Search Results
Results for: 'Electrical changes in the heart'
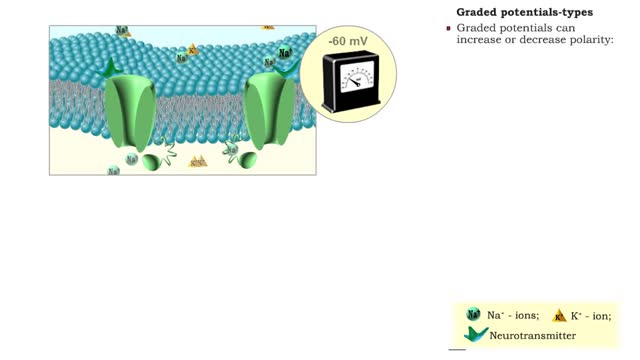
Graded potentials - electrical characteristics and types
By: HWC, Views: 11146
• A graded potential occurs when a gated channel is opened or closed, altering ion flow through the membrane. • Changes in ion and charge distributions cause voltage changes to the resting membrane potential. • The strength of the stimulus determines the number of gated channels affect...
Labor and Delivery - Infant Cord Apgar
By: Administrator, Views: 453
As soon as your baby is born, a delivery nurse will set one timer for one minute and another for five minutes. When each of these time periods is up, a nurse or physician will give your baby her first "tests," called Apgars. This scoring system (named after its creator, Virginia Apgar) helps t...
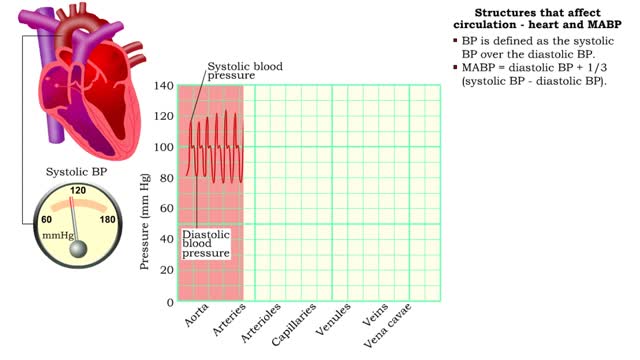
Structures that affect circulation - heart and MABP
By: HWC, Views: 10475
■ BP is defined as the systolic BP over the diastolic BP. ■ MABP = diastolic BP + 1/3 (systolic BP - diastolic BP). ■ MABP accounts for diastole lasting longer than systole; mean is not equidistant between the two pressures.
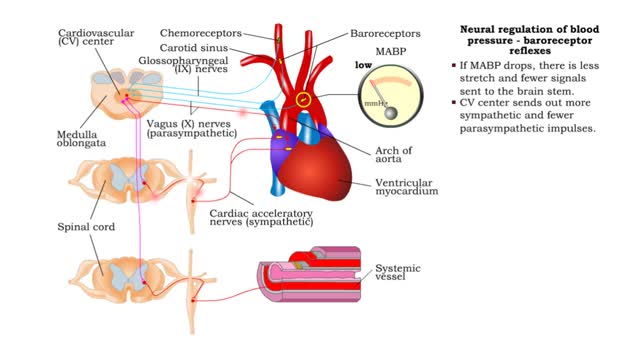
Neural regulation of blood pressure - baroreceptor and chemoreceptor reflexes
By: HWC, Views: 11301
• The nervous system regulates blood pressure with two reflex arcs: baroreceptor and chemoreceptor. ■ Baroreceptors (pressure) and chemoreceptors (chemical) are located in the carotid sinus and aortic arch. • Carotid sinus reflex helps maintain normal blood pressure in brain. • Ba...
By: Administrator, Views: 13879
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell. Synapses are essential to neuronal function: neurons are cells that are specialized to pass signals to individual tar...
Autonomic Nervous System Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14191
Parasympathetic Division Works to conserve energy and innervate the digestive system. When activated, it: stimulates the salivary and digestive glands. decreases the metabolic rate. slows the heart rate. reduces blood pressure. promotes the passage of material through the intestines along...
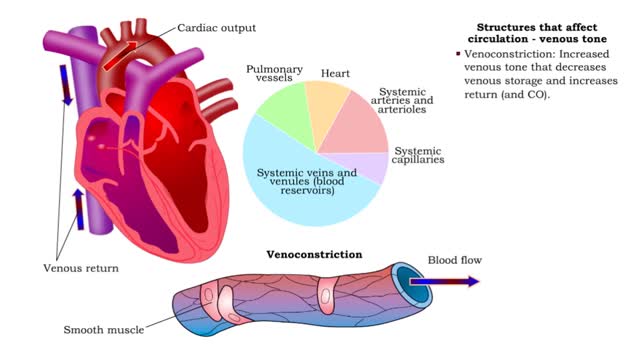
Structures that affect circulation - kidneys and blood volume and skeletal muscle pumping
By: HWC, Views: 11572
• Kidneys regulate blood volume and blood osmolarity via salt and water reabsorption. • Increased reabsorption increases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Decreased reabsorption Increases urine production, which decreases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Systemi...
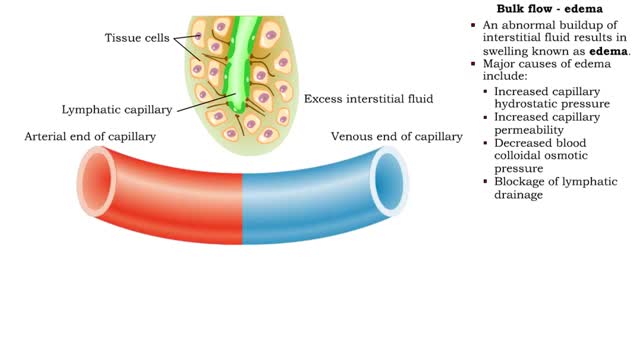
Net filtration pressure and lymph formation, edema & blood velocity
By: HWC, Views: 10767
Bulk flow -net filtration pressure and lymph formation • The net filtration pressure (NFP) is the force promoting filtration minus the force promoting reabsorption. • At the arterial end of an ideal capillary, the filtration pressures are stronger. The result: net filtration. • At t...
Advertisement