Search Results
Results for: 'Non-specific disease resistance mechanisms'
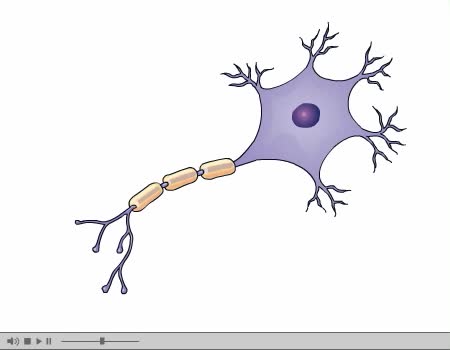
Nerve Impulse Transmission Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14331
How nerves transmit impulses. Stimulation of a nerve occurs at a receptor. Sensory receptors Specialized to specific types of stimulation such as heat, cold, light, pressure, or pain. React by initiating a chemical change or impulse. All-or-none principle Means that no transmission occ...
Sister chromatids of a metaphase chromosome animation
By: HWC, Views: 9092
At metaphase, the chromosomes are duplicated and are at their most condensed. In each chromosome. two identical sister chromatids are held together at a constricted region called the centromere. When a chromosome is condensed, interactions among chromosomal proteins keep loops of DNA tightly ...
By: Administrator, Views: 13755
Kidney stones (renal lithiasis, nephrolithiasis) are hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form inside your kidneys. Kidney stones have many causes and can affect any part of your urinary tract — from your kidneys to your bladder. Often, stones form when the urine becomes concentrate...
By: HWC, Views: 11077
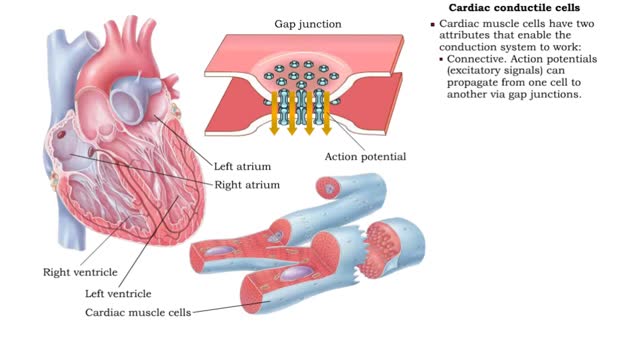
• In order for the heart to function properly, all of its cells must contract in a specific sequence. This sequence is determined by a pathway known as the conduction system. • Cardiac muscle cells have two attributes that enable the conduction system to work: • Connective. Action pot...
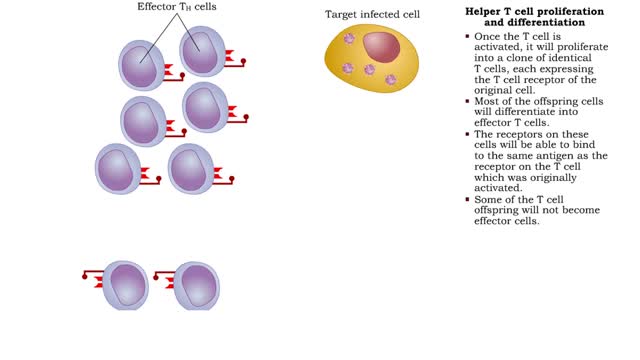
Helper T cell receptors, activation, proliferation, differentiation & action
By: HWC, Views: 11064
• Most cells which have CD4 on their surface become Helper T cells (TN cells). • The CD4 1 cells only recognize a foreign antigen when it is presented with an antigen presenting immune cell (APC) that includes MHC-II protein. • The Helper T cell antigen receptor must match the presented...
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
By: Administrator, Views: 13984
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body in both health and disease. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the or...
By: Administrator, Views: 13767
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), poor nourishment, poor circulation, loss of hormonal support, loss of nerve supply to the target organ, excessive amount of apoptosis of c...
By: HWC, Views: 5496
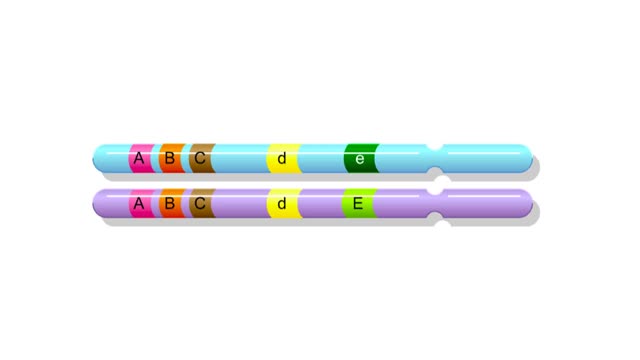
Diploid organisms have pairs of genes, on pairs of homologous chromosomes. Each gene has a specific location on the chromosome. We call this the gene's locus. In this species, the locus for gene B is always between the loci for genes A and C. Most genes come in two or more slightly differen...
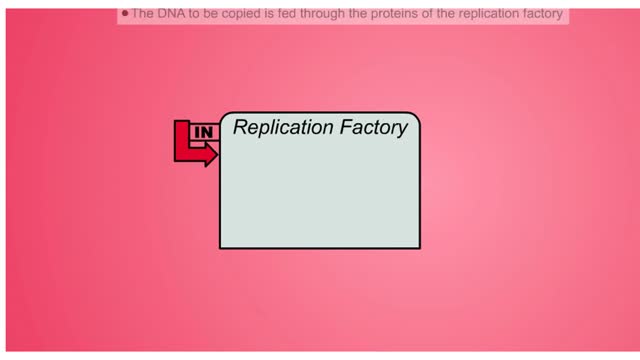
DNA Replication Factory and Protein
By: HWC, Views: 10504
DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) carries all the genetic information needed to re-create itself and to pass on the characteristics of the organism. The “factory” model of DNA replication hypothesizes a specific nuclear structure in which the molecular machinery for replication forks are brou...
Advertisement