Search Results
Results for: 'Brush-border enzymes'
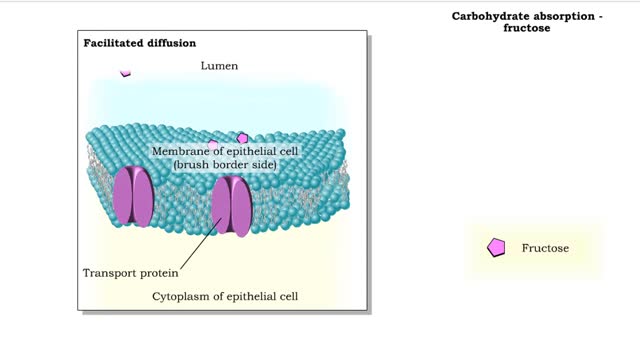
Carbohydrate digestion (brush border enzymes, end products) & Carb absorption (fructose, galactose)
By: HWC, Views: 11627
• Carbohydrate digestion concludes in microvilli of the small intestine, in brush border epithelial cells. Carbohydrate digestion -brush border enzymes • Four brush-border enzymes are involved: • Alpha-dextrinase breaks down alpha-dextrin chains by removing glucose units. • Sucras...
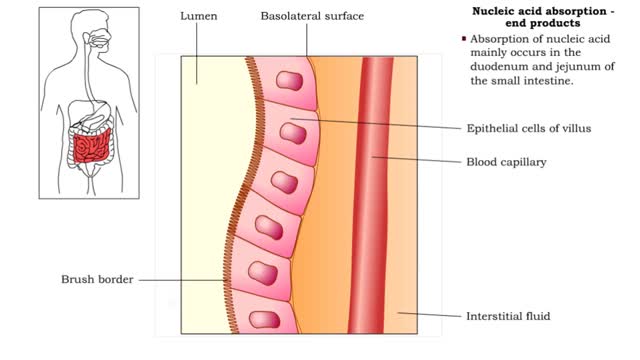
Nucleic acid digestion - brush border enzymes, end products & transport mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 11539
• Further digestion occurs at the microvilli (brush border) of the epithelial cells of the villi in the small intestine. • Two brush border enzymes complete nucleic acid digestion: • Phosphatases, which catalyze the cleavage of a phosphate to form a nucleoside (nitrogenous base and pent...
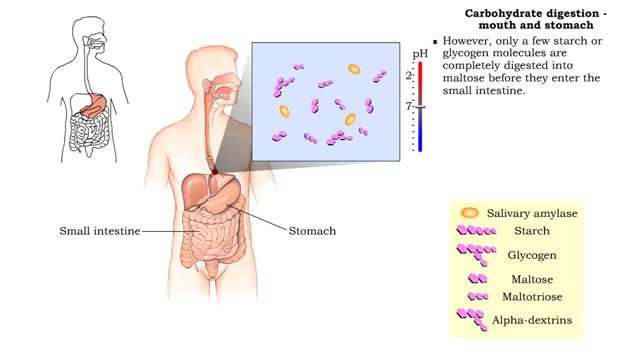
Carbohydrate digestion - mouth and stomach & pancreas and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11574
• Digestion of complex carbohydrates (starches and glycogen) involves: • Amylases produced by the salivary glands and pancreas. • Brush-border enzymes in small intestine. • In the mouth, amylase from the parotid and submandibular salivary glands begins carbohydrate digestion. �...
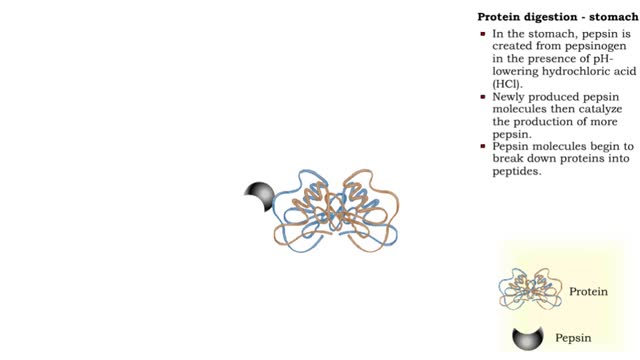
Protein digestion - stomach & small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11248
• Protein digestion occurs in the stomach and small intestine. • The stomach enzyme pepsin initiates the process. • Pancreatic and intestinal brush border enzymes complete the digestive process. • In the stomach, pepsin is created from pepsinogen in the presence of pH-lowering hyd...
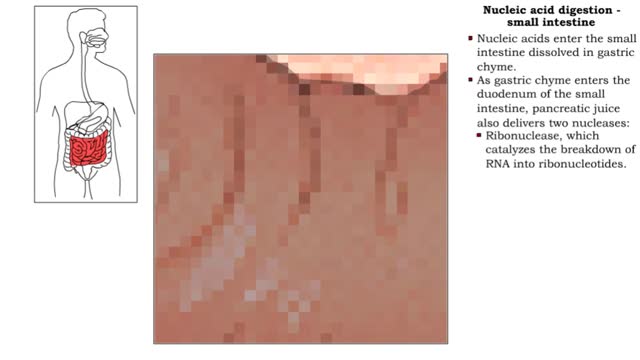
Nucleic acid digestion -small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11817
Nucleic acid digestion, which takes place in the small intestine, involves: • Pancreatic nucleases. • Brush-border enzymes in the small intestine. • Nucleic acids enter the small intestine dissolved in gastric chyme. • As gastric chyme enters the duodenum of the small intestine, p...
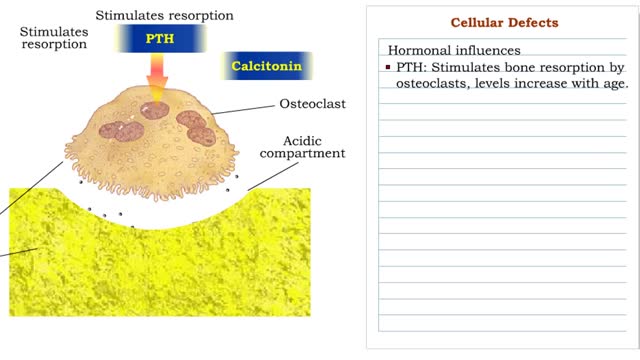
Cellular Defects - Osteoblasts, Osteoclasts and Osteocytes
By: HWC, Views: 11342
■ Metabolically active bone-building cells that secrete astroid. ■ Cover surfaces of newly formed bone and respond to growth stimuli ■ Less responsive to growth factors as the body ages. ■ Contribute to hone loss once their reproductive and biosynthetic potential lessens....
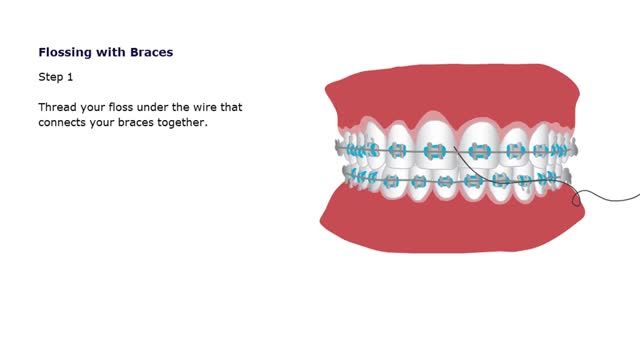
Oral Hygiene & Braces Animation
By: HWC, Views: 11173
Caring for Your Retainer Retainers, just like your teeth collect plaque, bacteria and food particles. You should clean your retainer everyday! Keep your retainer soaking when it is not in your mouth. Use a mouthwash rinse to freshen it up and keep it free of bacteria. Keep your retainer away fr...
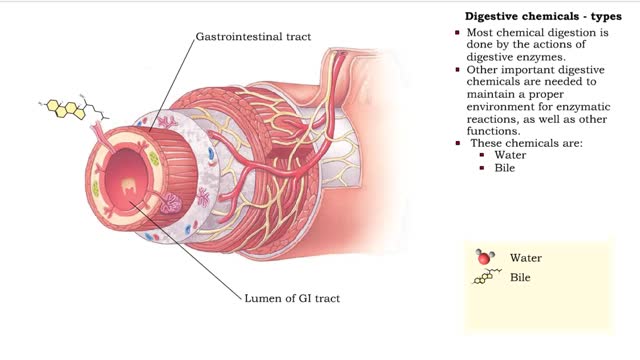
Digestive chemicals - types & enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 11770
• Chemical digestion breaks down food as it moves through the digestive tract. • Using enzymes and other digestive chemicals, the process reduces food particles into nutrient molecules that can be absorbed. • Most chemical digestion is done by the actions of digestive enzymes. • O...
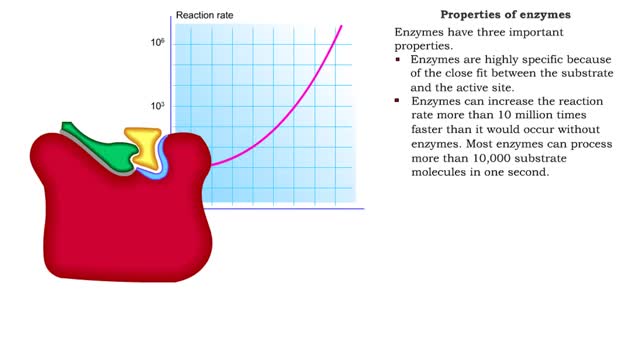
Enzyme structure - Properties of enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 11670
■ Enzymes are proteins that catalyze reactions. ■ Some enzymes have two parts: a protein or apoenzyme and a non-protein or cofactor. ■ Cofactor can be a metal ion or another organic molecule called a coenzyme. ■ Coenzymes often come from vitamins. ■ Cofactors affect the shape of...
Advertisement