Search Results
Results for: 'Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen'
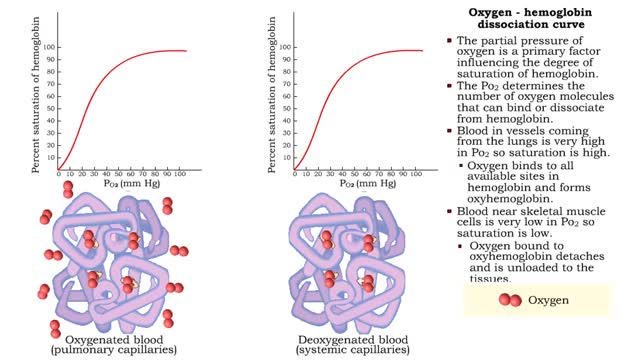
Oxygen - hemoglobin dissociation curve & Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - acidity
By: HWC, Views: 11894
• The partial pressure of oxygen is a primary factor influencing the degree of saturation of hemoglobin. • The Po2 determines the number of oxygen molecules that can bind or dissociate from hemoglobin. • Blood in vessels coming from the lungs is very high in Po2 so saturation is high. ...
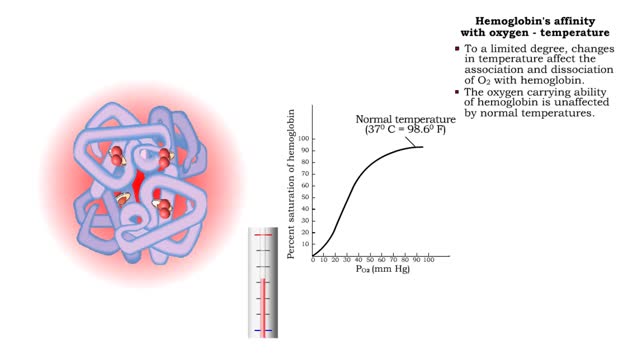
Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - carbon dioxide, temperature and bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
By: HWC, Views: 11297
• The carbon dioxide gas is temporarily converted to carbonic acid in red blood cells by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, and then further converted to hydrogen and bicarbonate ions. • The result of increased carbon dioxide is decreased pH causing the Bohr effect. • Elevated carbon dioxid...
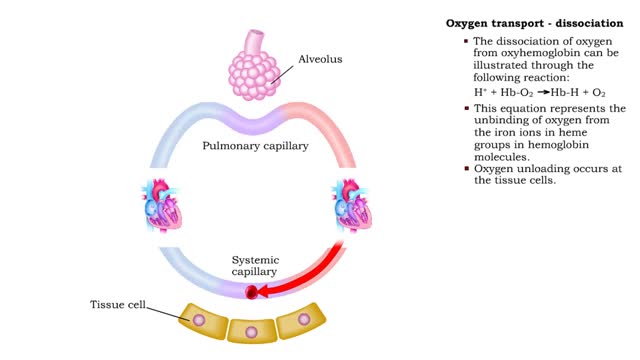
Oxygen transport: association and dissociation & Factors that affect hemoglobin's saturation with O2
By: HWC, Views: 11224
• The production of oxyhemoglobin can be illustrated through the following reaction: 02 + Hb-H --) Hb-02 + H+ • This equation represents the binding of oxygen to the iron ions in heme groups in hemoglobin molecules. • Oxygen binding or loading occurs at the lungs • The dissociatio...
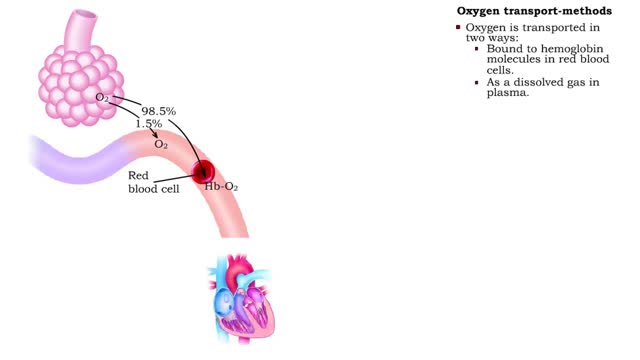
Oxygen transport - methods and oxyhemoglobin
By: HWC, Views: 11167
• The blood is the medium used for gas transport throughout the body. • Oxygen is only available in the lungs. Because the partial pressure of oxygen is higher in the alveoli than in the blood, oxygen diffuses into the blood and is transported to systemic cells. • At the tissues the par...
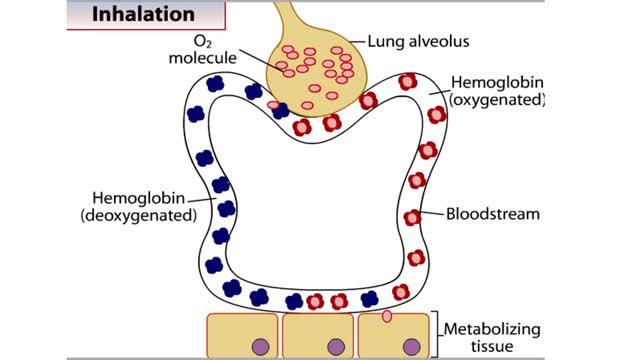
How Hemoglobin Picks Up and Delivers Oxygen
By: HWC, Views: 10727
All of the cells in our bodies require oxygen (02) for survival and must release carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste product. The respiratory and circulatory systems work together as delivery systems for these gases. The lungs exchange these gases between the environment and the bloodstream. The bloo...
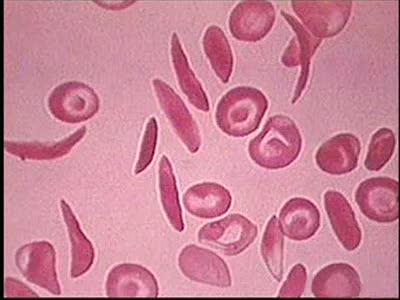
Introduction to Sickle Cell Anemia
By: Administrator, Views: 14842
Sickle cell anemia (sickle cell disease) is a disorder of the blood caused by an inherited abnormal hemoglobin (the oxygen-carrying protein within the red blood cells). The abnormal hemoglobin causes distorted (sickled appearing under a microscope) red blood cells.
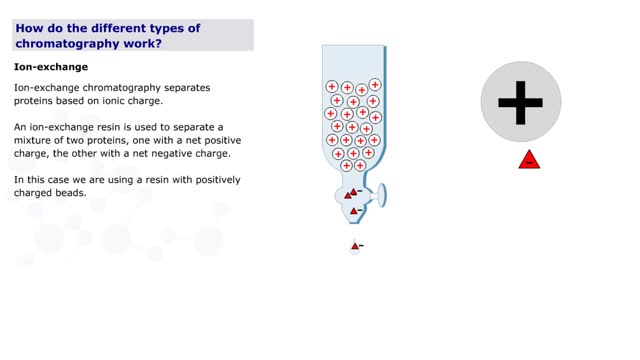
How do the different types of chromatography work? (No Audio)
By: HWC, Views: 10803
Chromatography is a term for a variety of techniques in which a mixture of dissolved components is fractionated as it moves through some type of porous matrix. A glass column is filled with beads of an inert matrix. The mixture of proteins to be purified is dissolved in a solution and passed ...
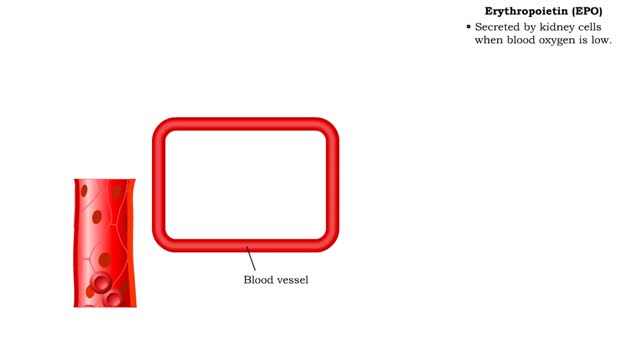
Red Blood Cells - Erythropoietin (EPO)
By: HWC, Views: 11236
• The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone aft...
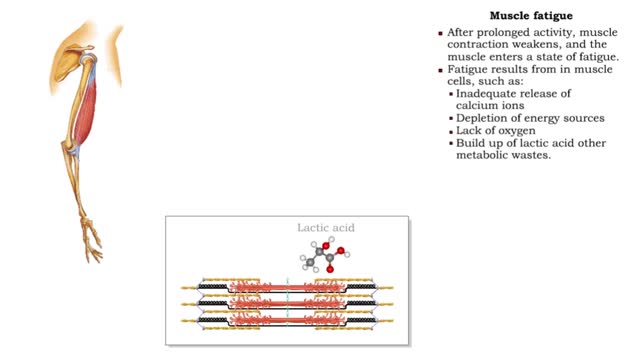
By: HWC, Views: 11039
• After prolonged activity, muscle contraction weakens, and the muscle enters a state of fatigue. • Fatigue results from in muscle cells, such as: • Inadequate release of calcium ions • Depletion of energy sources • Lack of oxygen • Build up of lactic acid other metabolic w...
Advertisement