Search Results
Results for: 'enzymatic'
By: HWC, Views: 10839
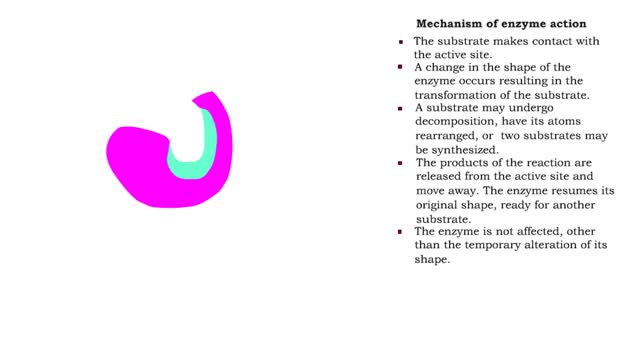
â– The substrate makes contact with the active site. â– A change in the shape of the enzyme occurs resulting in the transformation of the substrate. â– A substrate may undergo decomposition, have its atoms rearranged, or two substrates may be synthesized. â– The products of the reaction...
By: HWC, Views: 11252
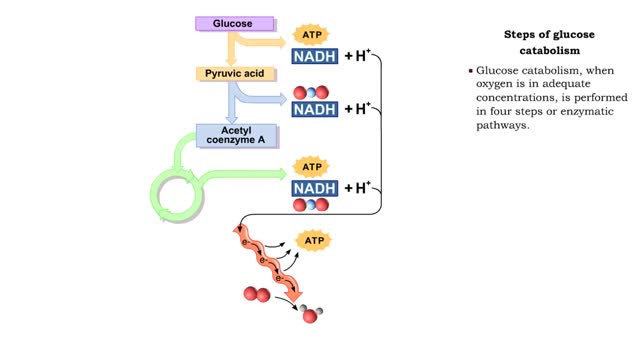
• During digestion, complex carbohydrates are hydrolyzed into monosaccharides, primarily glucose. • The catabolism of glucose is the primary source of energy for cellular production of ATP. • The anabolism of glucose is important in regulating blood glucose levels. • Glucose cat...
Digestive chemicals - types & enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 11059
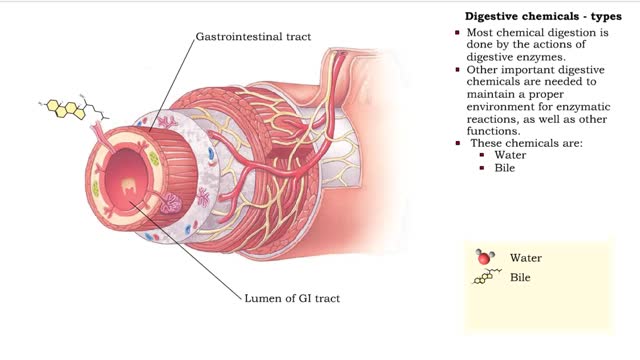
• Chemical digestion breaks down food as it moves through the digestive tract. • Using enzymes and other digestive chemicals, the process reduces food particles into nutrient molecules that can be absorbed. • Most chemical digestion is done by the actions of digestive enzymes. • O...
Types of energy transfer reactions: oxidation-reduction reactions and ATP generation reactions
By: HWC, Views: 11666
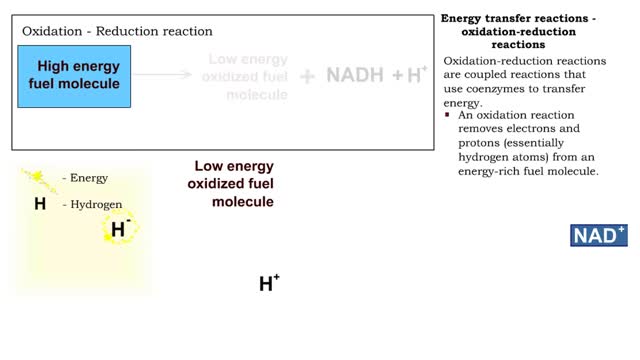
â– Metabolism balances anabolic and catabolic reactions. â– Anabolism is energy transfer from ATP to simpler molecules in order to build them up into larger, more complex molecules. â– Catabolism is breaking down larger, more complex molecules, usually to transfer energy from them in order...
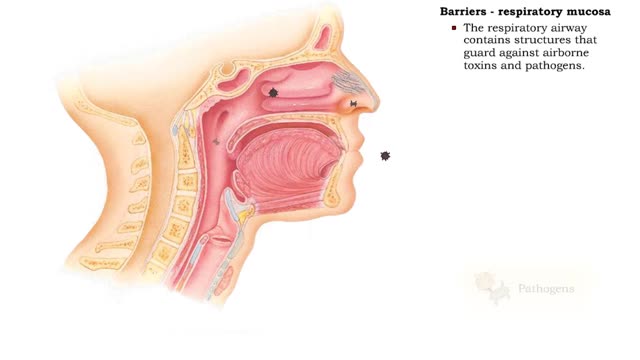
Barriers - eye structures, digestive mucosa, respiratory mucosa & genitourinary mucosa
By: HWC, Views: 11320
• Eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes and conjunctiva serve to trap microbes preventing their invasion. • Tearing (lacrimation) is a protective mechanism that washes away microbes that attempt to enter the eyes. • Salts, mucus, and lysozymes in tears neutralize substances and bacteria. â€...
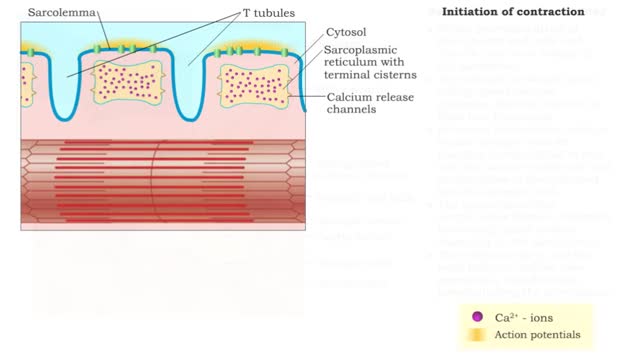
Nervous pathway to the Neuromuscular (NMJ)
By: HWC, Views: 11517
• A nervous impulse, also called an action potential, starts from the brain or spinal cord to signal skeletal muscle cell contraction. Action potentials continue along a motor neuron to the muscle cell. • The signal to contract must cross a synapse - the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) - betwe...
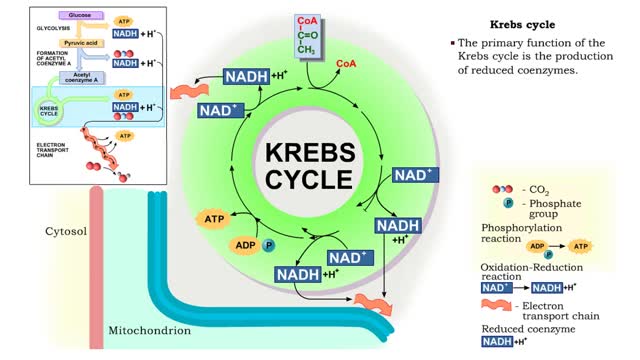
Krebs cycle : Formation of acetyl coenzyme A and Electron transport chain
By: HWC, Views: 11236
The oxidation of glucose to produce ATP is cellular respiration. Four sets of reactions are involved: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Krebs cycle reactions Electron transport chain reactions • The second pathway of glucose catabolism, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, is a transi...
Advertisement