Search Results
Results for: 'multicelled animal'
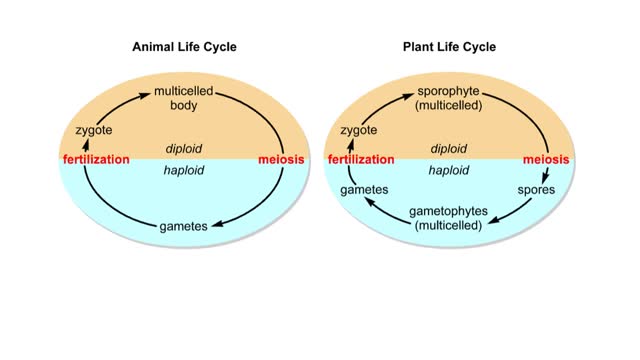
Generalized life cycles for plants and animals Animation
By: HWC, Views: 6017
But the life cycles of plants and animals differ in their details. In animals, a multicelled diploid stage gives rise to single-celled haploid gametes, the eggs and sperm. These gametes combine at fertilization to form a diploid zygote, which grows and develops into a new multicelled animal...
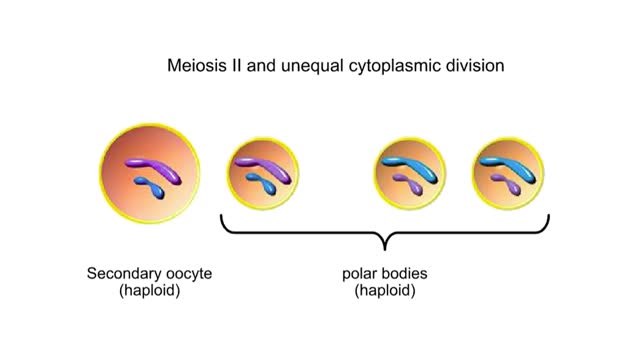
Egg and Sperm Formations in Animals Animation
By: HWC, Views: 6165
Inside the ovaries of a female animal are diploid germ cells called oogonia. An oogonium grows to become a primary oocyte. This large cell is still diploid. Meiosis I followed by unequal cytoplasmic division produces one large secondary oocyte and a smaller polar body. Both are haploid. ...
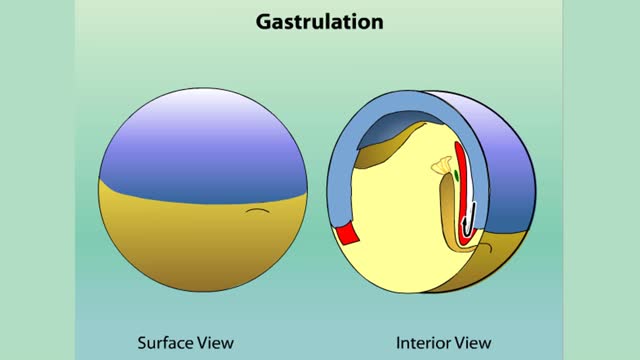
Gastrulation: cross section of the frog
By: HWC, Views: 10842
Gastrulation Most animals enter a phase early in development called gastrulation. In this phase, a tiny ball or disc of cells rearranges to form three embryonic layers of tissue, called germ layers. The germ layers of the embryo—now called a gastrula—are called the endoderm, mesoderm, and eco...
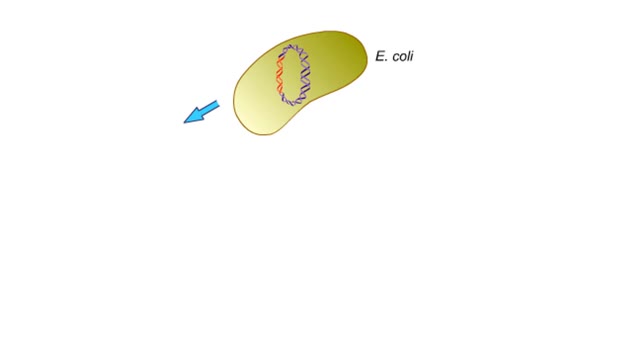
Transferring genes into plants Animation
By: HWC, Views: 9175
Researchers extract DNA from an organism that has a trait they want to introduce into a plant. The genetic donor can be a bacterial cell, a plant cell. or even an animal cell. The desired gene will be transferred into a plasmid, a small circle of bacterial DNA. The gene is cut out of th...
Bacteriophage (Virus) - Mice Experiment
By: HWC, Views: 11411
Also known as phages, these viruses can be found everywhere bacteria exist including, in the soil, deep within the earth's crust, inside plants and animals, and even in the oceans. Bacteriophages (phages) are viruses of bacteria that can kill and lyse the bacteria they infect. ... The lethalit...
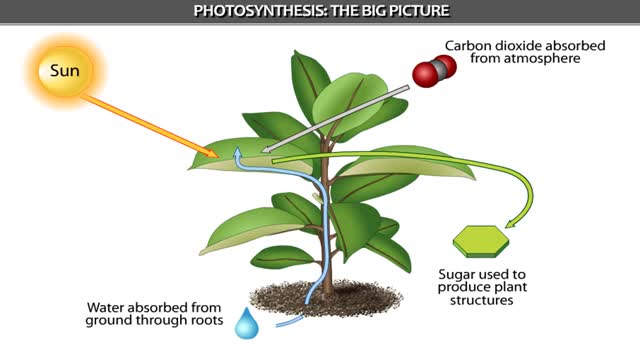
Brief Summary on Photosynthesis - Animation
By: HWC, Views: 10730
Can increase its weight by 150 pounds as it grows. Where does the new tissue come from? From the soil? From water? Or possibly from the air? The amazing truth is that new material. comes from an invisible gas in the air. In the process of photosynthesis, plants capture carbon dioxide ga...
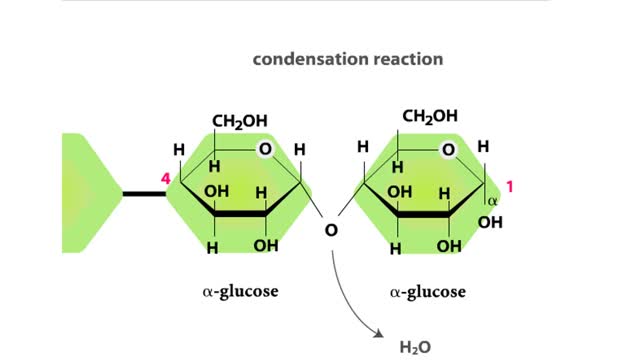
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Carbohydrates
By: HWC, Views: 11262
Carbohydrates include simple sugars (monosaccharides) as well as large polymers (polysaccharides). Glucose is a hexose, a sugar composed of six carbon atoms, usually found in ring form. A starch macromolecule is a polysaccharide composed of thousands of glucose units. Glucose molecules can be ...
By: HWC, Views: 8926
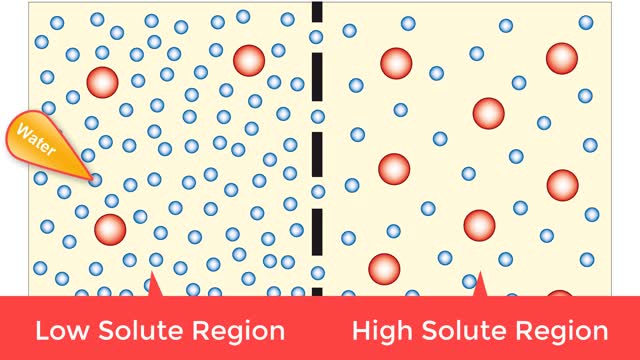
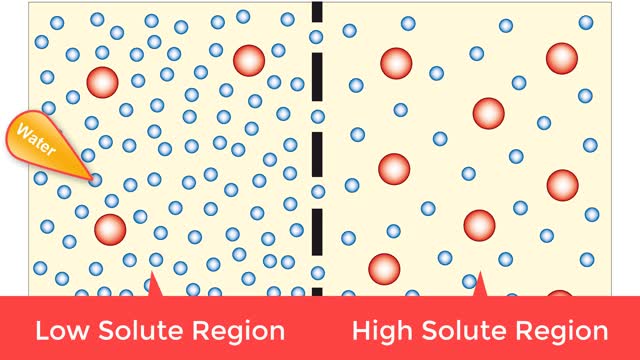
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
By: HWC, Views: 9438
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
Advertisement