Search Results
Results for: 'metabolic reactions'
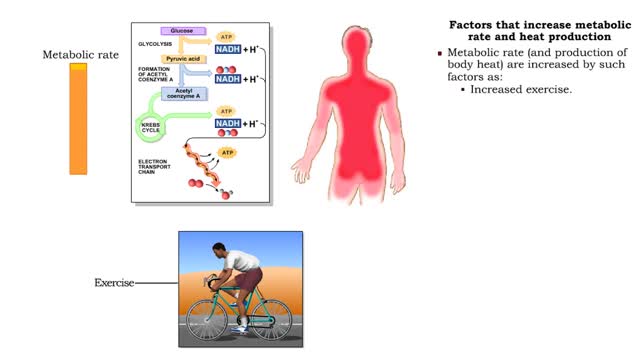
Factors that increase metabolic rate and heat production
By: HWC, Views: 11610
• All vital biochemical reactions are temperature dependent. • The overall rate at which metabolic reactions use energy is known as the metabolic rate. • Metabolic rate greatly determines body temperatures. • Temperature is maintained by balancing the loss of heat to the environment...
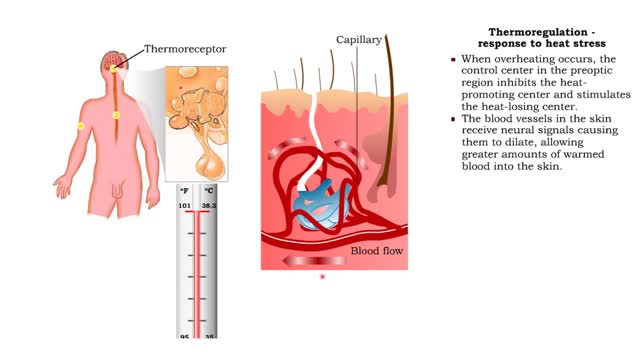
Metabolic Rate, Heat and Thermoregulation - response to heat and cold stresses
By: HWC, Views: 11696
• A neuron group in the anterior portion of the hypothalamus controls heat balance. • Neurons in the preoptic region of the hypothalamus integrate signals that come from thermoreceptors. • The temperature control center in the preoptic region propagates control signals to two other part...
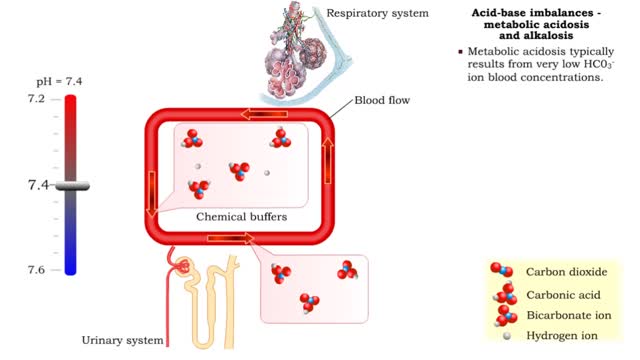
Acid-base imbalances - metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11607
• Metabolic acidosis typically results from very low HCO3- ion blood concentrations. • Metabolic alkalosis typically results from very high HCO3- ion blood concentrations.
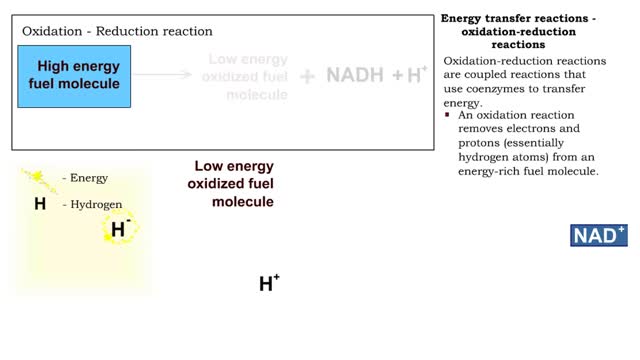
Types of energy transfer reactions: oxidation-reduction reactions and ATP generation reactions
By: HWC, Views: 12079
■ Metabolism balances anabolic and catabolic reactions. ■ Anabolism is energy transfer from ATP to simpler molecules in order to build them up into larger, more complex molecules. ■ Catabolism is breaking down larger, more complex molecules, usually to transfer energy from them in order...
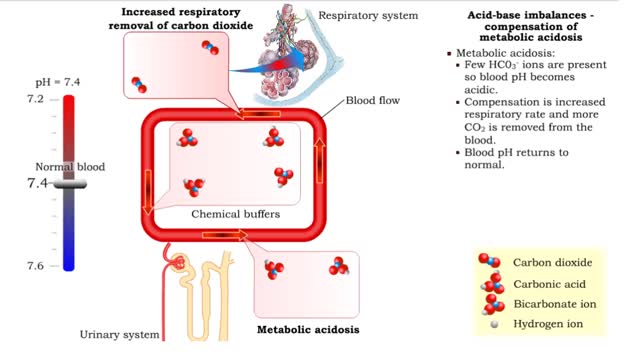
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11625
1. Metabolic acidosis: • Few HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased respiratory rate and more CO2 is removed from the blood. • Blood pH returns to normal. 2. Metabolic alkalosis: • Many HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes alkaline...
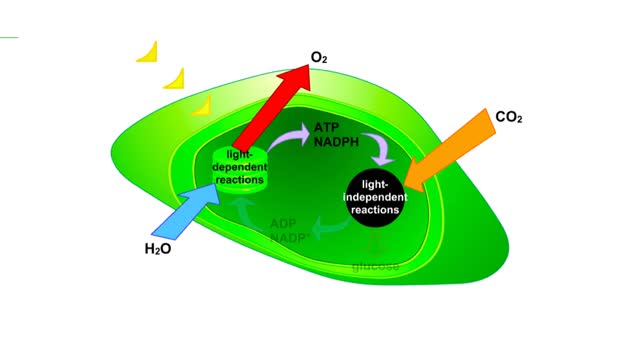
Photosynthesis overview Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5566
Illustration of the interrelationships of the light-dependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis. The light-dependent reactions split water, and produce ATP and NADPH. Oxygen is a by-product of these reactions. ATP and NADPH, together with carbon dioxide, are reactants in ...
By: HWC, Views: 11076
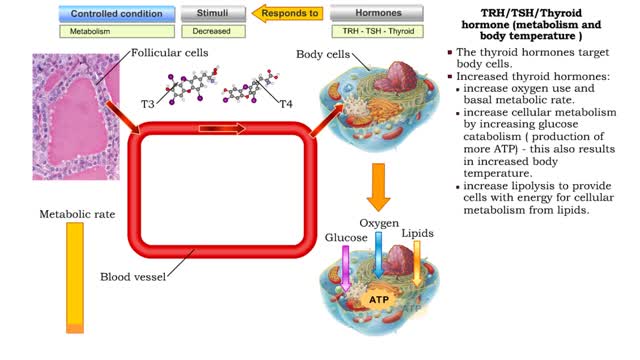
Thyroid hormone production • A decline in metabolic rate caused by increased metabolic need or physical exertion stimulates the production of thyrotropin hormone releasing (TRH) hormone from the cells of the hypothalamus. • Thyrotropin hormone releasing hormone targets the thyrotrophic ce...
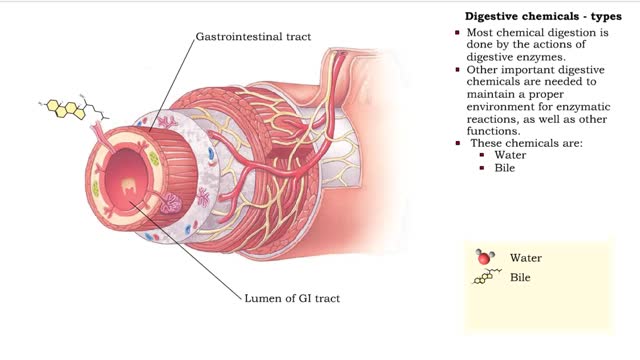
Digestive chemicals - types & enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 11525
• Chemical digestion breaks down food as it moves through the digestive tract. • Using enzymes and other digestive chemicals, the process reduces food particles into nutrient molecules that can be absorbed. • Most chemical digestion is done by the actions of digestive enzymes. • O...
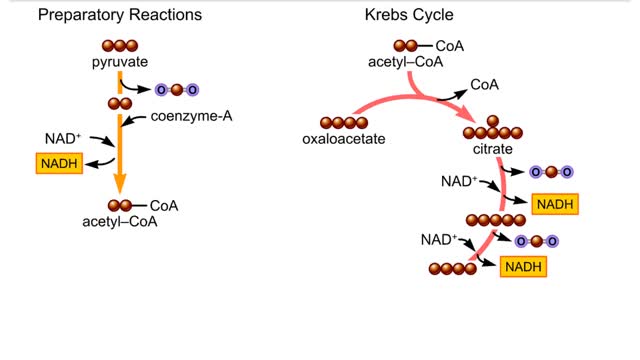
By: HWC, Views: 5705
The second-stage reactions of aerobic respiration. The second-stage reactions occur in a mitochondrion's inner compartment. In the first preparatory reaction, a carbon atom is stripped from pyruvate and released as carbon dioxide. The remaining carbons combine with coenzyme A and give ...
Advertisement