Search Results
Results for: 'Stimulus intensity and AP frequency'
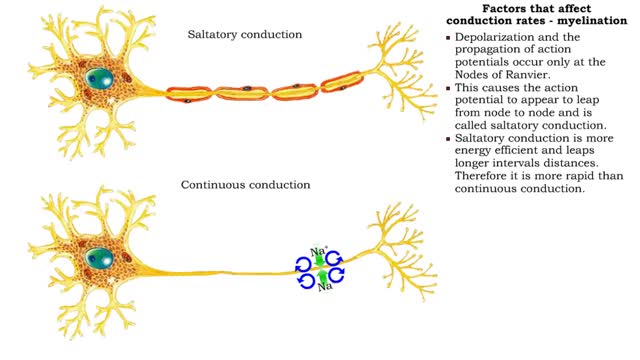
Factors that affect conduction rates (myelination, axon diameter & temperature)
By: HWC, Views: 11836
• Several factors determine the rate of conduction of action potentials: • Myelination • Axon diameter • Temperature • The step-by-step depolarization of an axon is called continuous conduction and occurs along unmyelinated axons. • Neurons in the PNS have many axons that ...
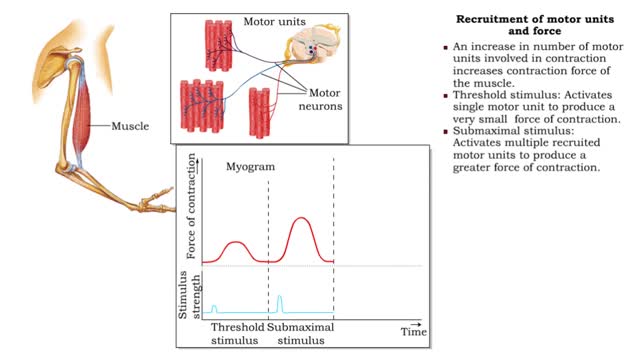
Frequency of stimulation and force (Recruitment of motor units and force)
By: HWC, Views: 11979
• Muscle tension depends on the frequency of stimulation. • Muscle twitch: First stimulus. • Wave summation: When a second stimulus excites a partially relaxed muscle, producing a stronger contraction. • Unfused tetanus: Successive stimulations at the same frequency, producing a se...
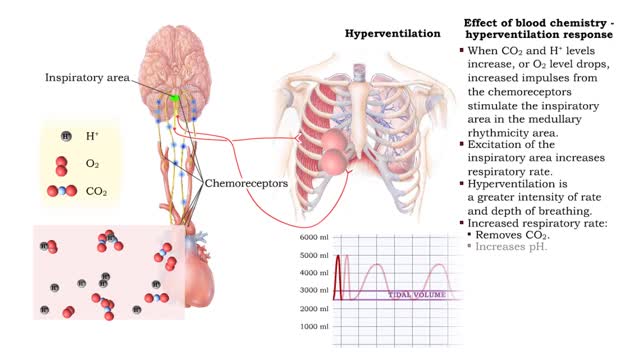
Effect of blood chemistry - stimuli, hyperventilation response and hypoventilation response
By: HWC, Views: 11349
• Respiratory rate is effected by changes in: • Blood pH. • Blood Pco2. • Blood P02. • Chemoreceptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems closely monitor the Fr, CO2 and 02 levels in blood. • Changes in frequency of impulses from Chemoreceptors affect respiratory r...
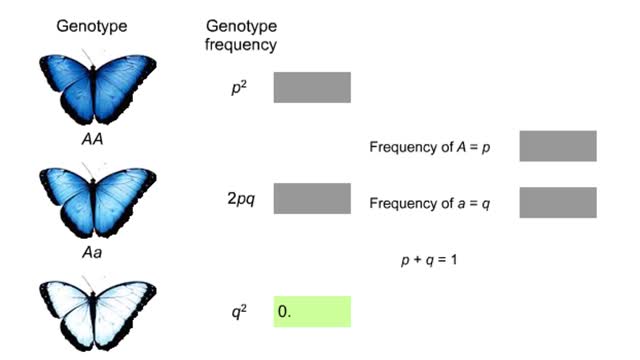
How to find out if a population is evolving?
By: HWC, Views: 8902
Imagine a butterfly population with a pair of alleles that influence wing color as shown. We will represent the frequency of the dominant allele as p and the recessive allele as q. The Hardy-Weinberg rule describes what happens if a population is at genetic equilibrium—if it is not evolving...
By: HWC, Views: 11400
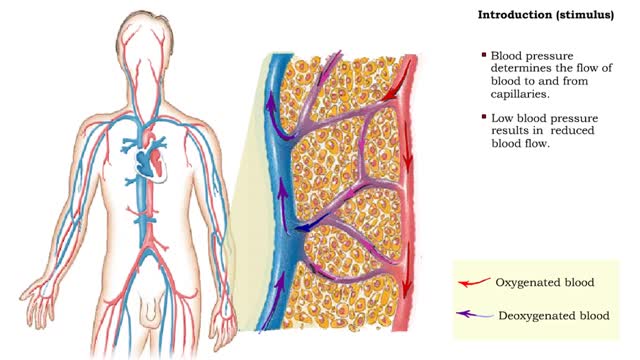
• Blood pressure determines the flow of blood to and from capillaries. • Low blood pressure results in reduced blood flow. • High blood pressure can cause blood vessels to break. In humans, sensitivity is due to portions of the nervous system called receptors. Receptors are typicall...
Muscle Twitch and Muscle Tension - Motor unit size and force
By: HWC, Views: 11973
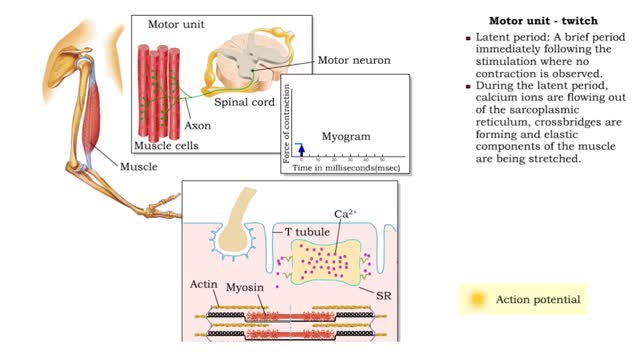
• A motor unit is a group of muscle cells controlled by a single neuron. • A stimulus of sufficient intensity will cause all the cells in the motor unit to contract. • A single contraction, caused by a single action potential, is called a muscle twitch. • Latent period: A brief per...
Flexor reflex & Crossed extensor reflex
By: HWC, Views: 11623
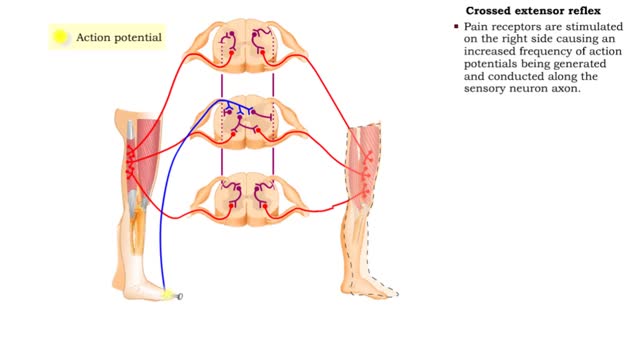
• The flexor reflex is a response to pain. This reflex is polysynaptic, ipsilateral, and intersegmental. • Pain receptors are stimulated causing increased frequency of action potentials to be generated and conducted along the sensory neuron axon. • The sensory impulses excite several ass...
Nerve Impulse Transmission Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 15161
How nerves transmit impulses. Stimulation of a nerve occurs at a receptor. Sensory receptors Specialized to specific types of stimulation such as heat, cold, light, pressure, or pain. React by initiating a chemical change or impulse. All-or-none principle Means that no transmission occ...
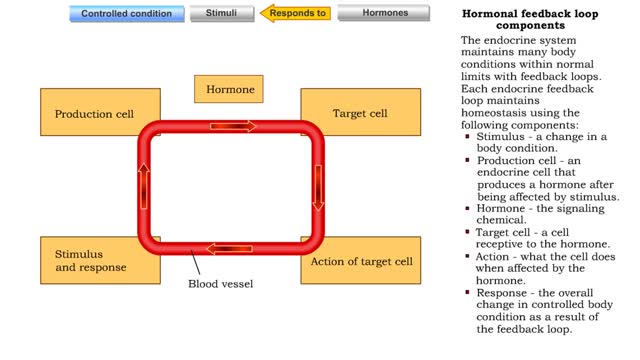
Hormonal feedback loop components
By: HWC, Views: 11878
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: ■ Stimulus - a change in a body condition. ■ Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after b...
Advertisement