Endocytosis -Types and Phagocytosis
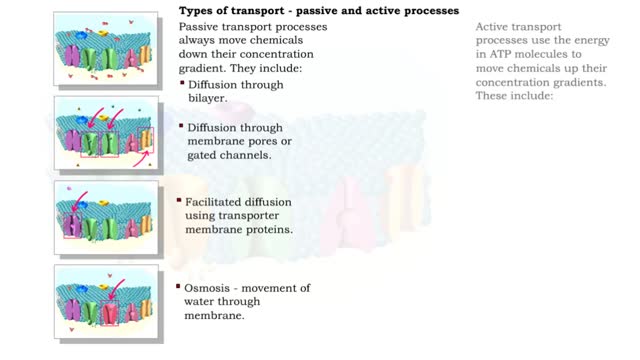
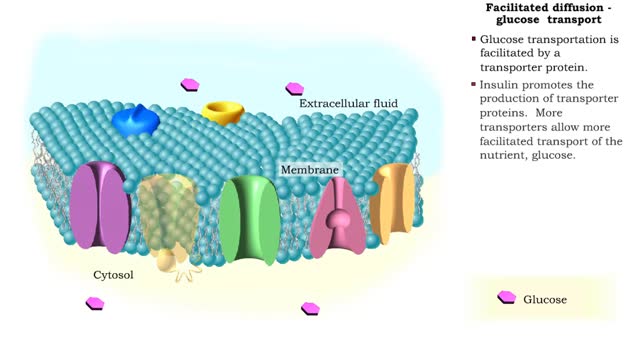
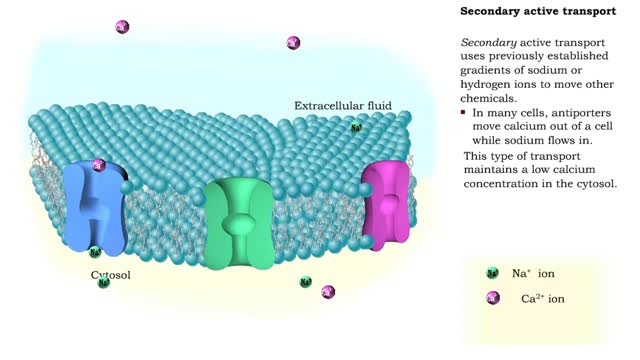
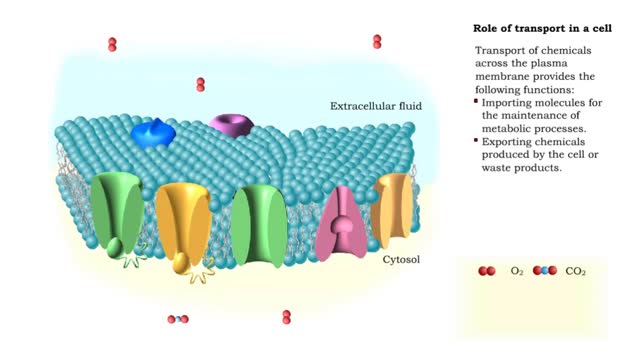
Endocytosis is the process by which a substance is brought inside a cell without having to pass through the cell membrane. It is the opposite of endocytosis, the process by which substances exit the cell without having to pass through the cell membrane. Exocytosis – membrane-enclosed secretory vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane and release their contents into the extracellular fluid. Transcytosis – a combination of endocytosis and exocytosis used to move substances from one side of a cell, across it, and out the other side. A small, round sac called a vesicle is formed from the existing membrane and surrounds the particles to be transported. There are three types of endocytosis: pinocytosis, phagocytosis, and receptor mediated endocytosis. phagocytosis (cell eating) is the process by which cells engulf and digest large molecules. The cell send out projections of its cytoplasm called pseudopodia. Cells, like blood cells, that engage in phagocytosis are called phagocytes. Bacteria binds to a receptor causing the membrane and cytosol to flow and extend to form pseudopods. The phagosome (Pseudopods that surround the bacteria) will fuse with a lysosome and enzymes in the lysosome will digest the bacteria.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.