Search Results
Results for: 'Types of Transport'
By: Administrator, Views: 14593
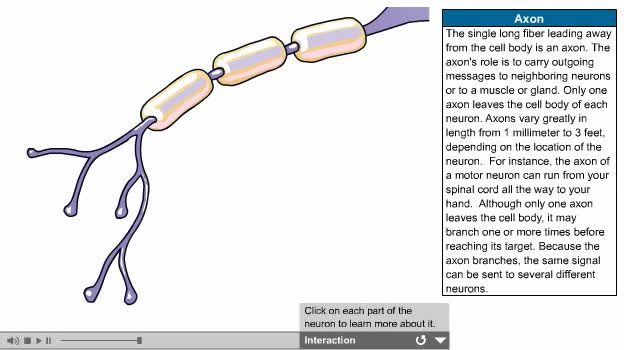
There are several types of neurons, three of which are: Motor neurons, Sensory neurons, Interneurons. The nervous system is usually described as having two interconnected divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). CNS: Includes the brain and spinal...
Osmosis - Isotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic Solutions
By: HWC, Views: 11081
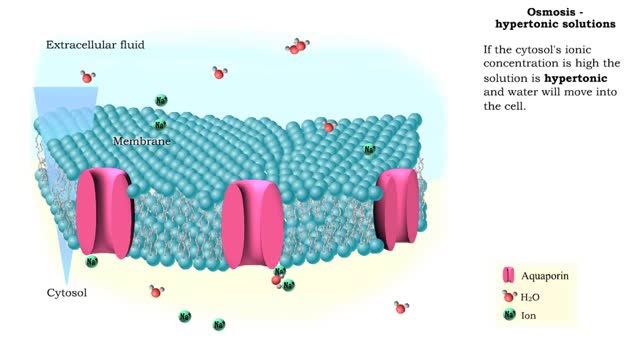
Isotonic: Equal Water moves in and out of the cell at an equal rate. The cell remains unchanged. Hypotonic: "hypo" hippo Water moves into the cell, making it swell and get fat (like a hippo). Eventually the cell can rupture and burst (aka lyse). Hypertonic: "like a raisin" Water leaves...
Role of the respiratory system - effect of altered ventilation rates
By: HWC, Views: 11582
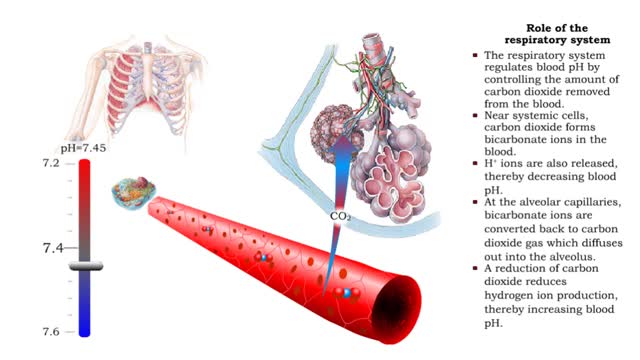
• The respiratory system regulates blood pH by controlling the amount of carbon dioxide removed from the blood. • Near systemic cells, carbon dioxide forms bicarbonate ions in the blood. H+ ions are also released, thereby decreasing blood pH. • At the alveolar capillaries, bicarbonate io...
Carbohydrate digestion (brush border enzymes, end products) & Carb absorption (fructose, galactose)
By: HWC, Views: 10896
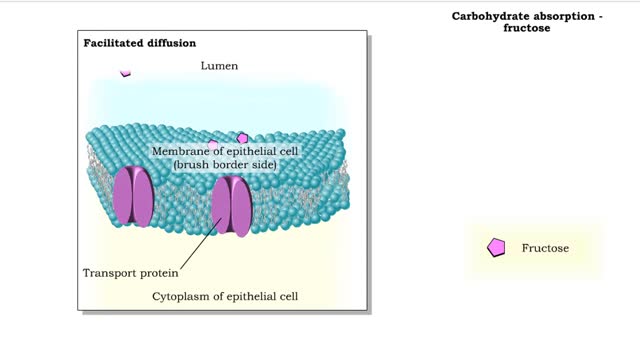
• Carbohydrate digestion concludes in microvilli of the small intestine, in brush border epithelial cells. Carbohydrate digestion -brush border enzymes • Four brush-border enzymes are involved: • Alpha-dextrinase breaks down alpha-dextrin chains by removing glucose units. • Sucras...
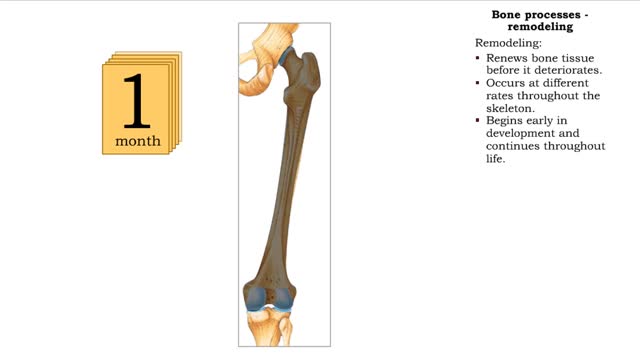
Bone processes - resorption and deposition, remodeling and response to stress in adult bones
By: HWC, Views: 11228
• The process of remodeling bone tissues involves bone cells resorbing or depositing minerals into bone tissue. • During resorption, bone cells break down bone tissue and release calcium and other minerals for use by other cells in the body. • Bone cells also rebuild bone tissue by depo...
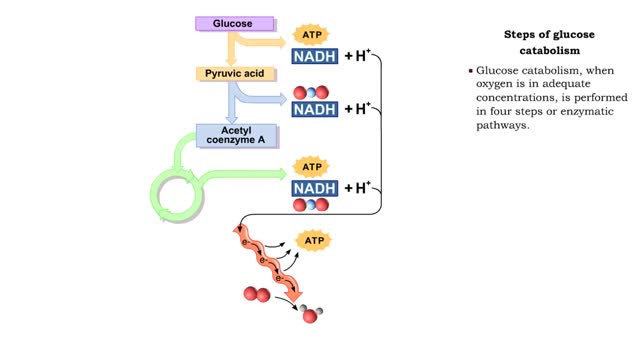
By: HWC, Views: 11220
• During digestion, complex carbohydrates are hydrolyzed into monosaccharides, primarily glucose. • The catabolism of glucose is the primary source of energy for cellular production of ATP. • The anabolism of glucose is important in regulating blood glucose levels. • Glucose cat...
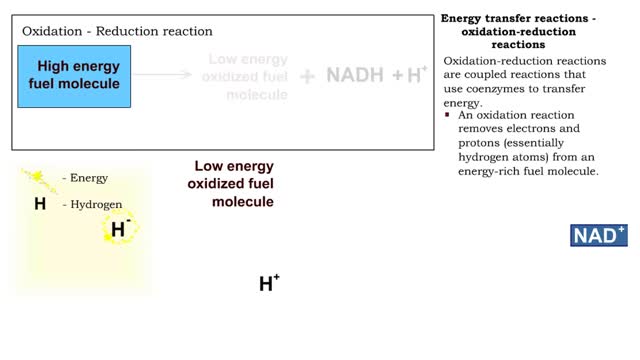
Types of energy transfer reactions: oxidation-reduction reactions and ATP generation reactions
By: HWC, Views: 11627
■ Metabolism balances anabolic and catabolic reactions. ■ Anabolism is energy transfer from ATP to simpler molecules in order to build them up into larger, more complex molecules. ■ Catabolism is breaking down larger, more complex molecules, usually to transfer energy from them in order...
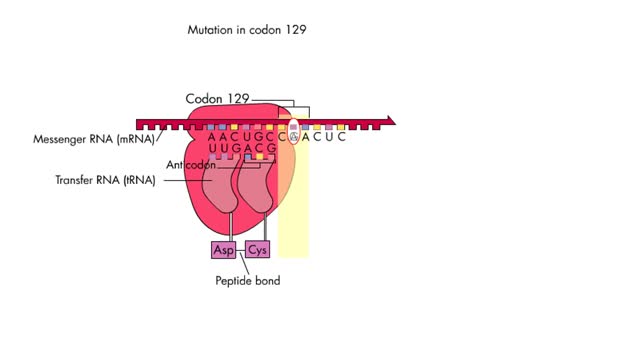
By: HWC, Views: 7526
A mutation, which may arise during replication and/or recombination, is a permanent change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA. Damaged DNA can be mutated either by substitution, deletion or insertion of base pairs. Mutations, for the most part, are harmless except when they lead to cell death or t...
By: Administrator, Views: 13674
Shock is a life-threatening condition in which delivery of oxygen to the organs is low, causing organ damage and sometimes death. Blood pressure is usually low.
Advertisement