Search Results
Results for: 'nephron'
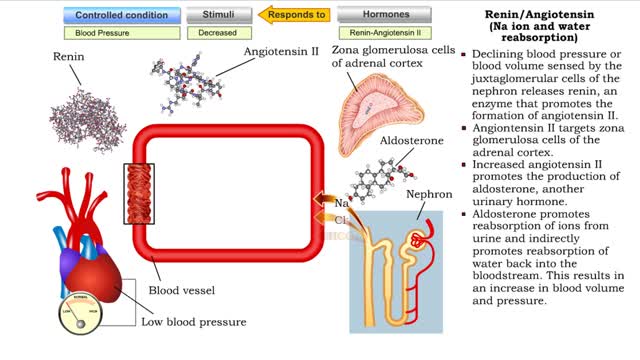
Renin/Angiotensin (water gain from urine & Na ion and water reabsorption)
By: HWC, Views: 11440
• Sensing declining blood pressure or blood volume, juxtaglomerular cells of the nephron release renin, an enzyme that promotes the formation of angiotensin II. • Angiotensin II targets smooth muscle cells in blood vessels that provide blood to the nephron. • Angiotensin II causes thes...
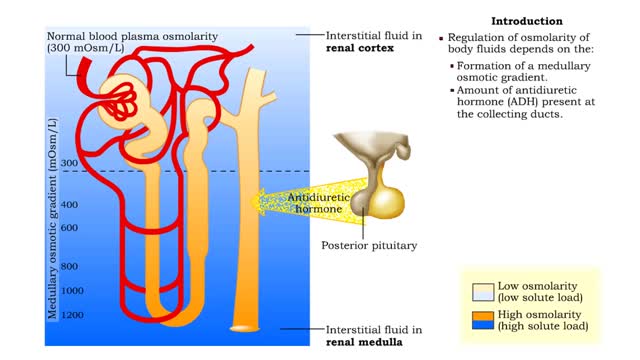
Medullary osmotic gradient - influencing factors
By: HWC, Views: 11917
▪ Maintenance of fluid volume and composition, despite changes in water input and output, is crucial to a healthy life. ▪ Regulation of blood's osmolarity, or solute concentration, is a function of the nephron. • Normal osmolarity is maintained by the ability of the nephron to alter uri...
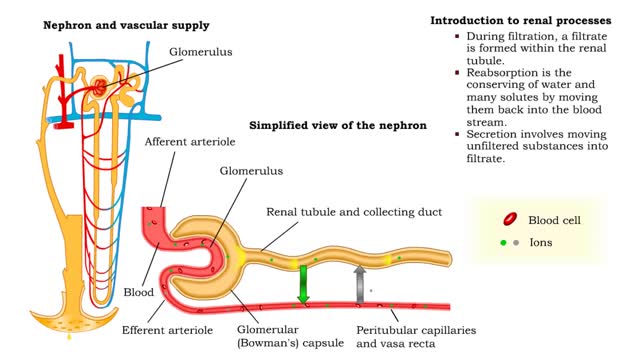
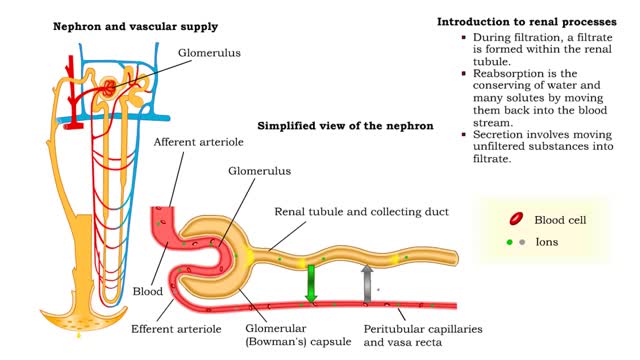
Introduction to filtration - filtrate formation and composition
By: HWC, Views: 11627
• At the nephron, the three process responsible for the formation of urine include: • Glomerular filtration. • Tubular reabsorption. • Tubular secretion. • During filtration, a filtrate is formed within the renal tubule. • Reabsorption is the conserving of water and many s...
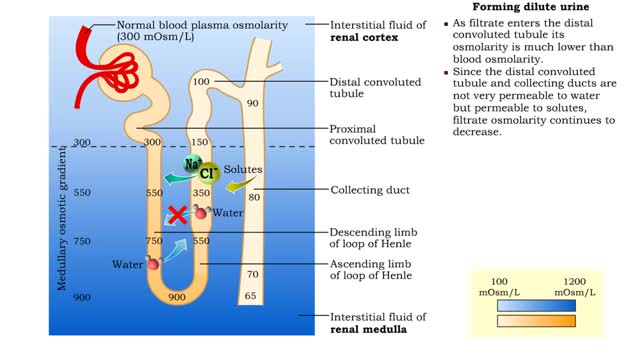
Forming urine ( influencing factors), Forming dilute urine & Forming concentrated urine
By: HWC, Views: 11968
• The amount of urine produced by the nephron depends on : • Body fluid volume. • Body fluid composition. • Dilute urine is formed when the body is normally hydrated. • The medullary osmotic gradient determines the osmolarity of the filtrate. • Filtrate osmolarity increase...
Carbohydrate Metabolism: Introduction to renal processes and filtrate formation and composition
By: HWC, Views: 11623
• At the nephron, the three process responsible for the formation of urine include: • Glomerular filtration. • Tubular reabsorption. • Tubular secretion. • During filtration, a filtrate is formed within the renal tubule. • Reabsorption is the conserving of water and many s...
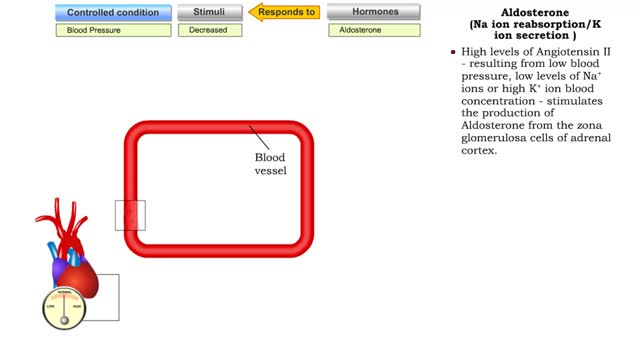
Atrial natriuretic peptide (vasodilation) & Aldosterone
By: HWC, Views: 11217
• Certain situations will cause the body's stress level to rise. • increased blood pressure will stretch the atria of the heart, stimulating the secretion of atria natriuretic peptide (MP). • ANP causes muscle cells in blood vessels to relax. • Blood pressure is lowered as a result ...
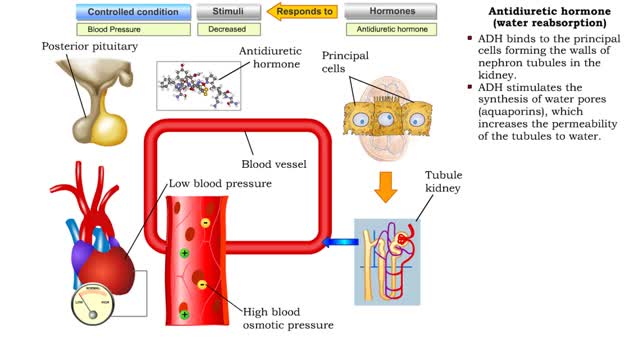
Antidiuretic hormone (vasoconstriction, water reabsorption & sweat inhibition)
By: HWC, Views: 11305
• Dehydration, blood loss, and low amounts of water in the blood can cause blood volume and pressure to decrease. • Neurosecretoxy cells in the posterior pituitary release antidiuretic hormone(ADH). • ADH binds to smooth muscle cells in blood vessel walls, stimulating them to vasoconstr...
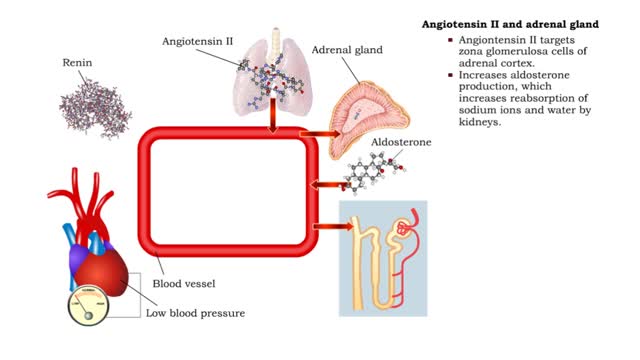
Angiotensin II - kidneys, adrenal glands and dehydration
By: HWC, Views: 11555
• Angiontensin II targets cells in the proximal convoluted tubule of the nephron. ■ The reabsorption of Na+ and Cl- ions sets up an osmotic gradient favoring the retention of water. • Decreases urine production and increases blood volume and pressure. • Angiontensin II targets zon...
By: HWC, Views: 12269
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
Advertisement