Search Results
Results for: 'Insulin Production'
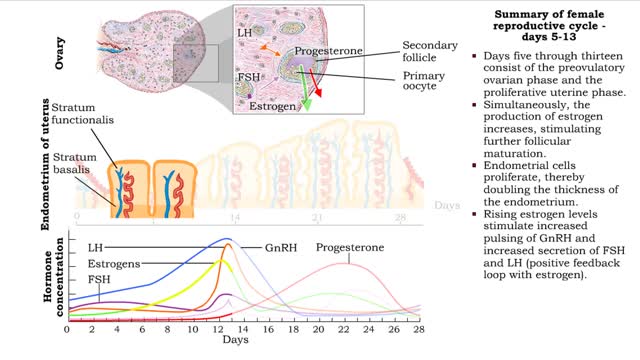
Summary of female reproductive cycle days 1-28
By: HWC, Views: 11508
■ The first five days of the cycle include the menstrual phase. ■ Progesterone and estrogen levels are low. ■ Menses occurs. ■ GnRH pulses more frequently promoting FSH and LH levels to rise. ■ Primary follicles are stimulated to develop. ■ Days five through thirteen consist o...
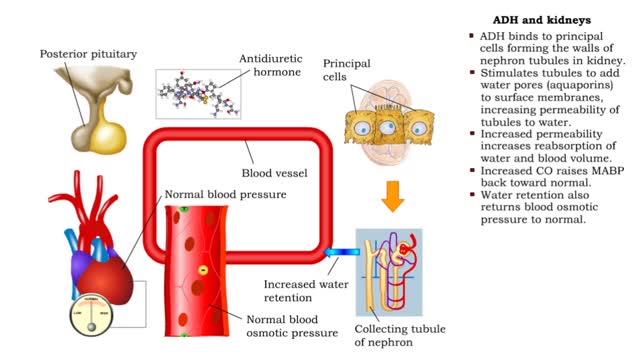
ADH and the arterioles, kidneys, sweat glands and the Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
By: HWC, Views: 11126
• ADH is also known as vasopressin. • Produced by hypothalmus and secreted by neurosecretory cells in posterior pituitary gland. • Responds to high blood osmotic pressure representing low amounts of water in the blood. • Binds to smooth muscle cells in walls of arterioles, stimulate...
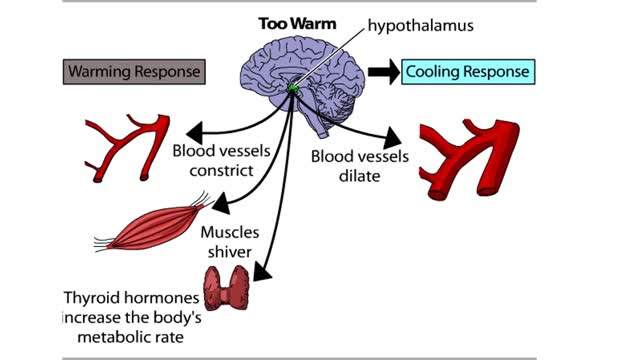
The Hypothalamus: The Body's Thermostat (Human Thermostat)
By: HWC, Views: 10237
Normal body function requires a relatively constant body temperature, which is regulated by the body's thermostat, a region of the brain called the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus generates a temperature set point for the body and appears to be the major site for the integration of temperature inf...
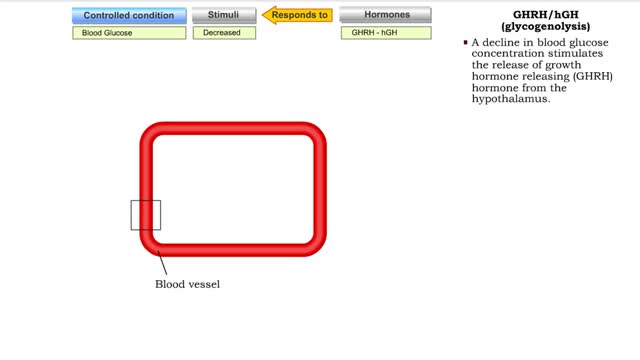
Hormonal feedback loop components & Glucagon (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 10835
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after ...
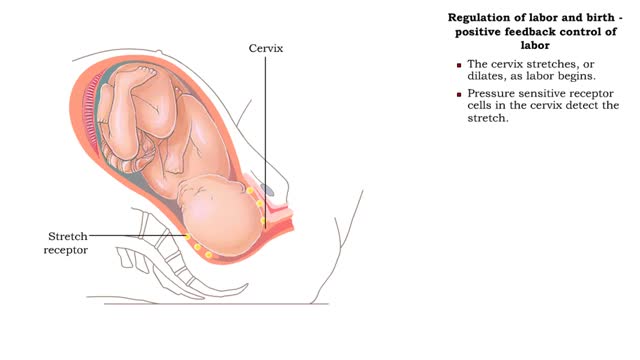
Labor and Childbirth - The Three Stages of Labor: Dilation, Expulsion & Placental مراحل الولادة
By: HWC, Views: 11447
Regulation of labor and birth - effects of estrogen and oxytocin on onset of labor • Just prior to birth, high placental corticotropin-releasing hormone levels stimulate the production of more estrogen. • High estrogen levels overcome the inhibitory effects of progesterone on uterine sm...
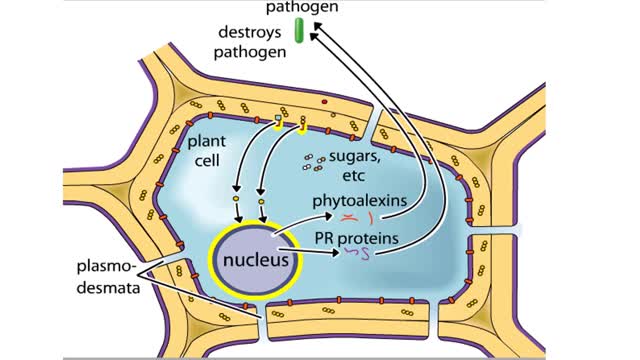
Plant Defense Mechanisms from Pathogens
By: HWC, Views: 10418
Plants and pathogens have coevolved such that pathogens can recognize plants by the sugars, or other molecules, they produce. Plants, in turn, can recognize pathogens by the molecules they produce. The ability to recognize pathogens allows plants to activate defense systems that can prevent wides...
Advertisement