Search Results
Results for: 'membrane attack complex'
By: HWC, Views: 10616
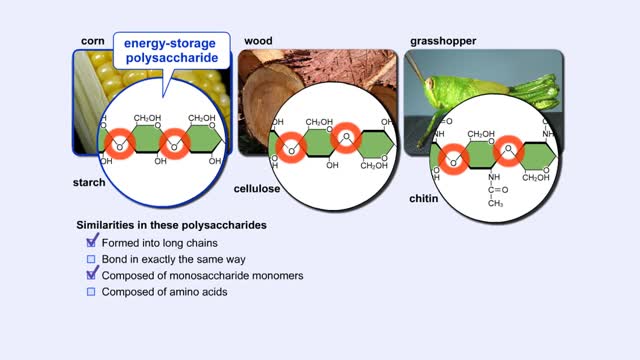
More complex sugars are called polysaccharides (from "poly" meaning "many" and "saccharum" meaning "sugar"). Many things in nature are made of polysaccharides. Here we show one of the polysaccharides in corn, another in wood, and another in the exoskeletons of insects like grasshoppers. How are a...
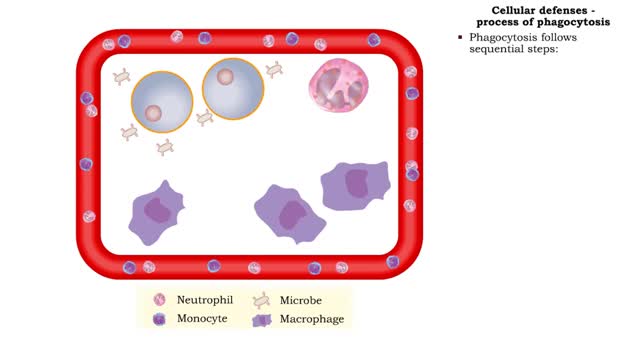
Cellular defenses (natural killer cells, phagocyte types & process of phagocytosis)
By: HWC, Views: 10723
• Lymphocytes that rapidly defend against abnormal (cancer) or virus-infected cells. • Found in blood, spleen, lymph nodes, and red bone marrow. • Lack receptors for binding with specific antigens. • Act upon cells displaying abnormal MHC antigens. • NK cells destroy cells in ...
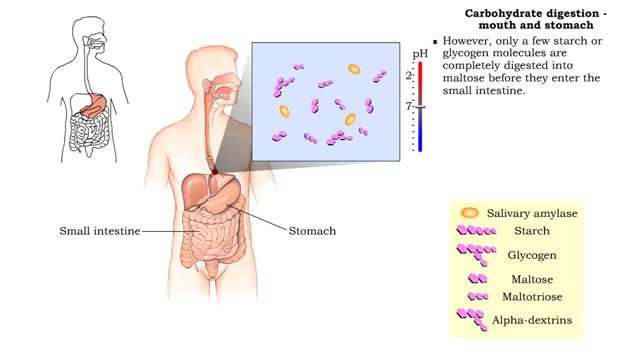
Carbohydrate digestion - mouth and stomach & pancreas and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 10842
• Digestion of complex carbohydrates (starches and glycogen) involves: • Amylases produced by the salivary glands and pancreas. • Brush-border enzymes in small intestine. • In the mouth, amylase from the parotid and submandibular salivary glands begins carbohydrate digestion. �...
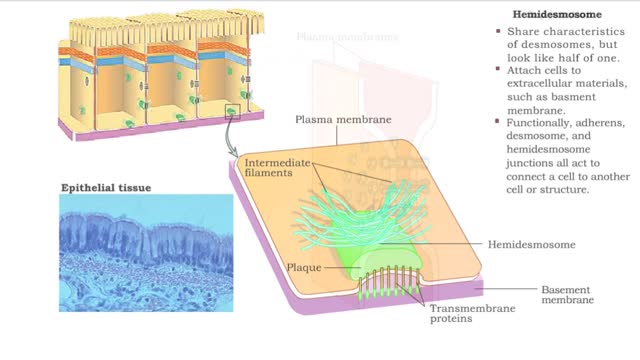
Type of Cell Junctions - Desmosome, Hemidesmosomes and Gap Junctions
By: HWC, Views: 11334
Cell Junctions: Cell junctions are found in some multi-cellular organisms. They exist of complexes and are found between cells and between cells and other structures. The junctions provide a way for cells to connect and exchange signals. What are tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions...
By: HWC, Views: 10642
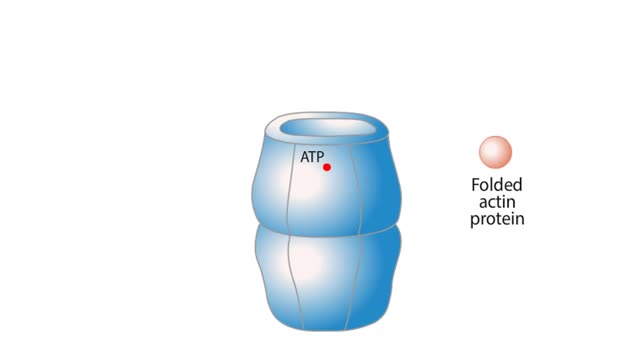
The life cycle of a typical protein begins with its synthesis on a ribosome. As the polypeptide chain grows, molecules of a chaperone protein bind along its length. This prevents misfolding of the nascent polypeptide. ATP binding causes chaperone release. For most proteins, the polypeptide th...
By: HWC, Views: 5198
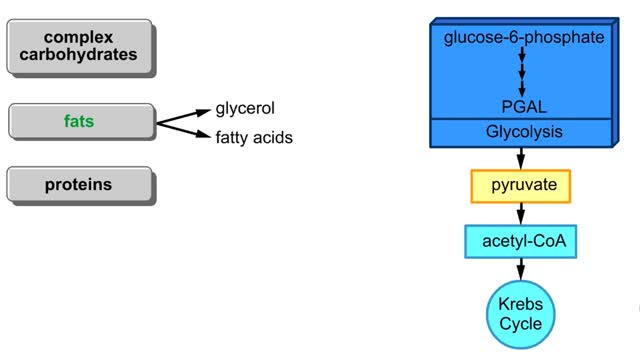
Points at which organic compounds enter the reaction stages of aerobic respiration. Complex carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, such as glucose. They become the substrates for glycolysis. If your body doesn't need to burn glucose for energy, glucose-6-phosphate can be co...
By: HWC, Views: 10403
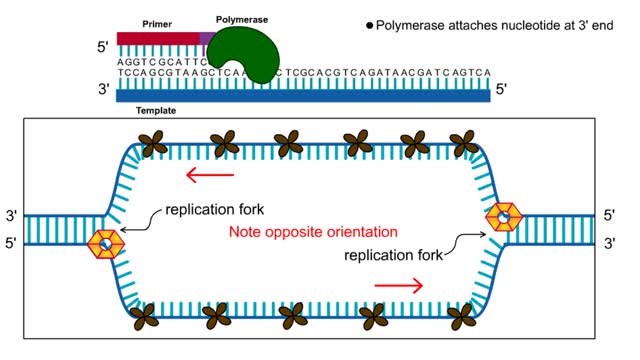
First step: strands are separated • Helicase unwinds the DNA double helix at the replication fork • SSBs coat the single strands to prevent reannealing • Polymerase attaches nucleotide at 3' end • Synthesis is in 5' to 3' direction DNA Polymerase: • Only extends nucleic ac...
By: Administrator, Views: 14244
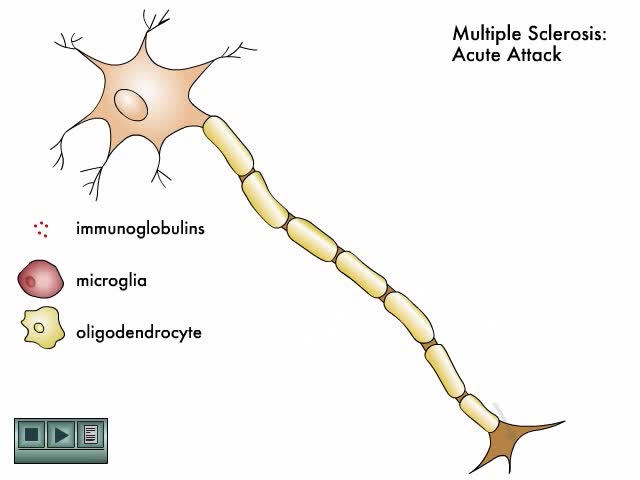
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a demyelinating disease in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to communicate, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, mental, and so...
By: Administrator, Views: 14064
Status epilepticus (SE) is a single epileptic seizure lasting more than five minutes or two or more seizures within a five-minute period without the person returning to normal between them. Previous definitions used a 30-minute time limit. The seizures can be of the tonic–clonic type, with a re...
Advertisement