Search Results
Results for: 'Types of Transport'
Types of Transport - Uniport, Antiport and Symport (Glucose and Na+K+ Transporters)
By: HWC, Views: 11061
Some transport proteins bind and transport molecules very selectively. Uniport is the transport of one solute molecule. Symport is the transports of two solute molecules in the same direction. Antiport is the transports of two solute molecules in opposite directions. 1. Glucose bin...
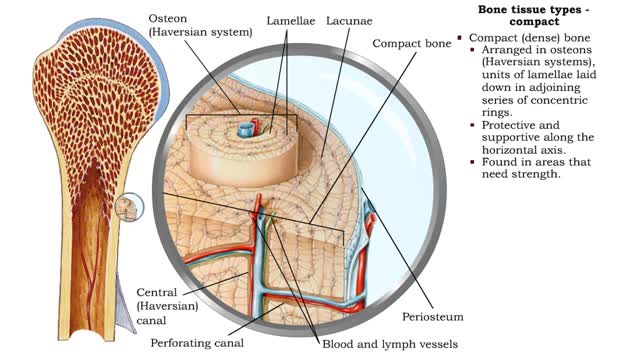
Bone tissue types - compact and spongy
By: HWC, Views: 11394
Bone tissue types • There are two types of bone tissue: compact and spongy. • All the bones of the skeleton have both kinds of bone tissue. • Compact (dense) bone • Arranged in osteons (Haversian systems), units of lamellae laid down in adjoining series of concentric rings. • P...
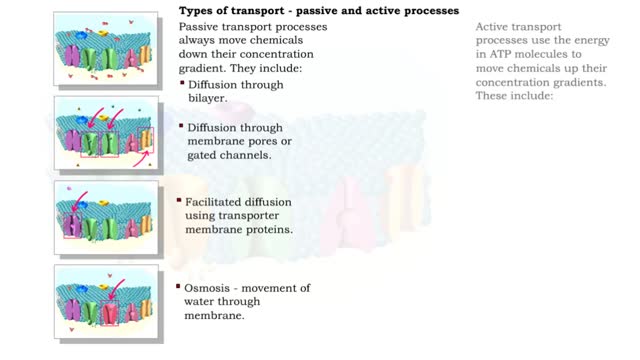
Type of Transport - Active and Passive Processes
By: HWC, Views: 11698
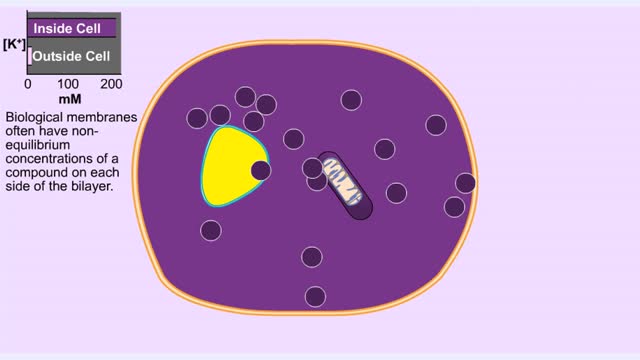
Active transport moves materials from lower to a higher concentration, while passive transport moves materials from higher to lower concentration. Active transport requires energy to proceed, while passive transport does not require the input of extra energy to occur. Transport processes that ...
By: HWC, Views: 11997
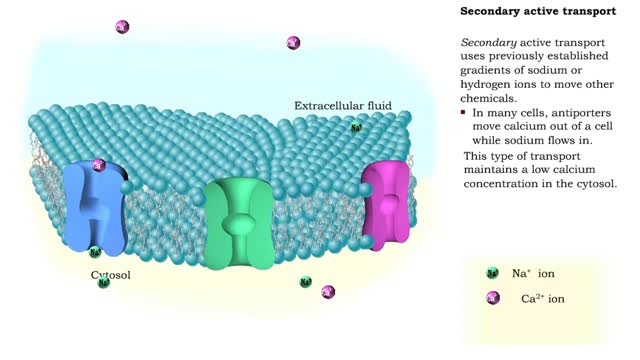
Energy stored (in a hydrogen or sodium concentration gradient) is used to drive other substances against their own concentration gradients Secondary active transport, is transport of molecules across the cell membrane utilizing energy in other forms than ATP. In many cells, antiporters mov...
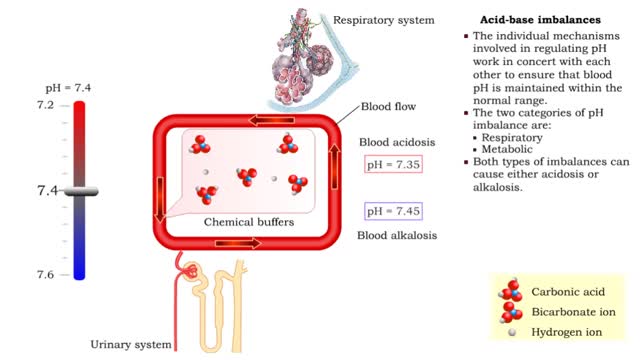
Acid-base imbalances - respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11729
• The individual mechanisms involved in regulating pH work in concert with each other to ensure that blood pH is maintained within the normal range. • The two categories of pH imbalance are: • Respiratory • Metabolic • Both types of imbalances can cause either acidosis or alka...
By: HWC, Views: 11535
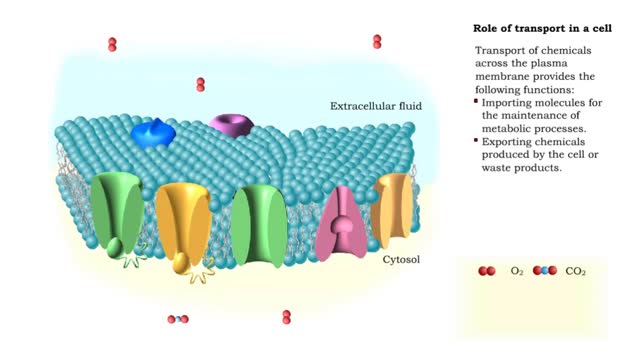
Transport of chemicals across the plasma membrane provides the following functions: Importing molecules for the maintenance of metabolic processes. Exporting chemicals produced by the cell or waste products. Communicating with other cells, allowing for the generation and conduction of a...
Endocytosis -Types and Phagocytosis
By: HWC, Views: 11443
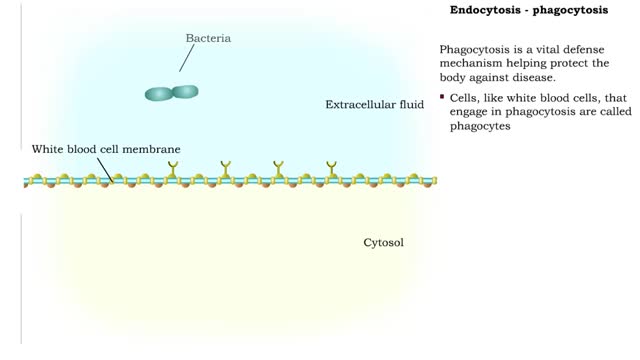
Endocytosis is the process by which a substance is brought inside a cell without having to pass through the cell membrane. It is the opposite of endocytosis, the process by which substances exit the cell without having to pass through the cell membrane. Exocytosis – membrane-enclosed secret...
Simple Diffusion - gases and nonpolar compounds transport
By: HWC, Views: 11922
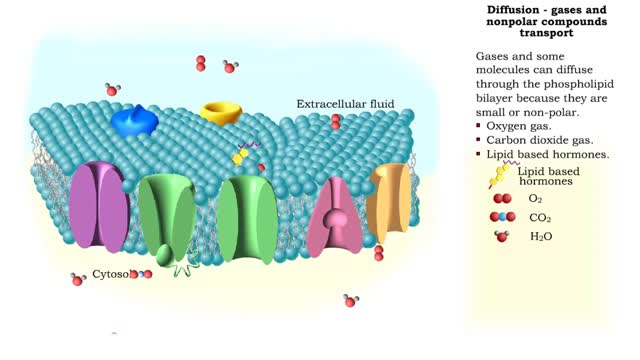
Gases and some molecules can diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer because they are small or non-polar. Oxygen gas. Carbon dioxide gas. Lipid based hormones. Plasma membranes are selectively permeable: The lipid bilayer is always permeable to small, nonpolar, uncharged molecules ...
Membrane Protein and Facilitated Transport (Passive Vs Active)
By: HWC, Views: 11027
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins span the membrane, with hydrophobic amino acids interacting with the lipid bilayer and hy...
Advertisement