Search Results
Results for: 'Plant Cell Animation'
By: HWC, Views: 9438
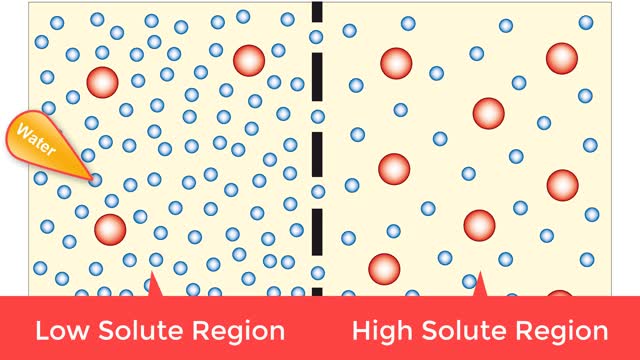
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
By: HWC, Views: 8926
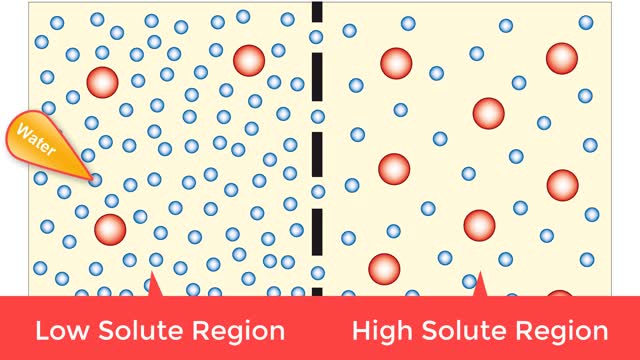
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
Proteins Defined, Hierarchy & Composition of Cells
By: HWC, Views: 11278
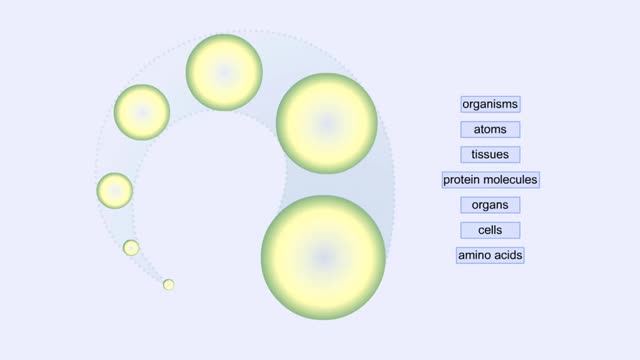
Proteins are long chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Together with the other three biological macromolecules—carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids—proteins are the building blocks of cells. Proteins are the most complex and abundant biological macromolecules in cel...
Nervous pathway to the Neuromuscular (NMJ)
By: HWC, Views: 12182
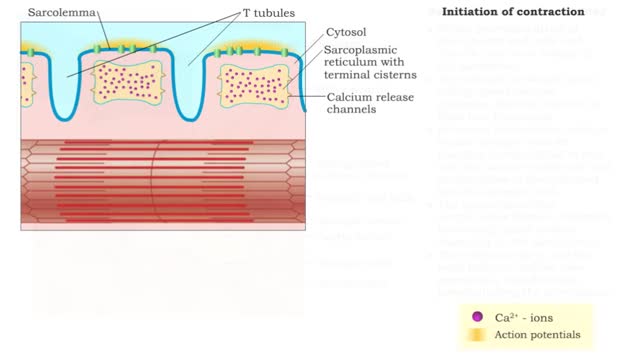
• A nervous impulse, also called an action potential, starts from the brain or spinal cord to signal skeletal muscle cell contraction. Action potentials continue along a motor neuron to the muscle cell. • The signal to contract must cross a synapse - the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) - betwe...
By: Administrator, Views: 14727
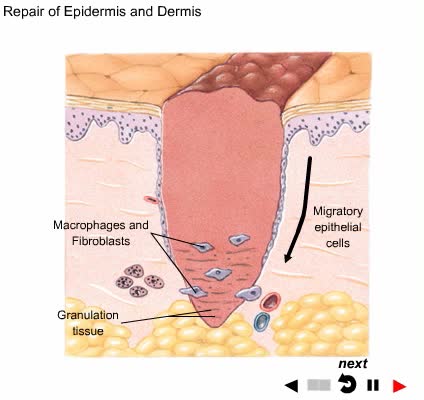
A wound is an injury to living tissue caused by a cut, blow, or other impact, typically one in which the skin is cut or broken.
ATPase function - membrane transport, contractile proteins and synthesis
By: HWC, Views: 12141
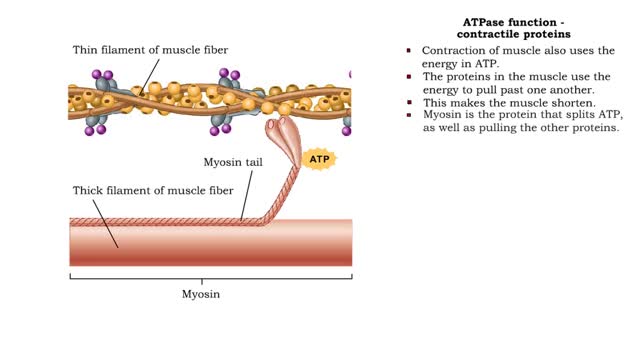
• Energy from ATP is used to move ions across the cell membrane during active transport. • This membrane protein transports sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell. As such, it is called a sodium-potassium pump. • Because this pump also acts as an enzyme to hydrolyze ATP it i...
Depolarization of the SA node, Action potentials of the myocardium & ANS effects
By: HWC, Views: 11573
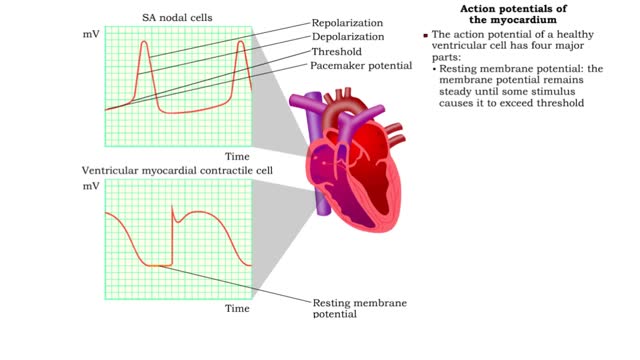
• A typical contractile cell in the myocardium has a resting membrane potential. • The resting membrane potential of cells in the SA node is not fixed, and is known as the pacemaker potential. • The action potential of a healthy SA nodal cell has three parts: • Pacemaker potential: ...
Non-polar compounds - insolubility
By: HWC, Views: 11801
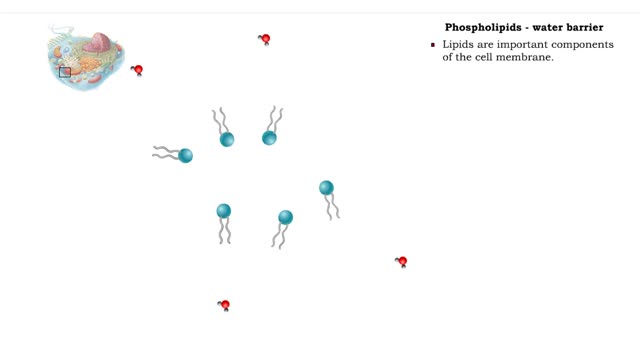
• A non-polar molecule has uniform distribution of electrons. • Non-polar compounds like fatty acids in lipids have a high proportion of carbon and hydrogen. • Lipids possess no charge or partial charge. • Lipids are not attracted to water molecules. • Lipids are not soluble in...
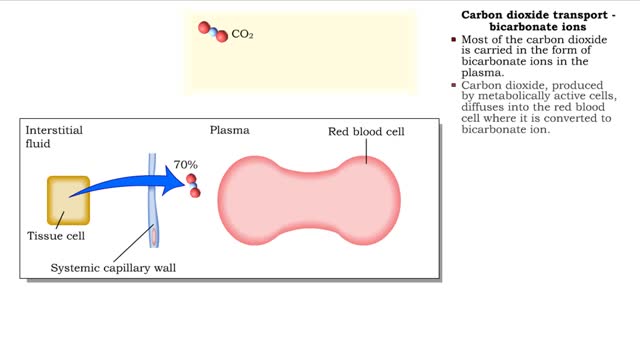
Methods of carbon dioxide transport - carbaminohemoglobin and bicarbonate ions
By: HWC, Views: 11771
• Carbon dioxide is transported three ways: • As bicarbonate ions in the plasma. • Bound to hemoglobin. • As a dissolved gas in the plasma. • A small percent of carbon dioxide is transported as a dissolved gas. • Some of the carbon dioxide is bound to hemoglobin, in the fo...
Advertisement