Search Results
Results for: 'fetal development'
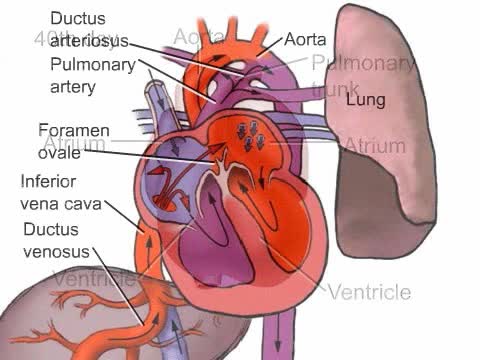
Fetal Development of the Cardiovascular System
By: Administrator, Views: 14336
How the heart develops in the uterus.
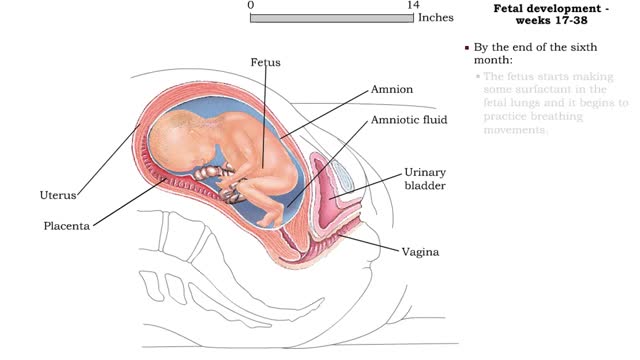
Fetal development - Weeks 9 to 38
By: HWC, Views: 11872
Weeks 9-12 • Fetal development during the third month includes: • A large head, about 1/2 the length of the fetus. • Visible eyes and ears. • A detectable heartbeat. • Kidneys that form urine. • Gender identification. • Weak, undetectable body movements. • By the e...
Rh blood type and complications during pregnancy & Fertilization
By: HWC, Views: 9167
Complications can arise if an Rh- woman is impregnated by an Rh+ man. The fetus maybe Rh+. During childbirth, some of the fetal Rh+ cells may leak into the maternal bloodstream. The woman's immune system views the Rh+ as foreign and makes antibodies against it. If the woman becomes pr...
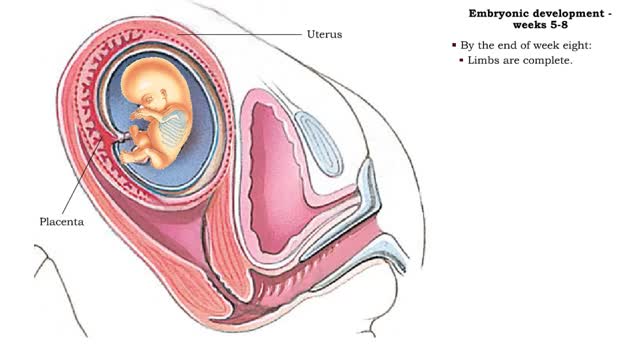
Embryonic development - Weeks 5 to 8
By: HWC, Views: 11795
• The second month of development is characterized by rapid development of the head and limbs as well as continued organogenesis. • During the fifth and sixth weeks growth of the brain, and therefore head, is rapid. • Hands and feets begin to form. • During week seven, even more deve...
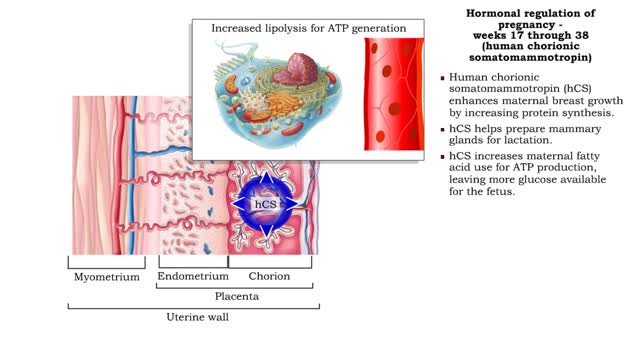
Hormonal regulation of pregnancy - weeks 17 through 38
By: HWC, Views: 11914
• Estrogens increase uterine blood flow, maintaining the endometrium during pregnancy. • High levels of estrogen and progesterone inhibit the synthesis of milk. Progesterone inhibits myometrial contractions of the uterus to prevent premature birth. • Relaxin inhibits myometrial contract...
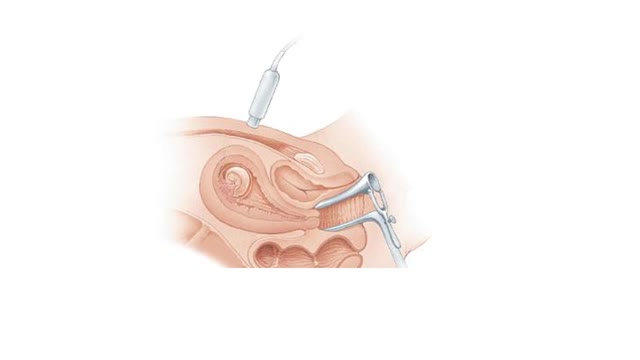
Amniocentesis and CVS Animation
By: HWC, Views: 8558
Amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling (CVS) are prenatal diagnostic tools. In amniocentesis, which can be performed as early as 14 weeks into the gestation period. A syringe needle is inserted through the abdominal and uterine walls to withdraw some amniotic fluid. The fluid contains...
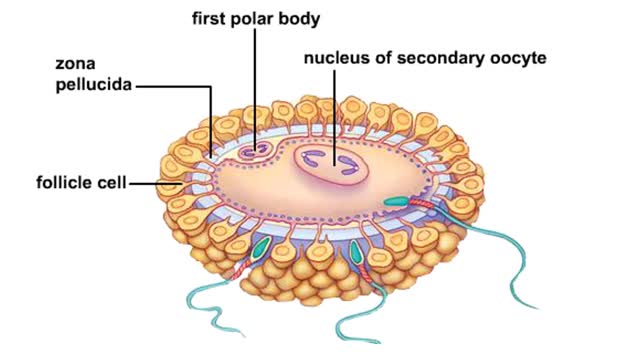
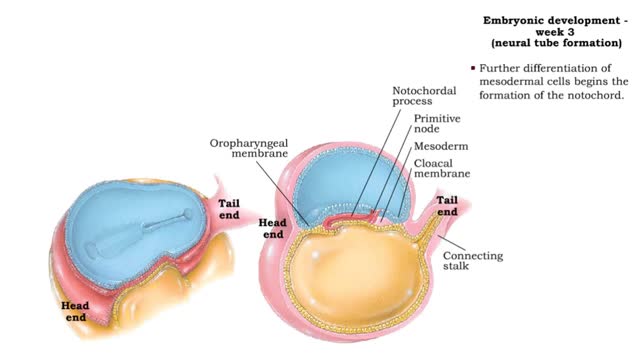
Embryonic development - Week 3
By: HWC, Views: 11721
Week 3 (gastrulation) • Three primary germ layers are formed which provide cells for organ formation in the following months. • These germ cell layers are formed by a process known as gastrulation, which involves rearranging epiblast cells. • As cells from the epiblast migrate, a fain...
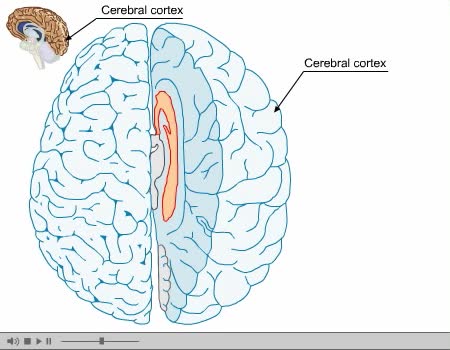
By: Administrator, Views: 15025
The cerebral cortex (plural cortices), also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain, in humans and other mammals. It is separated into two cortices, by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemisp...
Cognitive development by Piaget (Preoperational stage or intelligence)
By: HWC, Views: 10762
The next stage of cognitive development proposed by Piaget, is the preoperational stage, roughly between the ages of 2 and 7. At this stage Piaget asserted that a child has what he called preoperational intelligence. hey can mentally representing objects, but do not have a system for organising...
Advertisement