Search Results
Results for: 'paternal chromosomes'
Random alignment at Metaphase I Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5586
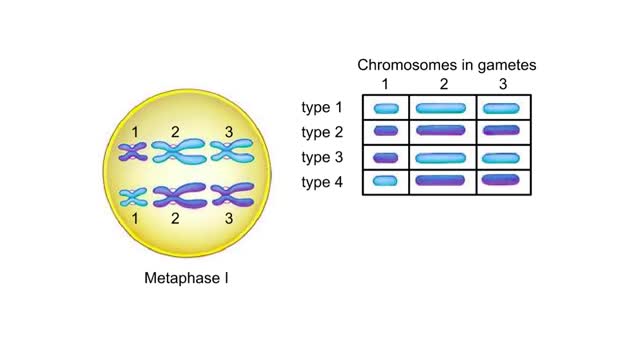
Possible outcomes of random alignment at metaphase I. In this example, three types of chromosomes are labeled 1, 2, and 3. Maternal chromosomes are dark blue; paternal ones are light blue. Suppose that at metaphase I all the maternal chromosomes became attached to one spindle pole and all the ...
By: HWC, Views: 9294
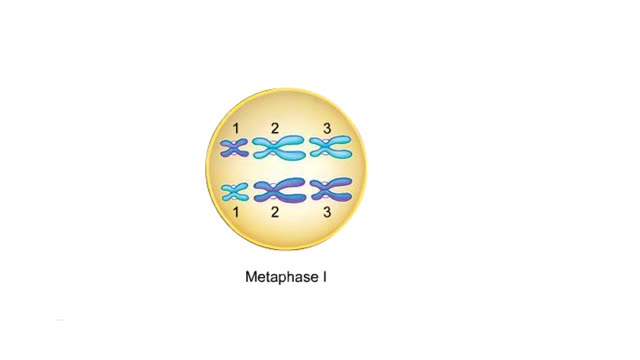
This is a cell during metaphase I. For each pair of chromosomes, any gamete produced by this cell could contain either the maternal chromosome or the paternal chromosome. How many different combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes are possible in the gametes produced by a cell with th...
Homologous chromosomes during prophase I - Animation
By: HWC, Views: 9057
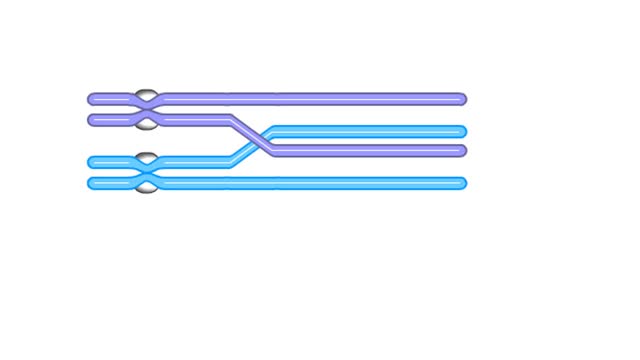
The chromosomes were duplicated during interphase and the sister chromatids are now in thin threadlike form. Each chromosome becomes zippered to its homologue, so that all four chromatids are closely aligned. The chromosomes are tightly aligned, but we will show them as separate so that y...
By: HWC, Views: 9118
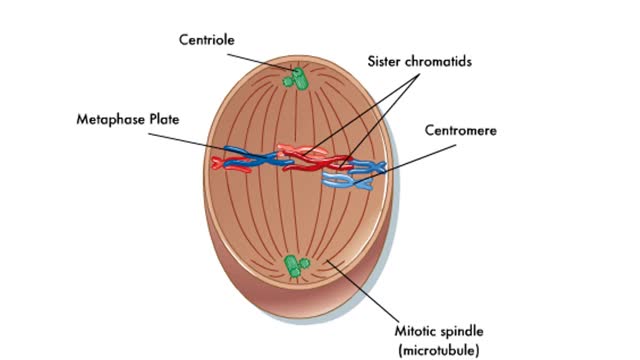
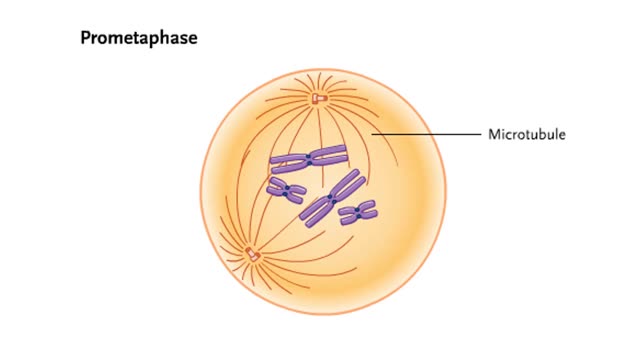
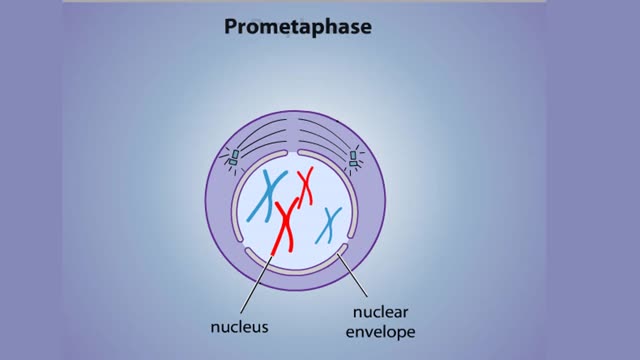
Prophase is the first step in the mitotic process. During prophase, the chromosomes condense. The centrosomes begin to form a spindle and move into position on opposite sides of the cell. Sister chromatids are held together by a protein called cohesin at the centromere. Prometaphase is the sec...
A Human Karyotype Preparation Animation
By: HWC, Views: 8429
Blood is collected from the person being analyzed. The blood is added to a growth medium that also contains a chemical that stimulates mitosis. The cells are allowed to grow in this medium for two or three days at body temperature. Colchicine is added to arrest cell division at metaphase. T...
By: HWC, Views: 9243
During interphase, the chromosomes will be duplicated in preparation for mitosis, which divides the chromosomes, and cytokinesis, which divides the cell's cytoplasm. In early prophase, the duplicated chromosomes begin to condense. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids joined at the...
Stages of Mitosis - Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase & Telophase
By: HWC, Views: 10878
In mitosis, the nucleus divides to produce two nuclei that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent nucleus. To prepare for division, the DNA replicates in the preceding interphase. Although the chromosomes are not yet compacted and visible as discrete bodies, we illustrate them ...
Hierarchical Sequencing Method - Sequence Tagged Sites
By: HWC, Views: 10367
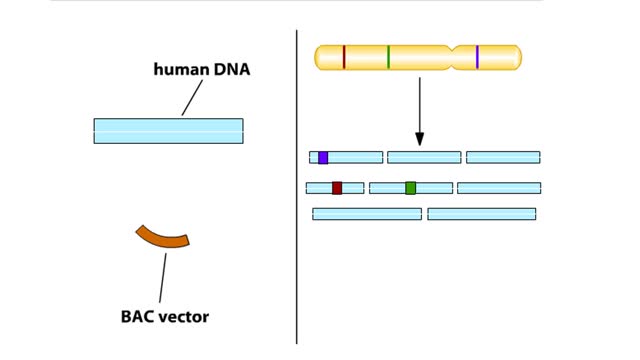
In the hierarchical sequencing method, researchers begin by collecting cells. In humans, each cell contains 23 pairs of chromo-somes. Here we specifically track the DNA from just one of the 23 pairs. Chromosomes have a series of unique DNA sequences, called sequence-tagged sites (STSs), that a...
By: HWC, Views: 5674
Diploid organisms have pairs of genes, on pairs of homologous chromosomes. Each gene has a specific location on the chromosome. We call this the gene's locus. In this species, the locus for gene B is always between the loci for genes A and C. Most genes come in two or more slightly differen...
Advertisement