Search Results
Results for: 'Protein catabolism'
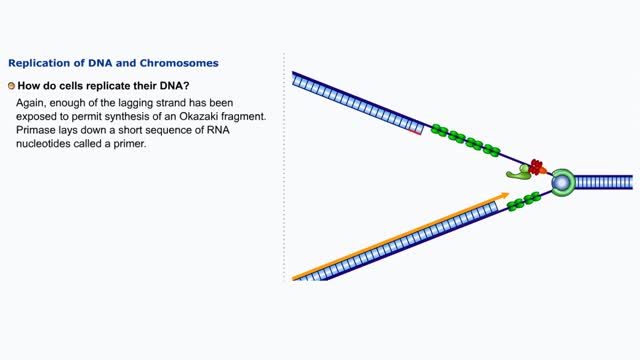
Replication of DNA and Chromosomes/ How do cells replicate their DNA? (Animation) no Audio
By: HWC, Views: 10901
DNA replication in E. coil begins at a site called oriC where a replication bubble forms. At either end of this bubble is a replication fork. Since DNA polymerase Ill can read its DNA template strand only in the 3' to 5' direction this means that one strand (leading) can be read continuously b...
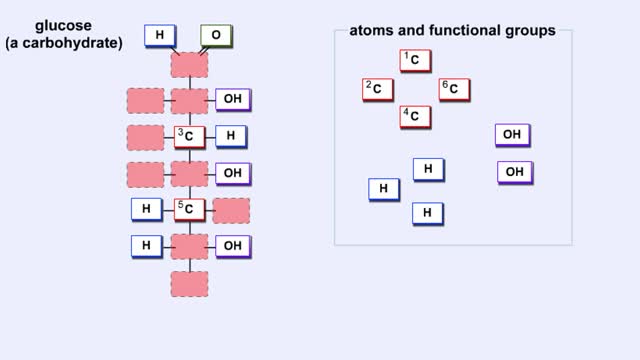
What Are Carbohydrates? Importance of Carbs & High Carb Food
By: HWC, Views: 11187
We hear a lot about carbohydrates in the news. Everybody seems to be on a low-carb diet. The news media often has stories on this diet fad, and companies are busy producing products with reduced carbohydrates. What's this fascination with carbohydrates? In a word: "Diet." The fact is that carb...
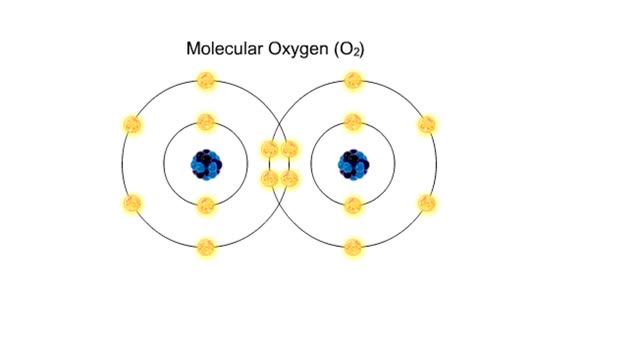
Bond in biological molecules (Ionic, Covalent and Hydrogen bonds)/ How atoms bond?
By: HWC, Views: 8346
Sodium atoms and chloride atoms have unfilled orbitals in their outer shells. The lone electron in the outermost shell of a sodium atom can be pulled or knocked out. This ionizes the atom. It is now a positively charged sodium ion. A chlorine atom has an electron vacancy in its outer shell and...
By: Administrator, Views: 14440
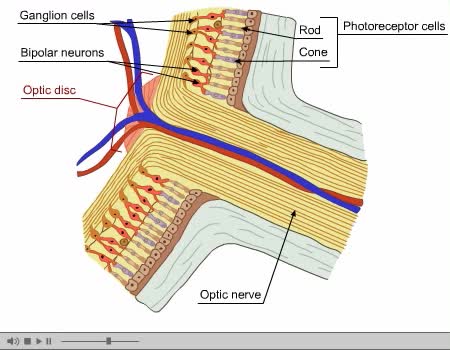
A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuroepithelial cell found in the retina that is capable of visual phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (visible electromagnetic radiation) into signals that can stimulate biological processes...
What are the Parts of a Plant Cell?
By: HWC, Views: 10049
Every chloroplast in a plant cell is packed with stacks of flattened sacs called thylakoids. The thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll, as well as most of the other components required for the light reactions of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll-containing structures within the membranes are c...
Advertisement