Search Results
Results for: 'pressure flow model'
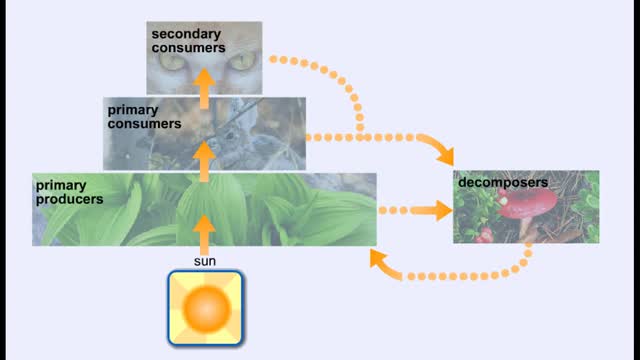
Energy Flow - Trophic Levels and Food
By: HWC, Views: 10160
All of these relationships between different species are founded on one thing: energy. Organisms get food in order to get energy, which is used by the organism for growth, maintaining health, and reproduction. We can classify the members of a community according to how they obtain food. Produc...
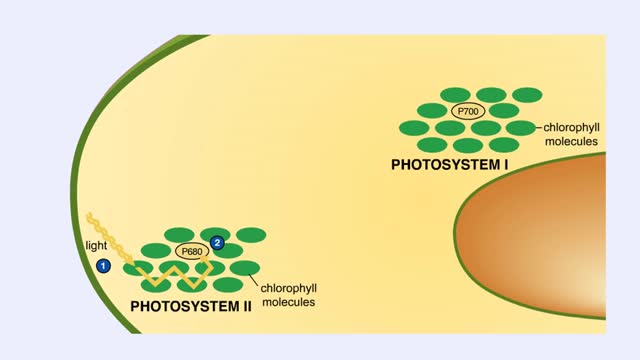
Chloroplast Structure & Light Dependent Reactions (Photosystem 1 and 2 Cyclic Electron Flow)
By: HWC, Views: 10043
The leaf is the principle photosynthetic organ of the plant. This is a cross section of a leaf. The rectangular-shaped cells are part of the photosynthetic tissue called the palisade mesophyll. Each photosynthetic cell can contain several hundred organelles known as chloroplasts. The chlorop...
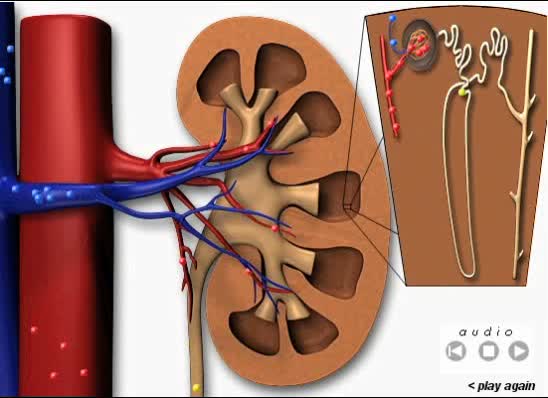
Blood Flow Through the Kidneys
By: Administrator, Views: 13301
Purplish-brown, bean-shaped organs located behind abdominal cavity (retroperitoneal area) on either side of spine, between thoracic vertebrae and lumbar region.
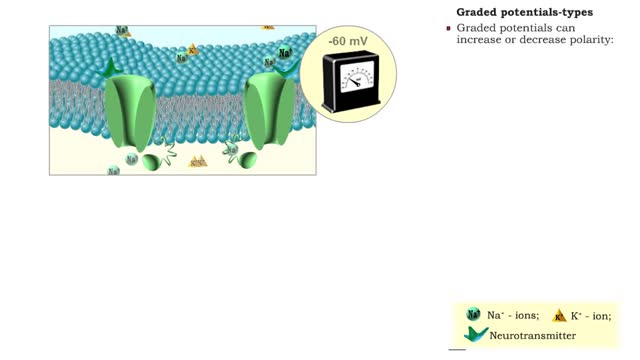
Graded potentials - electrical characteristics and types
By: HWC, Views: 10767
• A graded potential occurs when a gated channel is opened or closed, altering ion flow through the membrane. • Changes in ion and charge distributions cause voltage changes to the resting membrane potential. • The strength of the stimulus determines the number of gated channels affect...
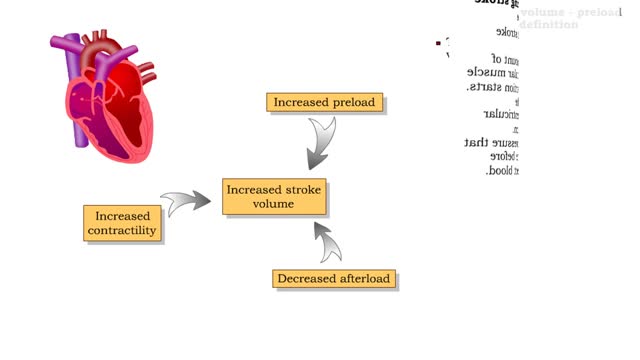
Definitions of stroke volume, preload definition & Factors influencing stroke volume
By: HWC, Views: 10331
• Stroke volume is directly correlated with cardiac output-the greater the stroke volume the greater the cardiac output. • Stroke volume represents the difference in the amount of blood between: • the volume in the ventricles at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume EDV); • the ...
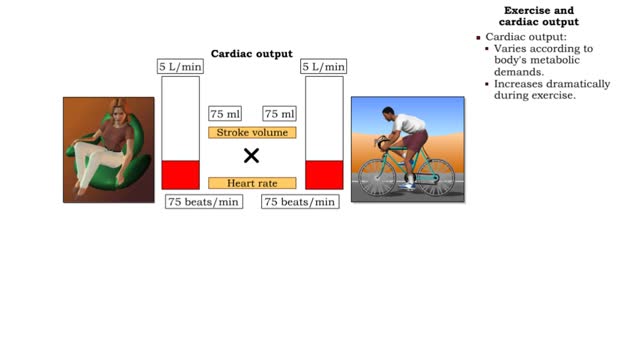
Exercise and cardiac output & Definition of stroke volume
By: HWC, Views: 10499
▪ Cardiac output: • Maintains blood flow throughout the body. • Measure of blood volume ejected from the heart over a given time. • Determined by multiplying heart rate by stroke volume (CO = SV x HR). • Heart rate: Number of beats/min. • Stroke volume: Amount of blood eject...
Labor and Delivery - Transition
By: Administrator, Views: 363
The last part of active labor – when your cervix dilates from 8 to a full 10 centimeters – is called the transition period because it marks the shift to the second stage of labor. This is the most intense part of labor. Contractions are usually very strong, coming every two and a half to t...
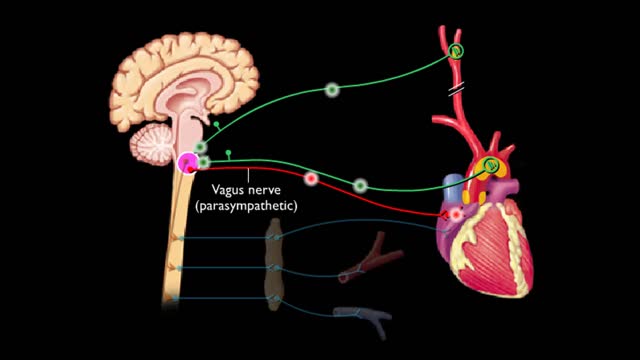
By: HWC, Views: 9829
Baroreceptors located In the carotid sinus and the arch of the aorta respond to increases in blood pressure. Increased blood pressure stretches the carotid arteries and aorta causing the baroreceptors to increase their basal rate of action potential generation. Action potentials are conduct...
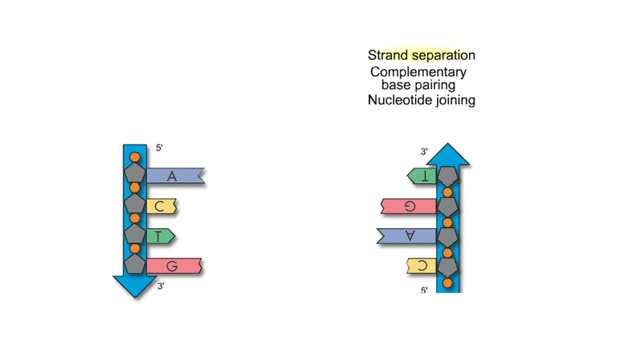
Subunits of DNA And Semi Conservative Replication
By: HWC, Views: 6861
Adenine is a purine with a double-ring structure. In double-stranded DNA, adenine base-pairs with thymine. Guanine is a purine with a double-ring structure. In double-stranded DNA, guanine base-pairs with cytosine. Thymine is a pyrimidine with a single-ring structure. In double-stranded DNA, th...
Advertisement