Search Results
Results for: 'carbon backbones'
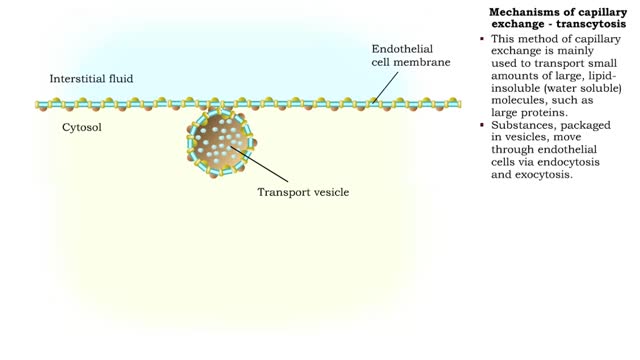
Mechanisms of capillary exchange
By: HWC, Views: 10827
■ The primary role of capillaries is to permit the exchange of nutrients and wastes between the blood and tissue cells (via interstitial fluid). ■ Oxygen and nutrients move from the blood to the cells. ■ Carbon dioxide and other wastes move from the cells to the blood. The three ba...
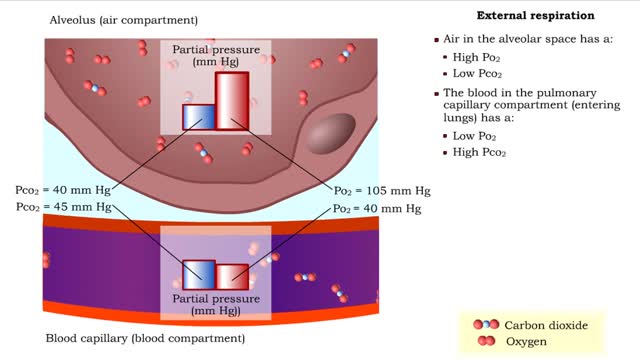
Gas exchange - partial pressure, locations, external and internal respiration
By: HWC, Views: 10803
▪ In a mixture, each individual gas exerts a pressure that is proportional to the concentration of that gas within the mixture. • This part of the total pressure is called a "partial pressure". • A gas moves along the part of the pressure gradient determined by its own concentration. ...
Labor and Delivery - Placenta Cord
By: Administrator, Views: 432
Soon after a baby is conceived, a support system, comprised of the placenta and umbilical cord, begins to develop. These two structures are essential for sustaining a healthy pregnancy, explains Donald Davis, an obstetrician in Medicine Hat, Alta., and past president of the Society of Obstetricia...
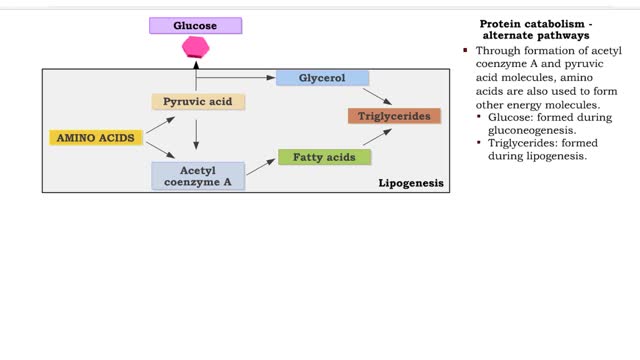
Protein catabolism (Krebs cycle) and Protein anabolism (protein synthesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11162
• Deaminated acids are brought into the Krebs cycle to be oxidized to CO2 and H2O. • Before entering the Krebs cycle, the deaminated acids are converted into intermediate products (pyruvic acid, acetyl coenzyme A, carbonic acids). • In the Krebs cycle, amino acids are oxidized to form r...
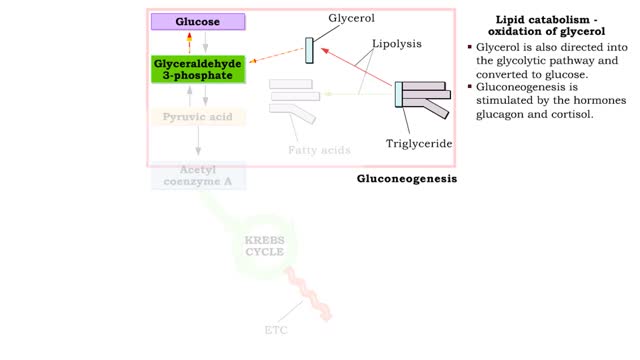
Lipid catabolism ( ketogenesis and oxidation of glycerol) and Lipid anabolism (lipogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 10963
• During excessive beta oxidation, the two-carbon fatty acid fragments are converted into acidic ketone bodies. • Ketosis, the overproduction of ketone bodies, can lead to acidosis (ketoacidosis) of the blood. • After lipolysis, glycerol is converted to pyruvic acid. • Pyruvic aci...
Advertisement