Exocytosis - secretion
Exocytosis is another method of vesicular transport that moves large volumes Of fluid or chemicals out of the cell. It is a process by which a cell transports secretory products through the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. A examples of cellular secretory products: 1. Secreted protein - enzymes, peptide hormones, and antibodies 2. Neurotransmitters from nerve cells 3. Plasma membrane proteins 4. Antigens - pieces of bacteria or other invaders which stimulate the immune response. Exocytosis can be either calcium-dependent or calcium-independent. In calcium-dependent exocytosis, an influx of calcium into the cell will stimulate secretion. This happens when a protein is only secreted when needed. • Vesicles seal to the plasma membrane and release their contents to the extracellular fluic ' Cells remove waste products resulting from endocytosis. • Secretion of neurotransmitters, hormones, and digestive enzymes is an important function of exocytosis.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



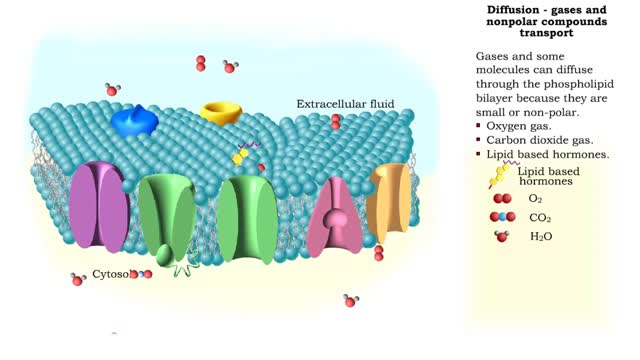
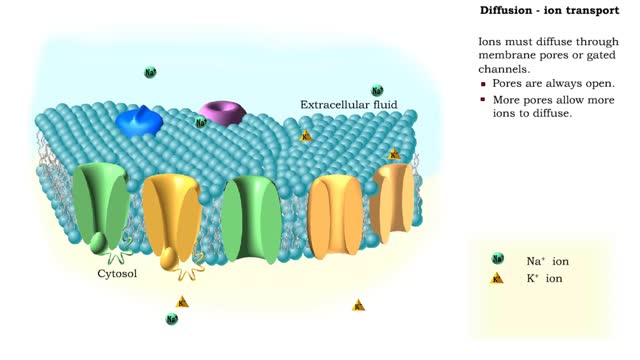
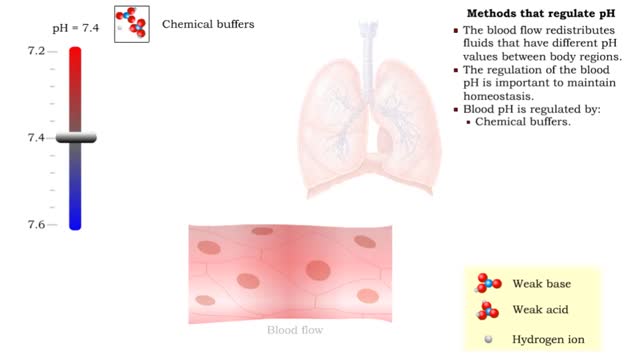
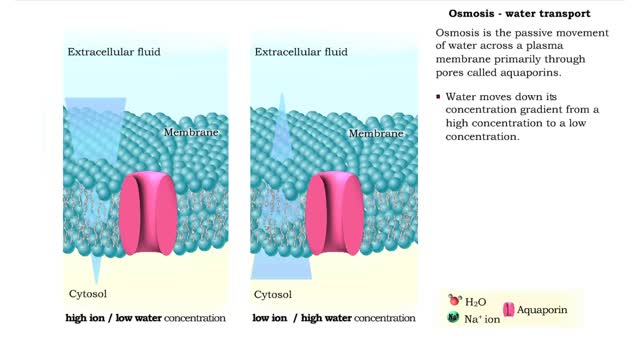
Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.