Search Results
Results for: 'hemoglobin'
Oxygen transport: association and dissociation & Factors that affect hemoglobin's saturation with O2
By: HWC, Views: 11494
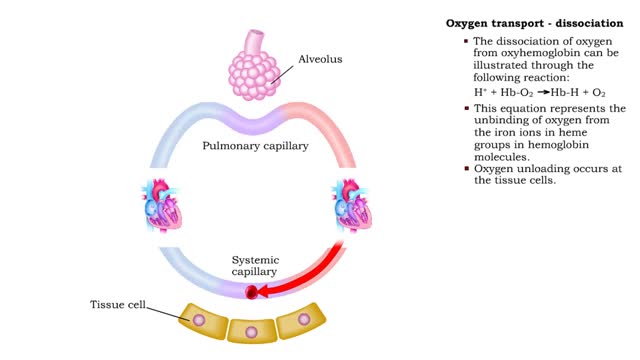
• The production of oxyhemoglobin can be illustrated through the following reaction: 02 + Hb-H --) Hb-02 + H+ • This equation represents the binding of oxygen to the iron ions in heme groups in hemoglobin molecules. • Oxygen binding or loading occurs at the lungs • The dissociatio...
Oxygen - hemoglobin dissociation curve & Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - acidity
By: HWC, Views: 12178
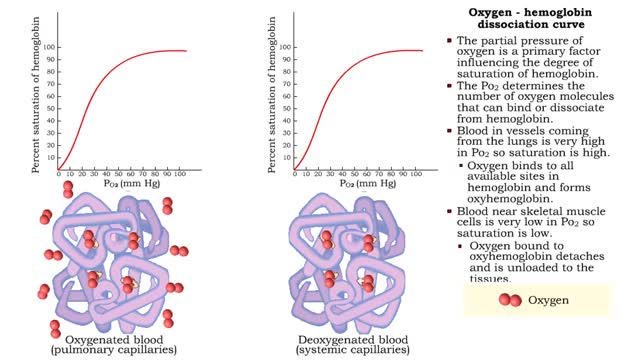
• The partial pressure of oxygen is a primary factor influencing the degree of saturation of hemoglobin. • The Po2 determines the number of oxygen molecules that can bind or dissociate from hemoglobin. • Blood in vessels coming from the lungs is very high in Po2 so saturation is high. ...
How Hemoglobin Picks Up and Delivers Oxygen
By: HWC, Views: 11010
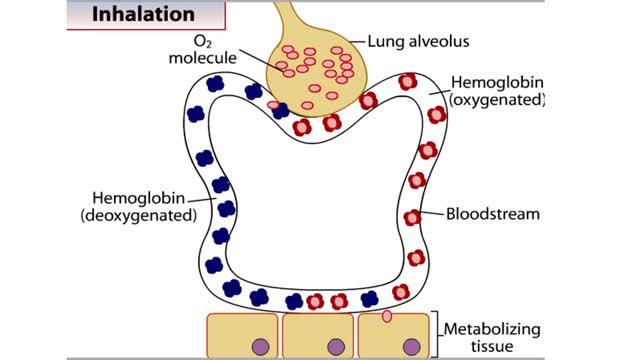
All of the cells in our bodies require oxygen (02) for survival and must release carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste product. The respiratory and circulatory systems work together as delivery systems for these gases. The lungs exchange these gases between the environment and the bloodstream. The bloo...
Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - carbon dioxide, temperature and bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
By: HWC, Views: 11605
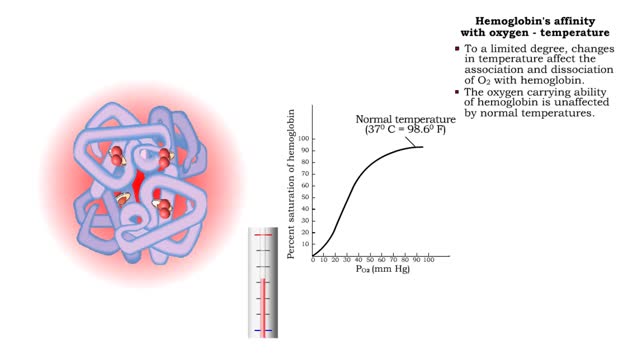
• The carbon dioxide gas is temporarily converted to carbonic acid in red blood cells by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, and then further converted to hydrogen and bicarbonate ions. • The result of increased carbon dioxide is decreased pH causing the Bohr effect. • Elevated carbon dioxid...
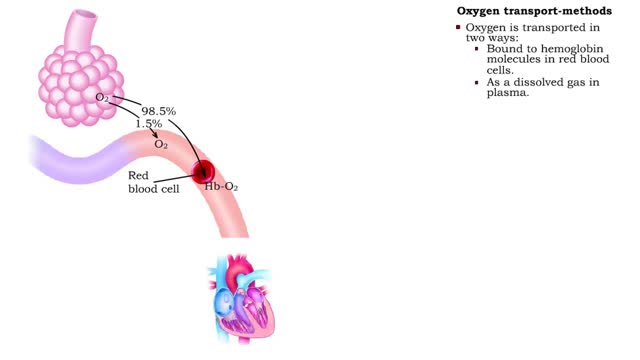
Oxygen transport - methods and oxyhemoglobin
By: HWC, Views: 11459
• The blood is the medium used for gas transport throughout the body. • Oxygen is only available in the lungs. Because the partial pressure of oxygen is higher in the alveoli than in the blood, oxygen diffuses into the blood and is transported to systemic cells. • At the tissues the par...
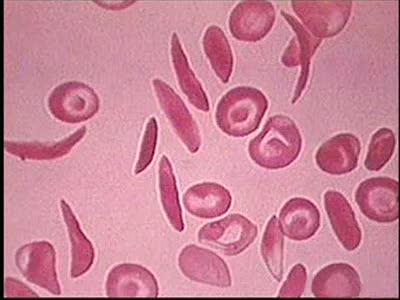
Introduction to Sickle Cell Anemia
By: Administrator, Views: 15121
Sickle cell anemia (sickle cell disease) is a disorder of the blood caused by an inherited abnormal hemoglobin (the oxygen-carrying protein within the red blood cells). The abnormal hemoglobin causes distorted (sickled appearing under a microscope) red blood cells.
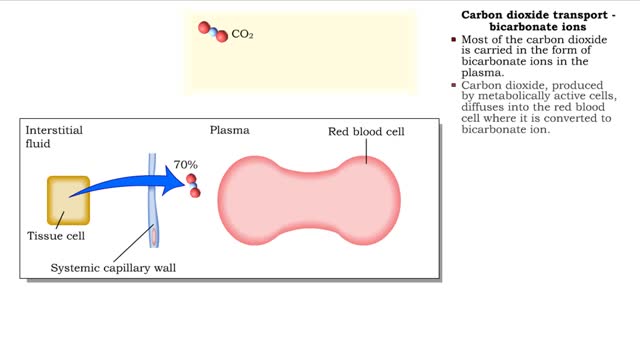
Methods of carbon dioxide transport - carbaminohemoglobin and bicarbonate ions
By: HWC, Views: 11685
• Carbon dioxide is transported three ways: • As bicarbonate ions in the plasma. • Bound to hemoglobin. • As a dissolved gas in the plasma. • A small percent of carbon dioxide is transported as a dissolved gas. • Some of the carbon dioxide is bound to hemoglobin, in the fo...
Apicomplexan life cycle Animation
By: HWC, Views: 6038
Malaria is caused by the sporozoan, Plasmodium. It is transferred to humans by mosquitoes. When an infected mosquito feeds, infective sporozoites move from her salivary glands into the human body. The bloodstream carries the sporozoites to the liver. Here, they reproduce asexually and...
Protein Structure - Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary
By: HWC, Views: 11485
A protein's first order structure, or primary structure, begins with the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain. The 20 different amino acids can be arranged in an infinite number of sequences. For example, the hormone insulin, which regulates the uptake of glucose from the blood into ce...
Advertisement