Search Results
Results for: 'Cellular slime mold life cycle Animation'
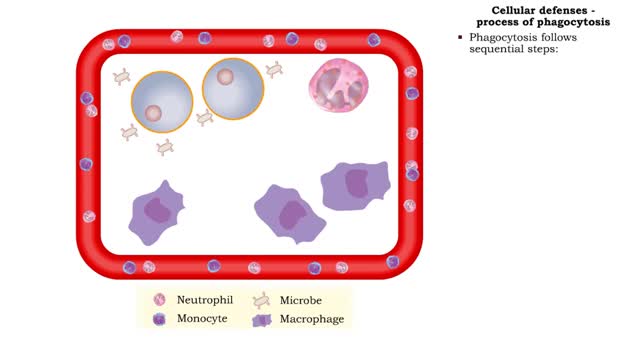
Cellular defenses (natural killer cells, phagocyte types & process of phagocytosis)
By: HWC, Views: 10223
• Lymphocytes that rapidly defend against abnormal (cancer) or virus-infected cells. • Found in blood, spleen, lymph nodes, and red bone marrow. • Lack receptors for binding with specific antigens. • Act upon cells displaying abnormal MHC antigens. • NK cells destroy cells in ...
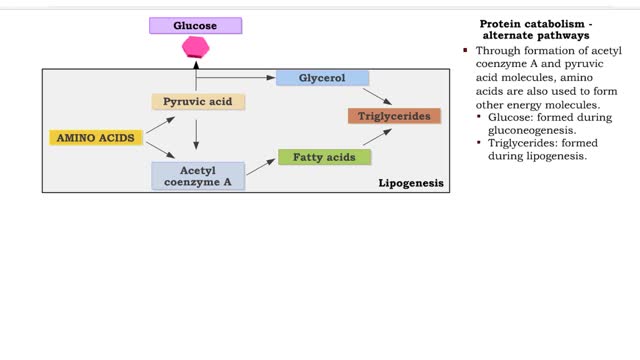
Protein catabolism (Krebs cycle) and Protein anabolism (protein synthesis)
By: HWC, Views: 10956
• Deaminated acids are brought into the Krebs cycle to be oxidized to CO2 and H2O. • Before entering the Krebs cycle, the deaminated acids are converted into intermediate products (pyruvic acid, acetyl coenzyme A, carbonic acids). • In the Krebs cycle, amino acids are oxidized to form r...
Cellular Defects - Osteoblasts, Osteoclasts and Osteocytes
By: HWC, Views: 10122
■ Metabolically active bone-building cells that secrete astroid. ■ Cover surfaces of newly formed bone and respond to growth stimuli ■ Less responsive to growth factors as the body ages. ■ Contribute to hone loss once their reproductive and biosynthetic potential lessens....
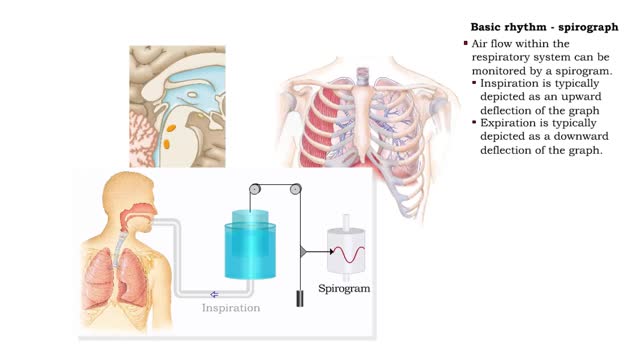
Basic rhythm - control centers in medulla oblongata, spirograph and normal tidal cycle
By: HWC, Views: 10294
• Normal ventilation is rhythmic and involves continuous cycles of inspiration and expiration. • Various regions of the brain closely regulate this rhythmic pattern of ventilation. • The rhythmicity area in the medulla regulates the basic rhythm of ventilation. • The medullary rhy...
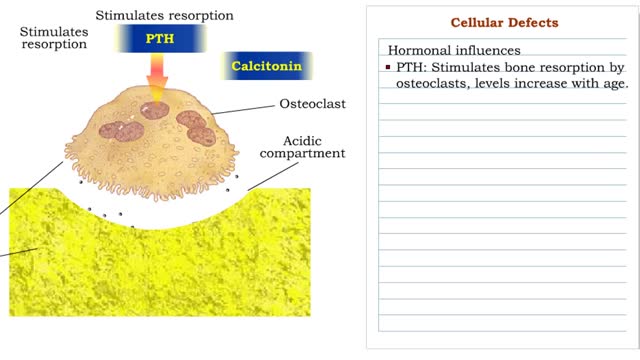
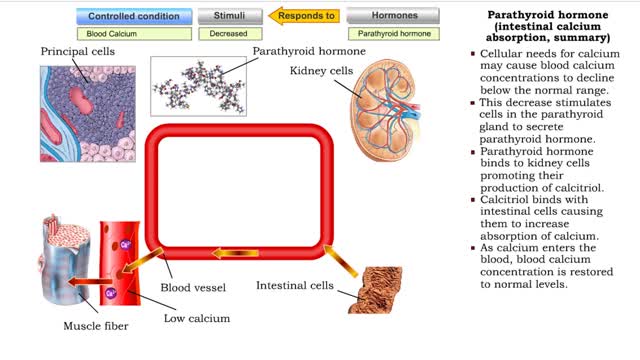
Parathyroid hormone (bone resorption) & Calcitonin (bone deposition)
By: HWC, Views: 10364
• Cellular needs for calcium may cause blood calcium concentrations to decline below the normal range. • This decrease stimulates cells in the parathyroid gland to secrete parathyroid hormone. • Binding of parathyroid hormone to osteoclasts in bone tissue promotes bone resorption and th...
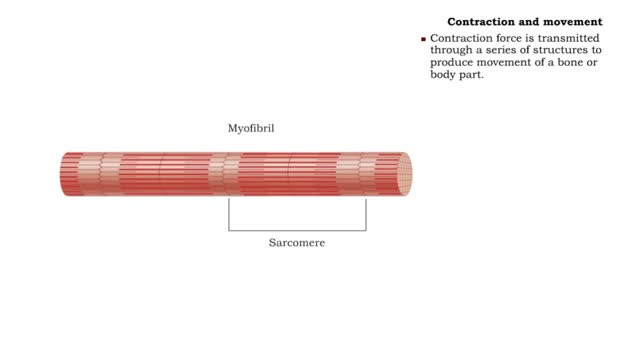
Contraction cycle of a sarcomere
By: HWC, Views: 10962
• A single nervous signal releases Ca2+ ions into the sarcoplasm and initiates the contraction cycle. step 1. ATP hydrolysis • ATP provides the to move myosin molecules back into the energized configuration necessary to perform the power stroke. Step 2. Crossbridge attachment • Myosin...
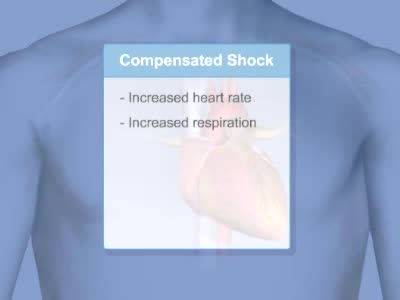
By: Administrator, Views: 13168
Shock is a life-threatening condition in which delivery of oxygen to the organs is low, causing organ damage and sometimes death. Blood pressure is usually low.
By: Administrator, Views: 13728
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) refers to physical and emotional symptoms that occur in the one to two weeks before a woman's period. Symptoms often vary between women and resolve around the start of bleeding. Common symptoms include acne, tender breasts, bloating, feeling tired, irritability, and mo...
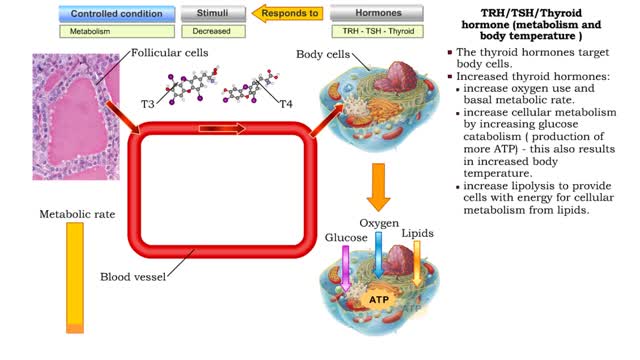
By: HWC, Views: 10021
Thyroid hormone production • A decline in metabolic rate caused by increased metabolic need or physical exertion stimulates the production of thyrotropin hormone releasing (TRH) hormone from the cells of the hypothalamus. • Thyrotropin hormone releasing hormone targets the thyrotrophic ce...
Advertisement