Mechanics of Sound Animation
By: Administrator
Date Uploaded: 05/02/2019
Tags: Sounds Listening Hearing Anatomy
Attachments: image.png (19KB) image.png (41KB) image.png (39KB) image.png (50KB) image.png (33KB) image.png (31KB)
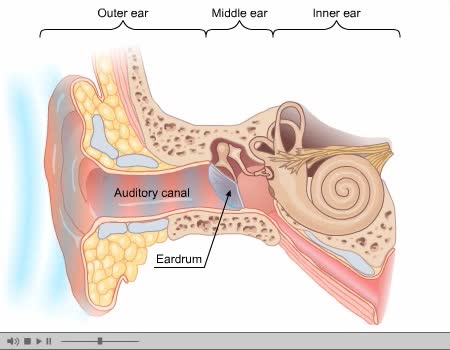
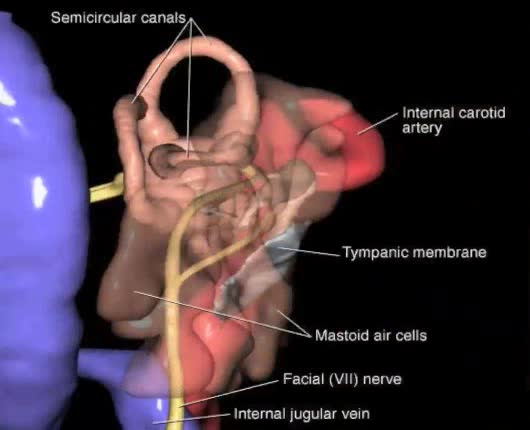
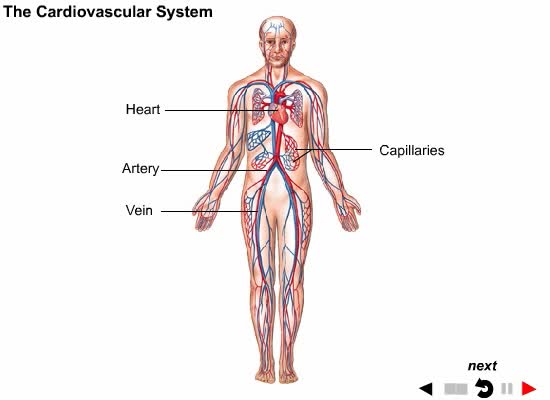
Process of Hearing Sound waves are directed to the eardrum, causing it to vibrate. These vibrations move the three small bones of the middle ear (malleus, incus, and stapes). Movement of stapes at oval window sets up pressure waves in the perilymph and endolymph. Process of Hearing The waves cause vibration of hair cells of the organ of Corti. These vibrations are picked up by auditory nerve fibers that transmit an electric nerve signal to the cerebral cortex of the brain, where it is interpreted as sound. Vestibule A bony structure located between the cochlea and the three semicircular canals. Contains the utricle and saccule, membranous pouches containing perilymph. Utricle: communicates with semicircular canals contains hair cell sensory receptors connected to fibers from the eighth cranial nerve These hair cells are a part of the sense of equilibrium. Semicircular Canals Superior, posterior, and inferior semicircular canals are located at right angles to each other. At the base of each canal is an enlargement called an ampulla containing nerve endings in the form of hair cells. Semicircular Canals Dizziness and motion sickness are associated with the continued movement of the fluid in the semicircular canals due to gravitational influences and the resulting sensory sensation in these areas.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement





Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.