Search Results
Results for: 'Net filtration pressure and lymph formation'
By: HWC, Views: 10483
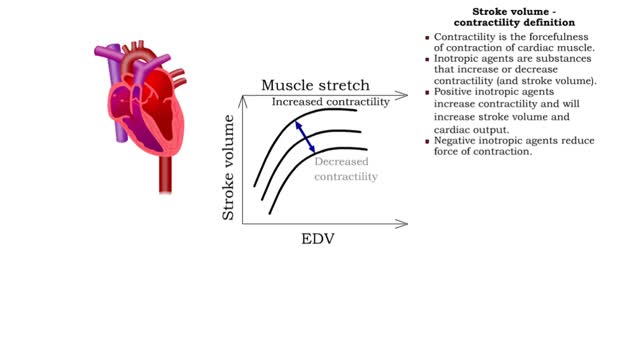
Preload definition • Preload is the degree of stretch of cardiac muscles cells prior to contraction. • The amount of stretch is related to the end-diastolic volume[EDV]. • Increased return blood flow from the veins increases end-diastolic volume. Cardiac muscle sarcomeres stretch and ...
By: HWC, Views: 10518
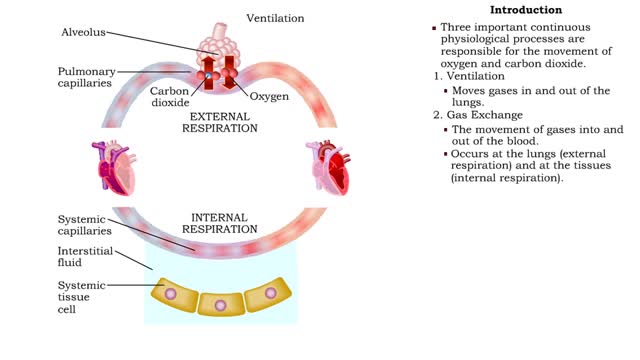
• The respiratory system is responsible for the movement of gases involved in cellular metabolism. • Oxygen is used up and carbon dioxide is generated during the aerobic breakdown of glucose and other fuel molecules in order to produce ATP. • Three important continuous physiological pro...
Types of antimicrobial substances (interferons & complement protein)
By: HWC, Views: 10576
• Found in blood and interstitial fluids. • Discourage microbial growth. • Include interferon and complement proteins. • Produced and released by virus-infected lymphocytes. • Enter new cells and inhibit viral replication. • Act against a large variety of viruses (non-speci...
Cellular defenses (natural killer cells, phagocyte types & process of phagocytosis)
By: HWC, Views: 10255
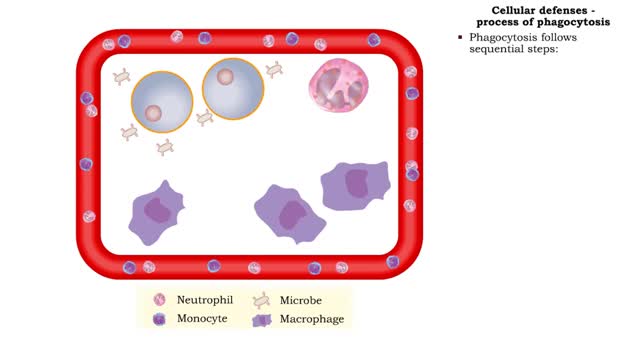
• Lymphocytes that rapidly defend against abnormal (cancer) or virus-infected cells. • Found in blood, spleen, lymph nodes, and red bone marrow. • Lack receptors for binding with specific antigens. • Act upon cells displaying abnormal MHC antigens. • NK cells destroy cells in ...
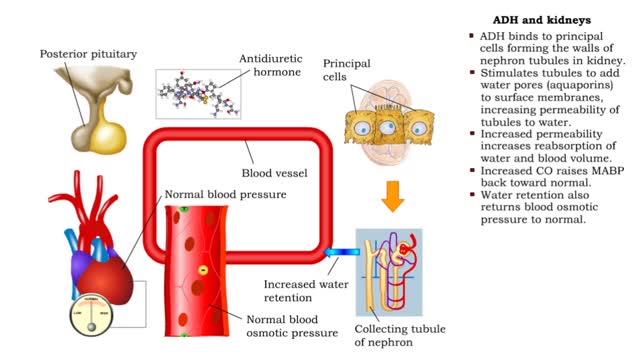
ADH and the arterioles, kidneys, sweat glands and the Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
By: HWC, Views: 10598
• ADH is also known as vasopressin. • Produced by hypothalmus and secreted by neurosecretory cells in posterior pituitary gland. • Responds to high blood osmotic pressure representing low amounts of water in the blood. • Binds to smooth muscle cells in walls of arterioles, stimulate...
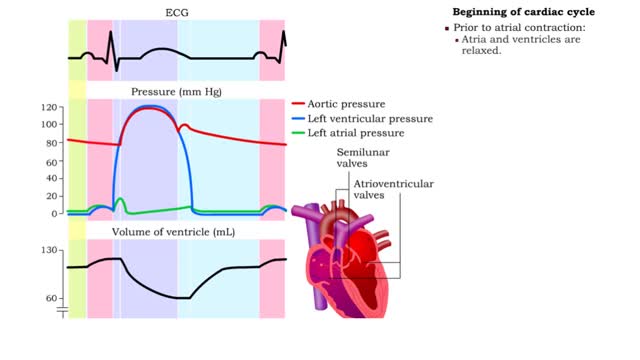
Five phases of cardiac cycle & Atrial contraction
By: HWC, Views: 10589
1. Atrial contraction (atrial systole). 2. Isovolumetric (ventricular) contraction. 3. Ventricular ejection. 4. Isovolumetric (ventricular) relaxation. 5. Passive ventricular filling. Beginning of cardiac cycle • Prior to atrial contraction: • Atria and ventricles are relaxed....
By: Administrator, Views: 13215
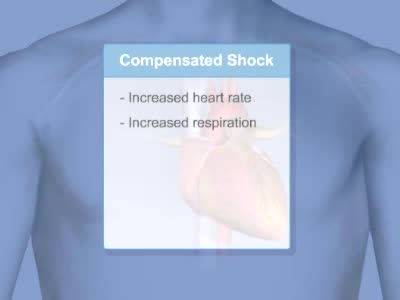
Shock is a life-threatening condition in which delivery of oxygen to the organs is low, causing organ damage and sometimes death. Blood pressure is usually low.
By: Administrator, Views: 13530
Shock is a life-threatening condition in which delivery of oxygen to the organs is low, causing organ damage and sometimes death. Blood pressure is usually low.
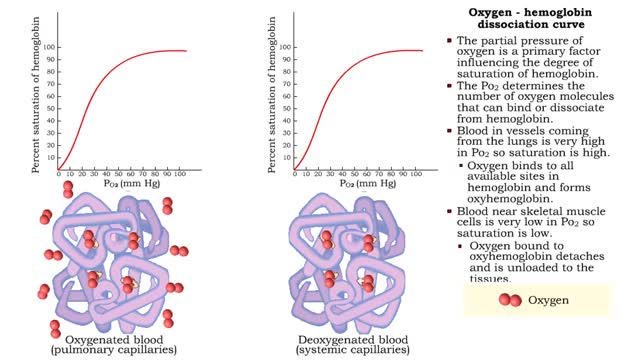
Oxygen - hemoglobin dissociation curve & Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - acidity
By: HWC, Views: 11127
• The partial pressure of oxygen is a primary factor influencing the degree of saturation of hemoglobin. • The Po2 determines the number of oxygen molecules that can bind or dissociate from hemoglobin. • Blood in vessels coming from the lungs is very high in Po2 so saturation is high. ...
Advertisement