Role of the respiratory system - effect of altered ventilation rates
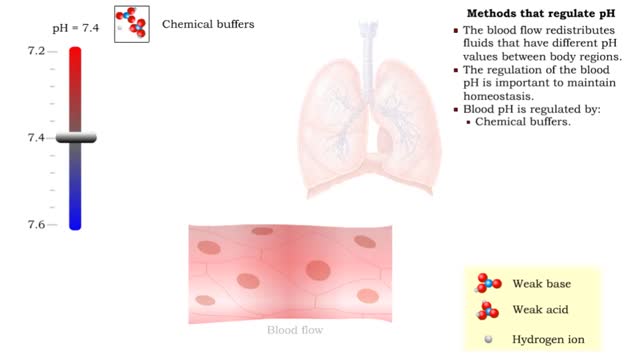
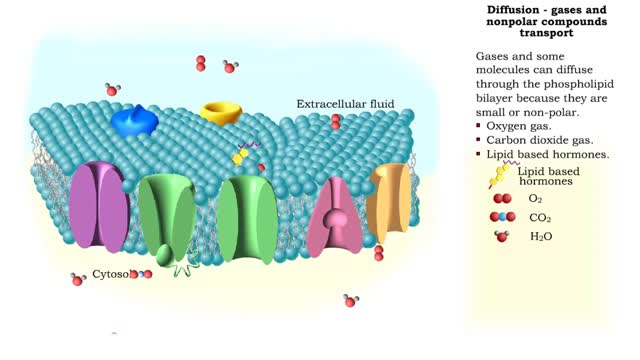
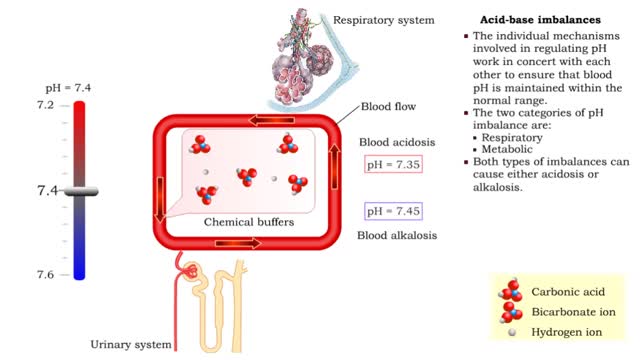
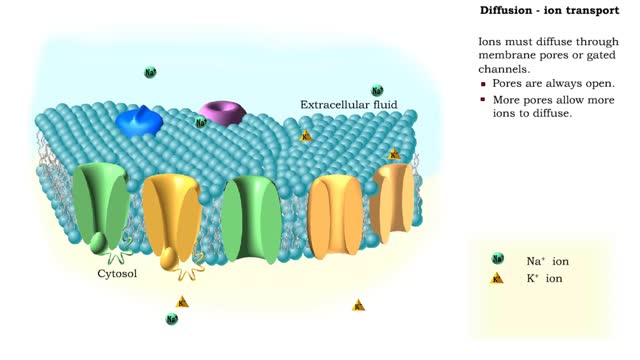
• The respiratory system regulates blood pH by controlling the amount of carbon dioxide removed from the blood. • Near systemic cells, carbon dioxide forms bicarbonate ions in the blood. H+ ions are also released, thereby decreasing blood pH. • At the alveolar capillaries, bicarbonate ions are converted back to carbon dioxide gas which diffuses out into the alveolus. • A reduction of carbon dioxide reduces hydrogen ion production, thereby increasing blood pH. • Altered ventilation rates change the blood concentrations of CO2 and pH. • When blood PCO2 is low, and blood pH is high, the respiratory center decreases ventilation rate. • Less CO2 is removed from the blood and blood pH goes down. • When blood PCO2 is high, and blood pH is low, the respiratory center increases ventilation rate. • More CO2 is removed from the blood and blood pH goes up.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.