Search Results
Results for: 'buffering gastric acid'
Gastrin (gastric emptying) & Secretin (buffering gastric acid)
By: HWC, Views: 10882
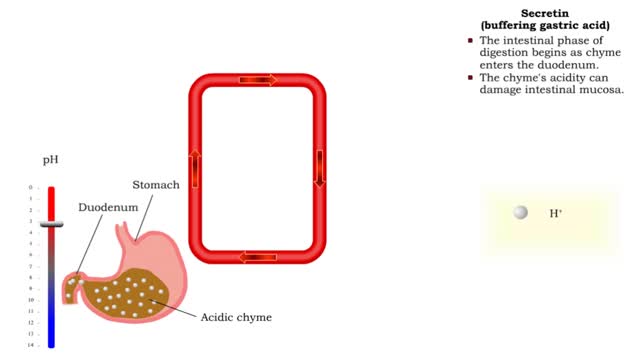
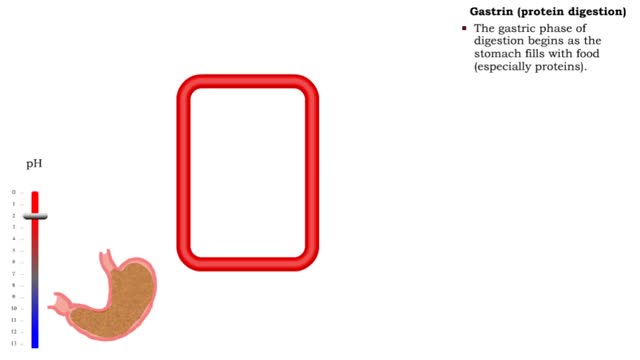
• Gastrin also binds to the smooth muscle cells in the stomach causing: • Increased gastric motility. • Opening of pyloric sphincter. • Increased gastric emptying. • The intestinal phase of digestion begins as chyme enters the duodenum. • The chyme's acidity can damage int...
Secretin (inhibiting gastric acid secretion), Cholecystokinin (fat digestion) & Cholecystokinin
By: HWC, Views: 11186
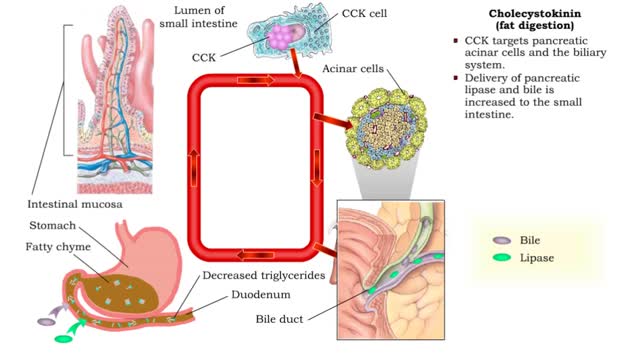
• As chyme approaches the small intestine, secretin also targets acid-producing parietal cells in the gastric mucosa. • Increased secretin inhibits gastric add secretion. • With less gastric acid produced, the chyme going into the intestine is less acidic. • The hormone CCK also reg...
Nucleic acid digestion -small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11455
Nucleic acid digestion, which takes place in the small intestine, involves: • Pancreatic nucleases. • Brush-border enzymes in the small intestine. • Nucleic acids enter the small intestine dissolved in gastric chyme. • As gastric chyme enters the duodenum of the small intestine, p...
Digestive chemicals - water, gastric acid, bile & bicarbonate
By: HWC, Views: 11074
• Water is the most abundant molecule in ingested fluids. • Water plays a primary role in hydrolytic digestive reactions. • Helps liquefy and transport digestive foodstuffs down the tract. • Transports secretions from accessory digestive organs to gastrointestinal tract. • Aids ...
By: HWC, Views: 11450
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after b...
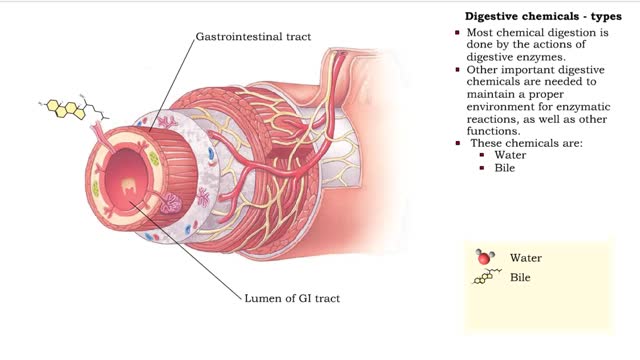
Digestive chemicals - types & enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 11378
• Chemical digestion breaks down food as it moves through the digestive tract. • Using enzymes and other digestive chemicals, the process reduces food particles into nutrient molecules that can be absorbed. • Most chemical digestion is done by the actions of digestive enzymes. • O...
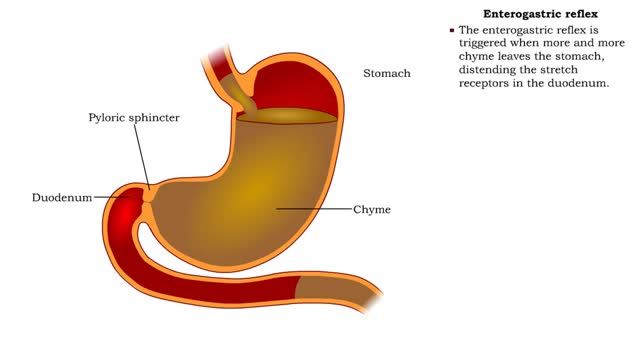
Stomach peristalsis & Enterogastric reflex
By: HWC, Views: 10767
• Food enters, distending the stomach. • Stretch receptors activate enteric reflexes that promote peristaltic movements. • These movements, called mixing waves, begin to mix the food with stomach secretions. • Mixing waves force the digesting food (chyme) toward and through the pylo...
The pH scale - Strong acids and Weak acids
By: HWC, Views: 11419
The pH scale • Expresses concentration of H+. • range: 0-14. • 7 is neutral. • Less 7 is acid. • greater 7 is basic (alkaline). Strong acids - role in the body ■ In strong acids all molecules dissociate. ■ HC1 is highly acidic and found only in the stomach. • H...
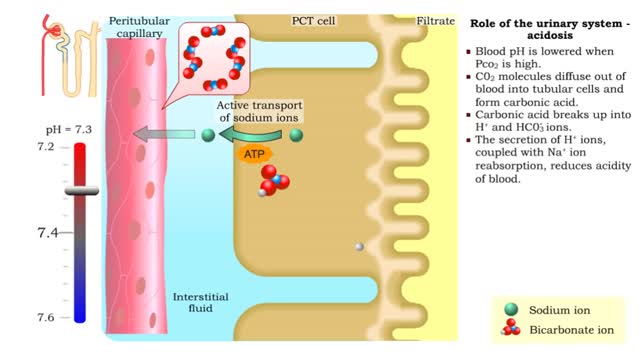
Role of the urinary system - acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11488
• Tubular cells of the proximal convoluted tubule and collecting tubules can alter filtrate pH and therefore blood pH. • These cells can affect blood pH with two coupled mechanisms: • Reabsorption of bicarbonate ions. • Secretion of hydrogen ions. • The reabsorption of bicarbonate...
Advertisement