Hormonal regulation of pregnancy - weeks 17 through 38
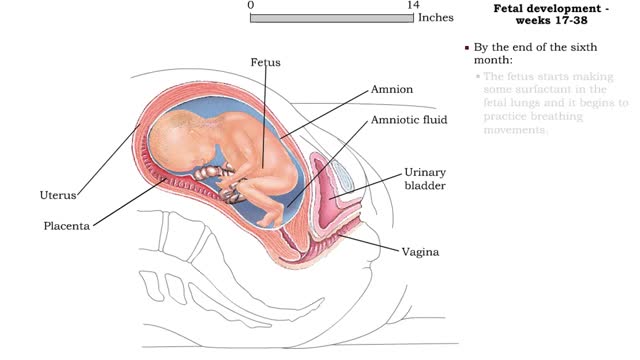
• Estrogens increase uterine blood flow, maintaining the endometrium during pregnancy. • High levels of estrogen and progesterone inhibit the synthesis of milk. Progesterone inhibits myometrial contractions of the uterus to prevent premature birth. • Relaxin inhibits myometrial contractions of the uterus. • Relaxin also increases the flexibility of the pubic symphysis to aid in birth. • Human chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS) enhances maternal breast growth by increasing protein synthesis. • hCS helps prepare mammary glands for lactation. • hCS increases maternal fatty acid use for ATP production, leaving more glucose available for the fetus. • inhibits glucose uptake by maternal cells, thereby leaving even more blood glucose available to the fetus. • Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) stimulates the fetal anterior pituitary gland to secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). • ACTH stimulates fetal cortisol, which triggers fetal lung maturation and surfactant production. • Placental CRH levels increase greatly toward the end of the pregnancy and stimulate the fetus and the placenta to produce more estrogens. • Increased levels of estrogen act as a timer for birth and preparation for lactation.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.