Search Results
Results for: 'The life cycle of protein'
By: Administrator, Views: 14845
Pre-eclampsia (PE) is a disorder of pregnancy characterized by the onset of high blood pressure and often a significant amount of protein in the urine. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In severe disease there may be red blood cell breakdown, a low blood platelet c...
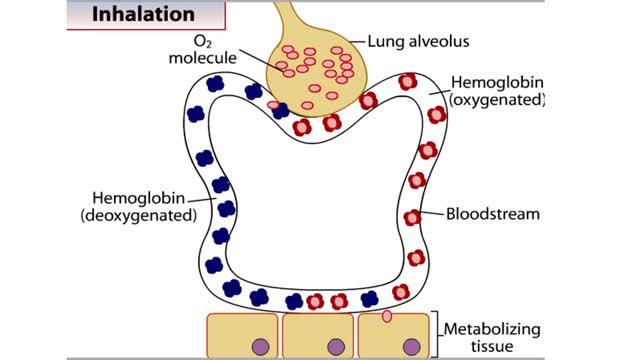
How Hemoglobin Picks Up and Delivers Oxygen
By: HWC, Views: 11142
All of the cells in our bodies require oxygen (02) for survival and must release carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste product. The respiratory and circulatory systems work together as delivery systems for these gases. The lungs exchange these gases between the environment and the bloodstream. The bloo...
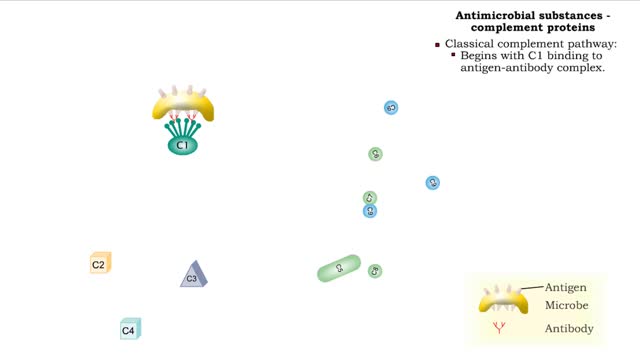
Types of antimicrobial substances (interferons & complement protein)
By: HWC, Views: 11791
• Found in blood and interstitial fluids. • Discourage microbial growth. • Include interferon and complement proteins. • Produced and released by virus-infected lymphocytes. • Enter new cells and inhibit viral replication. • Act against a large variety of viruses (non-speci...
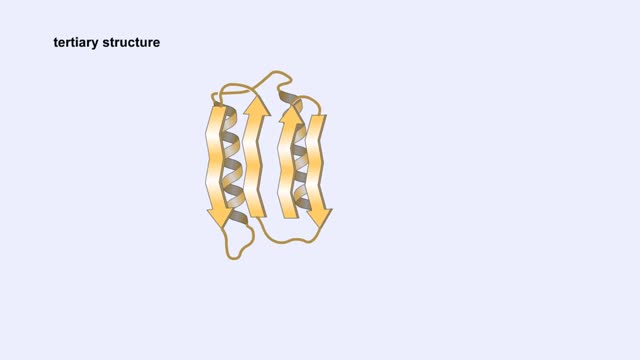
Protein Structure - Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary
By: HWC, Views: 11605
A protein's first order structure, or primary structure, begins with the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain. The 20 different amino acids can be arranged in an infinite number of sequences. For example, the hormone insulin, which regulates the uptake of glucose from the blood into ce...
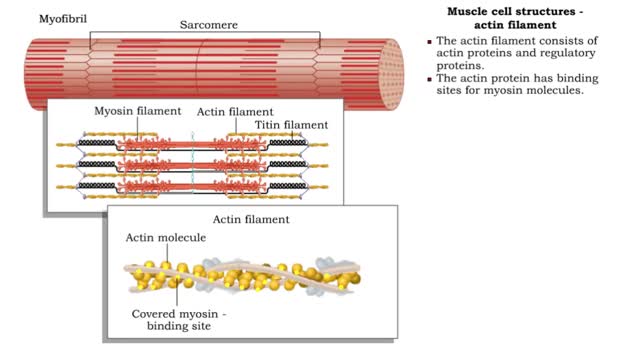
Muscle cell structures - actin, myosin and titin filaments
By: HWC, Views: 11995
Once the muscle cell has been excited it will contract. • A muscle action potential will trigger the release Of Ca2+ ions into the sarcoplasm. • The Ca2+ ions bind to the regulatory proteins and trigger contraction. • Within skeletal muscle cells are structures that provide the ability...
By: HWC, Views: 11955
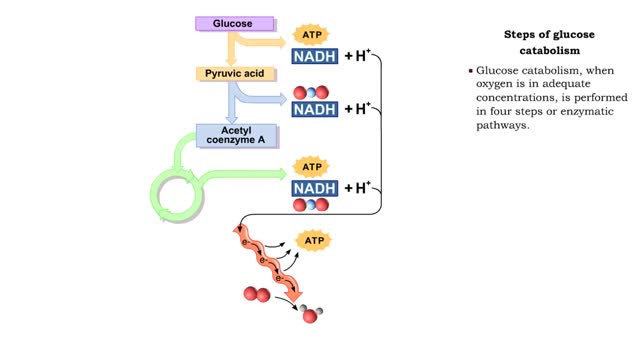
• During digestion, complex carbohydrates are hydrolyzed into monosaccharides, primarily glucose. • The catabolism of glucose is the primary source of energy for cellular production of ATP. • The anabolism of glucose is important in regulating blood glucose levels. • Glucose cat...
Conduction of action potentials
By: HWC, Views: 11866
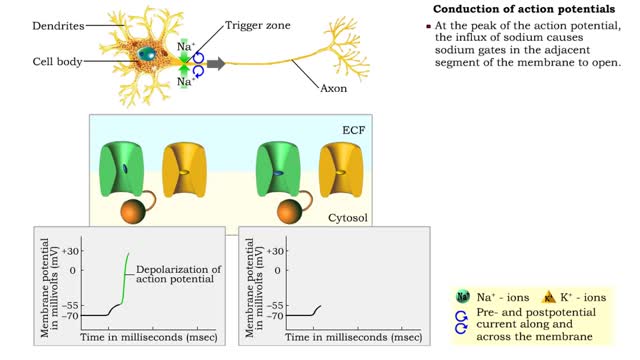
• Action potentials must be rapidly conducted over long distances in order for the nervous system to communicate with other cells. • Propagation of an action potential uses processes similar to those that generate the potential at the trigger zone. • a When a graded potential reaches ...
By: Administrator, Views: 14651
Shock is a life-threatening condition in which delivery of oxygen to the organs is low, causing organ damage and sometimes death. Blood pressure is usually low.
By: Administrator, Views: 14561
An aneurysm refers to a weakening of an artery wall that creates a bulge, or distention, of the artery. Most aneurysms do not show symptoms and are not dangerous. However, at their most severe stage, some can rupture, leading to life-threatening internal bleeding.
Advertisement