Search Results
Results for: 'glucose transport'
Types of Transport - Uniport, Antiport and Symport (Glucose and Na+K+ Transporters)
By: HWC, Views: 11061
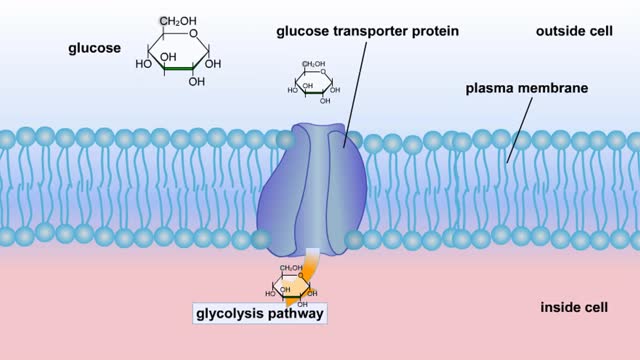
Some transport proteins bind and transport molecules very selectively. Uniport is the transport of one solute molecule. Symport is the transports of two solute molecules in the same direction. Antiport is the transports of two solute molecules in opposite directions. 1. Glucose bin...
Cellular Respiration & Glucose Mobilization (Glucose transport & Phosphorylation of Glucose)
By: HWC, Views: 11166
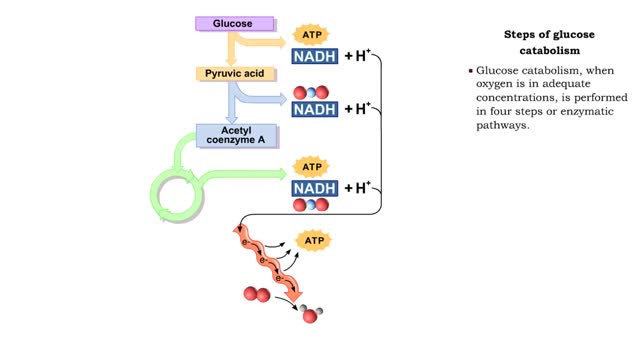
Glucose is completely broken down into CO2 and H2O during the process of cellular respiration, which includes 3 stages: 1) glycolysis; 2) the Krebs Cycle; and 3) the electron transport chain. Glucose enters this energy yielding pathway of cellular respiration in the first stage known as...
By: HWC, Views: 11672
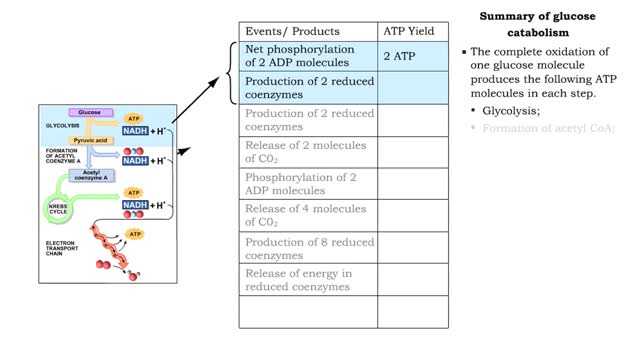
■ The complete oxidation of one glucose molecule produces the following ATP molecules in each step. • Glycolysis; • Formation of acetyl CoA; • Krebs cycle; • Electron transport chain. ■ In addition, glucose catabolism produces six CO2 molecules and water.
By: HWC, Views: 11614
• During digestion, complex carbohydrates are hydrolyzed into monosaccharides, primarily glucose. • The catabolism of glucose is the primary source of energy for cellular production of ATP. • The anabolism of glucose is important in regulating blood glucose levels. • Glucose cat...
Carbohydrate digestion (brush border enzymes, end products) & Carb absorption (fructose, galactose)
By: HWC, Views: 11302
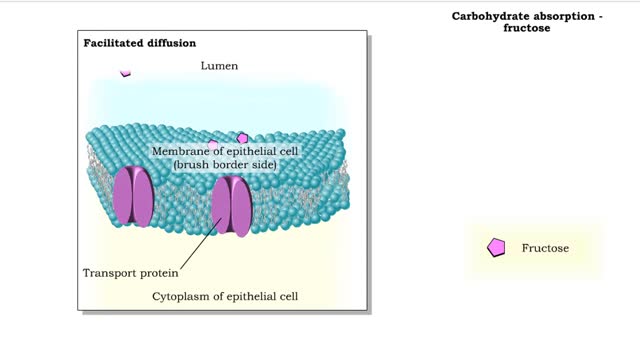
• Carbohydrate digestion concludes in microvilli of the small intestine, in brush border epithelial cells. Carbohydrate digestion -brush border enzymes • Four brush-border enzymes are involved: • Alpha-dextrinase breaks down alpha-dextrin chains by removing glucose units. • Sucras...
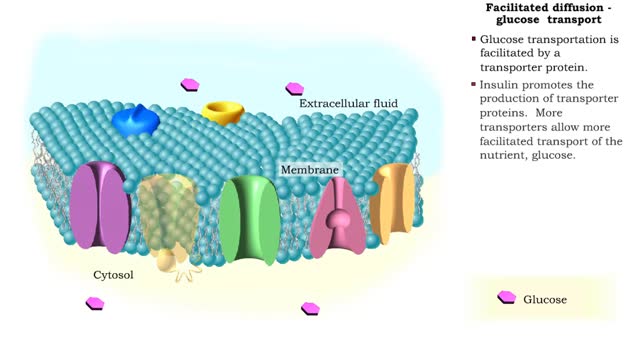
Facilitated Diffusion - Glucose transport
By: HWC, Views: 11629
Transmembrane proteins help solutes that are too polar or too highly charged move through the lipid bilayer The processes involved are: Channel mediated facilitated diffusion Carrier mediated facilitated diffusion In facilitated diffusion, molecules only move with the aid of a protein i...
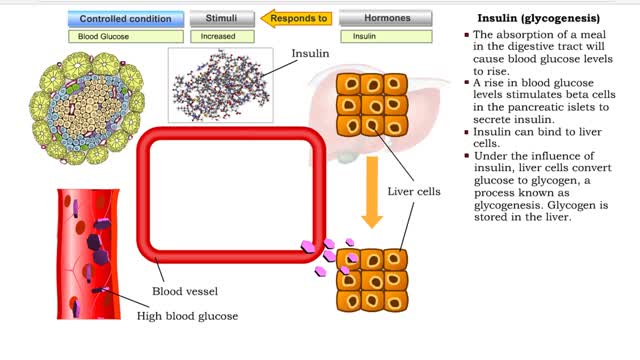
Insulin (glucose uptake by body cells), glycogenesis and lipogenesis
By: HWC, Views: 11618
Insulin is the regulator that allows the sugar from the foods we eat (be it a piece of cake or a stick of celery) to enter our tissues and become part of the metabolic process. Insulin is made by the Islets of Langerhans, which are found in the pancreas of every person. As we previously mentio...
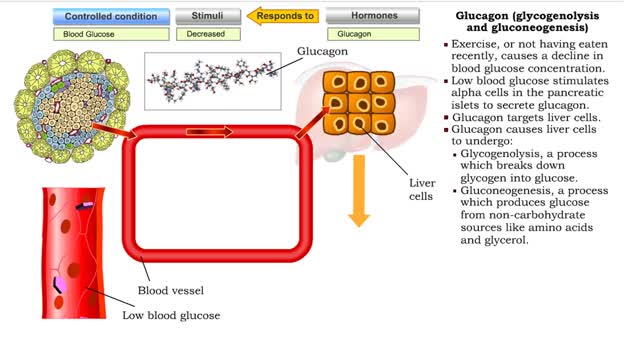
Glucagon (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11189
• Exercise, or not having eaten recently, causes a decline in blood glucose concentration. • Low blood glucose stimulates alpha cells in the pancreatic islets to secrete glucagon. • Glucagon targets liver cells. • Glucagon causes liver cells to undergo: • Glycogenolysis, a proce...
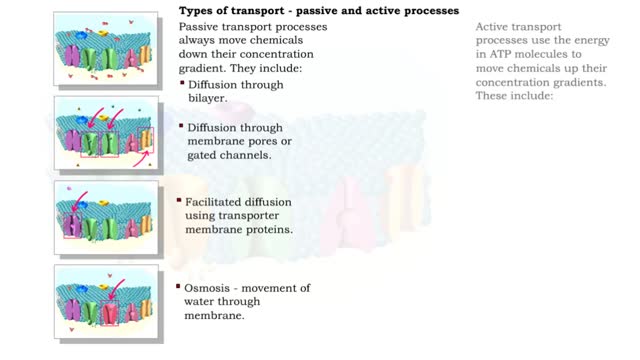
Type of Transport - Active and Passive Processes
By: HWC, Views: 11698
Active transport moves materials from lower to a higher concentration, while passive transport moves materials from higher to lower concentration. Active transport requires energy to proceed, while passive transport does not require the input of extra energy to occur. Transport processes that ...
Advertisement