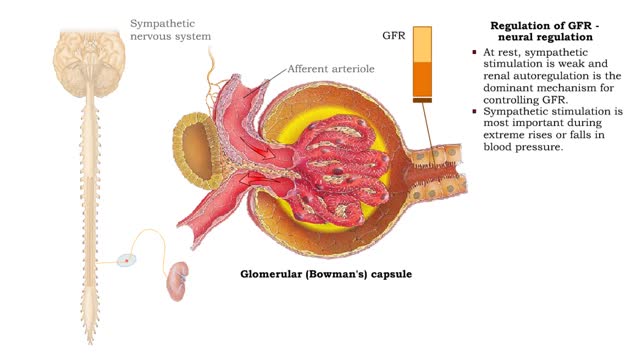
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via tubuloglomerular feedback, neural & hormonal regulation
By: HWC, Views: 11805
• When blood pressure is above normal, rapid filtrate flow reduces ion retention so filtrate in tubule has more Na+, C1-, and water. • It is believed that vasoconstricting chemicals from the juxtaglomerular cells are released when the macula densa cells detect higher water and ion levels in ...
By: HWC, Views: 5195
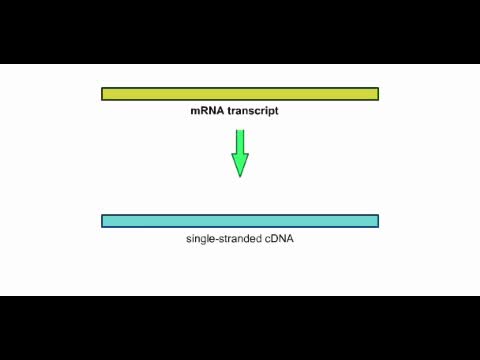
This animation shows how an mRNA transcript can be used to make a cDNA strand.
HIV replication/ Replication cycle of HIV
By: HWC, Views: 7928
Replication cycle of HIV, one of the retroviruses. The HIV virus is surrounded by a lipid envelope with embedded proteins. A coat of viral proteins surrounds two strands of RNA and the enzymes used during replication. The virus attaches to and enters the host cell. Viral reverse trans...
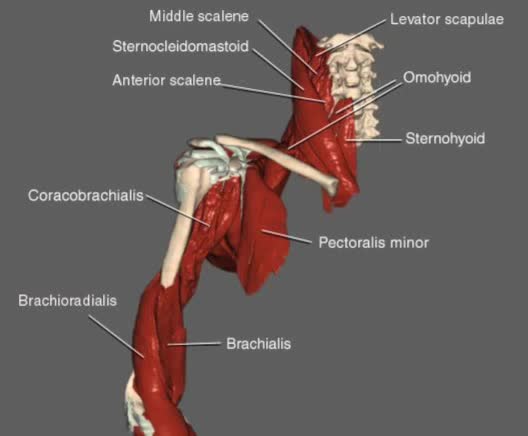
By: Administrator, Views: 771
Four muscles—the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis—make up the rotator cuff. It stabilizes the shoulder and holds the head of the humerus into the glenoid cavity to maintain the principal shoulder joint.
Advertisement