Search Results
Results for: 'electrons orbit'
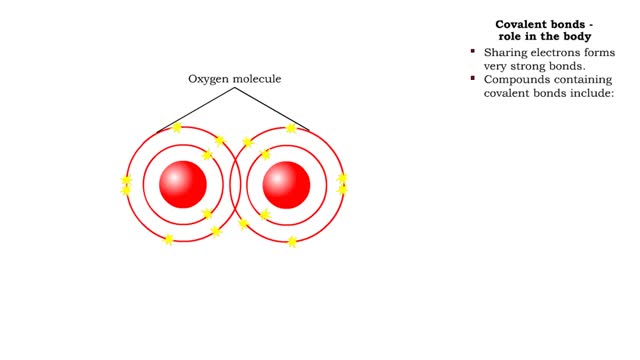
Covalent bonds - role in the body
By: HWC, Views: 11314
A covalent bond is formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. This is opposed to an ionic bond, where electrons are actually transferred from one atom to another. Formation • Atoms fill up the outer orbital by sharing electrons. • Two oxygen atoms sharing electrons form on...
Activation Energy - Valence Electrons
By: HWC, Views: 10780
■ Shared electrons in the outermost orbital form bonds. These electrons are called valence electrons. ■ Valence electrons are disrupted and can be rearranged into a new bond. ■ The energy necessary to start a reaction and break bonds is called the activation energy. ■ Reactants have...
Cavernous Sinus Larynx Middle Ear Orbit: Granulesm Animation
By: HWC, Views: 10612
The cavernous sinuses are located within the middle cranial fossa, on either side of the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone (which contains the pituitary gland). The cavernous sinuses, a rich plexuses of veins that surround the internal carotid arteries, lie lateral to the pituitary fossa. Ant...
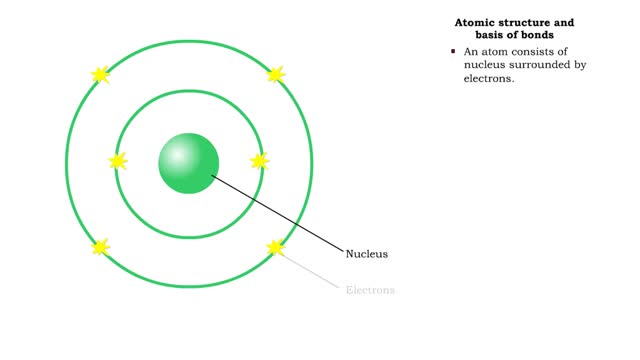
Bond types - Atomic structure and basis of bonds
By: HWC, Views: 11734
• Chemical bonds are fundamental to the structure and function of many types of molecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, gases, salts and water. ■ These molecules are composed of atoms that are held together by three different types of bonds. • The three types ...
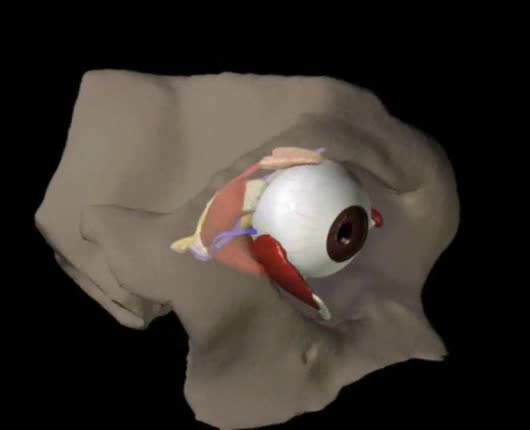
Structures of the Eye Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 2358
Orbit A cone-shaped cavity in the front of the skull that contains the eyeball. Formed by the combination of several bones and is lined with fatty tissue that cushions the eyeball. This cavity has several foramina (openings) through which blood vessels and nerves pass. Largest opening is the ...
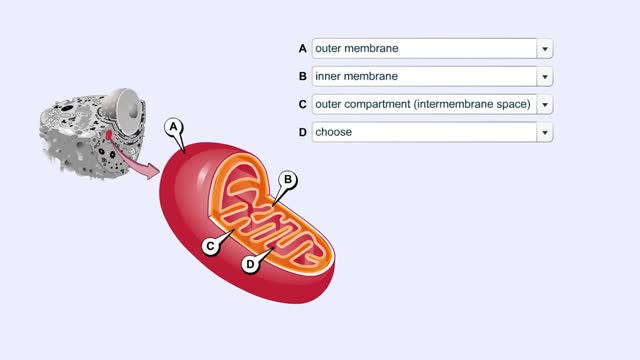
Mitochondrial Structure & ETC Protein Complexes (Protein Complexes and Electron Transport)
By: HWC, Views: 10941
The energy carrying molecules, NADH and FADH2, that were generated in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, now are processed in the mitochondria where their high energy electrons are deposited in an electron chain complex located in the inner mitochondrial membranes. These high-energy electrons now dr...
What are the Parts of a Plant Cell?
By: HWC, Views: 10372
Every chloroplast in a plant cell is packed with stacks of flattened sacs called thylakoids. The thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll, as well as most of the other components required for the light reactions of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll-containing structures within the membranes are c...
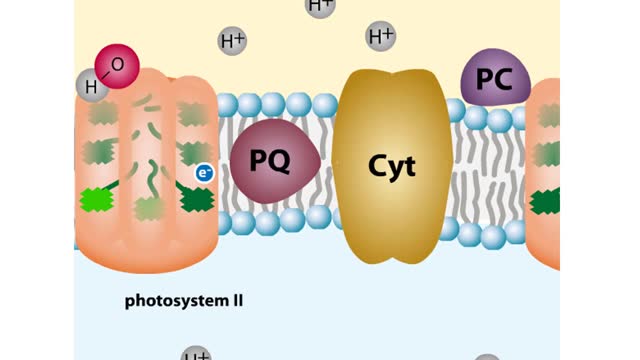
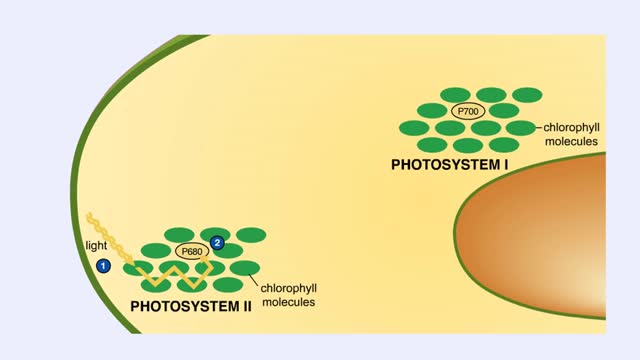
Chloroplast Structure & Light Dependent Reactions (Photosystem 1 and 2 Cyclic Electron Flow)
By: HWC, Views: 10856
The leaf is the principle photosynthetic organ of the plant. This is a cross section of a leaf. The rectangular-shaped cells are part of the photosynthetic tissue called the palisade mesophyll. Each photosynthetic cell can contain several hundred organelles known as chloroplasts. The chlorop...
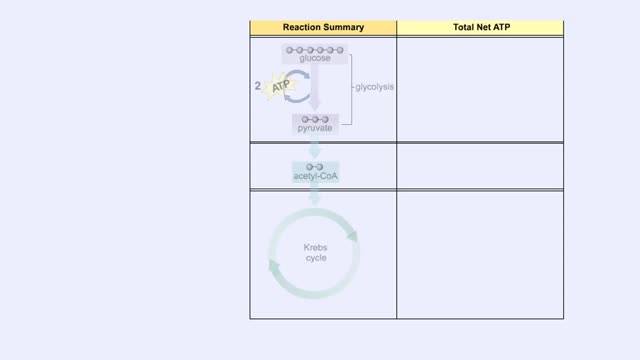
ETC Protein Complexes & Chemiosmosis (Total ATP Production and ATP Synthase)
By: HWC, Views: 11037
You will notice that FADH2 donates two electrons further downstream than NADH. This results in only two protons being pumped across the inner membrane. The final electron acceptor for these transported electrons is oxygen. Oxygen receives these electrons, plus protons from the aqueous matrix. ...
Advertisement