Search Results
Results for: 'capillary hydrostatic pressure'
Angiotensin II - kidneys, adrenal glands and dehydration
By: HWC, Views: 10576
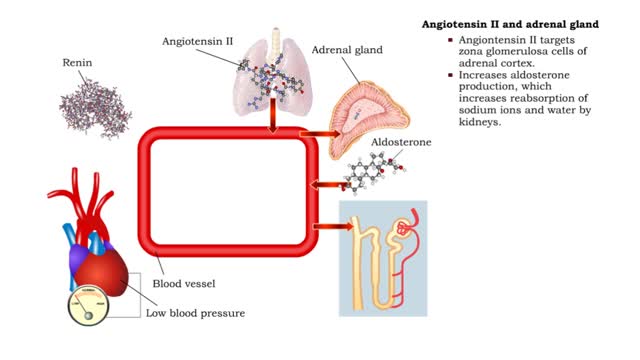
• Angiontensin II targets cells in the proximal convoluted tubule of the nephron. ■ The reabsorption of Na+ and Cl- ions sets up an osmotic gradient favoring the retention of water. • Decreases urine production and increases blood volume and pressure. • Angiontensin II targets zon...
By: HWC, Views: 11060
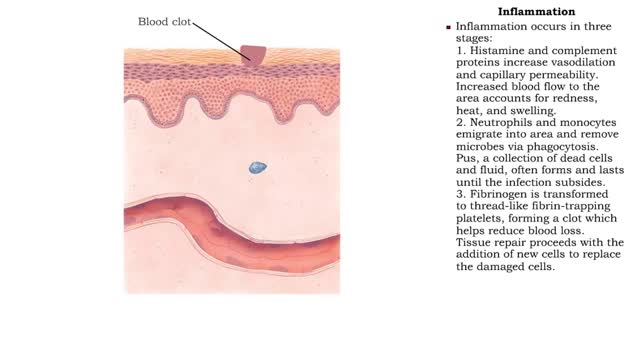
• Inflammation is an immune response that can occur anywhere in the body, but is observed most frequently on the skin. • It provides early protection by preventing infection from spreading to other parts of the body. • Inflammation also promotes repair of damaged tissues. Inflammat...
By: Administrator, Views: 13748
Carpal tunnel syndrome is numbness, tingling, weakness, and other problems in your hand because of pressure on the median nerve in your wrist. The median nerve and several tendons run from your forearm to your hand through a small space in your wrist called the carpal tunnel.
Cortisol (protein catabolism, gluconeogenesis, vasoconstriction & anti-inflammation)
By: HWC, Views: 10249
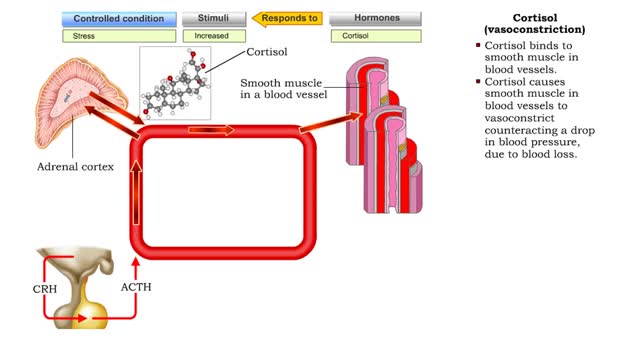
• Stressors stimulate production of hypothalamic releasing hormones, corticotropin releasing hormone, hormone (CRH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulate. • These hormones promote increased production of 1 cortisol from the zona fasciculata cells of the adrenal cortex. • Cort...
By: Administrator, Views: 13835
The integumentary system comprises the skin and its appendages acting to protect the body from various kinds of damage, such as loss of water or damages from outside. The integumentary system includes hair, scales, feathers, hooves, and nails. It has a variety of additional functions; it may serv...
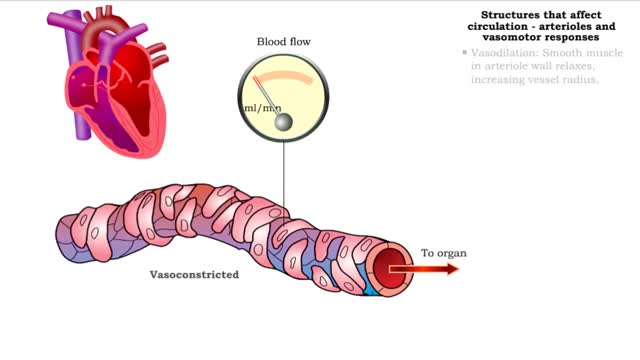
Structures that affect circulation - arterioles and vasomotor responses and venous return
By: HWC, Views: 10589
■ Small arteries and arterioles determine SVR. • Blood pressure drops significantly as blood passes through arterioles. • Decreasing arteriole radius and decreased wall elasticity are the main reasons for increased SVR. ■ Small changes in arteriole radius can cause large changes in ...
By: HWC, Views: 11358
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
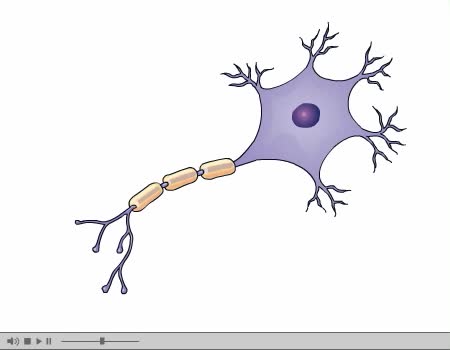
Nerve Impulse Transmission Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 13956
How nerves transmit impulses. Stimulation of a nerve occurs at a receptor. Sensory receptors Specialized to specific types of stimulation such as heat, cold, light, pressure, or pain. React by initiating a chemical change or impulse. All-or-none principle Means that no transmission occ...
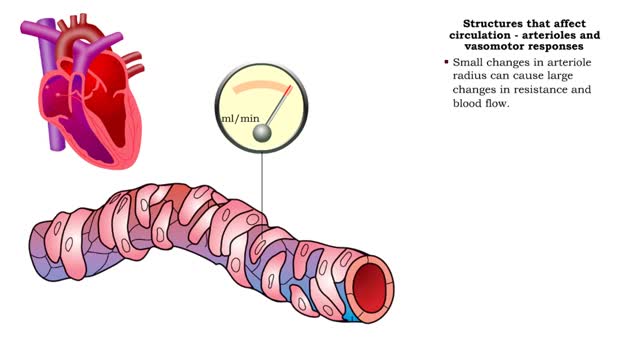
Structures that affect circulation - arterioles and vasomotor responses
By: HWC, Views: 10193
■ Small arteries and arterioles determine SVR. ■ Blood pressure drops significantly as blood passes through arterioles. ■ Decreasing arteriole radius and decreased wall elasticity are the main reasons for increased SVR. ■ Small changes in arteriole radius can cause large changes in ...
Advertisement