Search Results
Results for: 'weak%20acid'
Buffers definition and the role of buffer in the body
By: HWC, Views: 11053
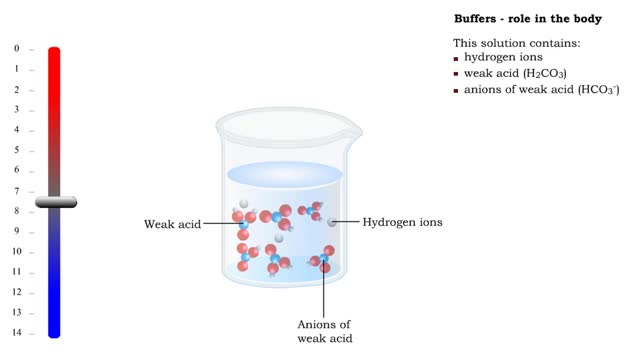
■ Too many H+ break hydrogen bonds and a protein comes apart. ■ Buffers react with excess H+ to protect proteins from breaking down. ■ Buffers consist of weak acid plus anions of that weak acid. This solution contains: • hydrogen ions • weak acid (H2CO3) • anions of we...
The pH scale - Strong acids and Weak acids
By: HWC, Views: 11092
The pH scale • Expresses concentration of H+. • range: 0-14. • 7 is neutral. • Less 7 is acid. • greater 7 is basic (alkaline). Strong acids - role in the body ■ In strong acids all molecules dissociate. ■ HC1 is highly acidic and found only in the stomach. • H...
What are Strong & Weak Acids and How they're different?
By: HWC, Views: 9805
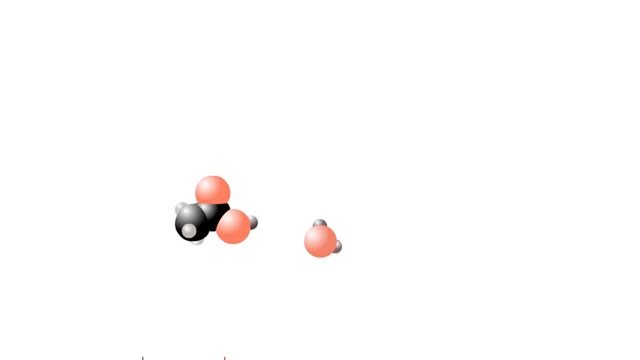
Let's consider the changes that take place when hydrogen chloride, HCI, is added to water. You will need to recognize space-filling models of HCI molecules, hydronium ions (H30+), chloride ions (C11, and water molecules (H20). They are shown at the right. When HC1 molecules dissolve in water, ...
Double Vacuum Process (Illustration No Audio)
By: HWC, Views: 10078
In this so-called low-pressure process, the wood is first subjected to a short and relatively weak initial vacuum, after which the treatment vessel is flooded with preservative solution and reduced to normal pressure The double vacuum container is loaded with timber. A partial vacuum is draw...
Ionic bonds - role of ions in the body
By: HWC, Views: 11291
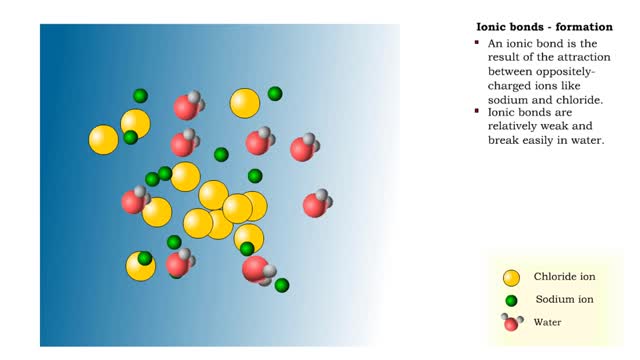
Ions • Atoms fill up the outer orbital by transferring electrons from one atom to another. • Atoms now bear a charge and are called ions. • Sodium ion, losing an electron, has a +1 charge. • Chlorine ion, gaining an electron, has a -1 charge. Formation • An ionic bond is t...
Fetal development - Weeks 9 to 38
By: HWC, Views: 11227
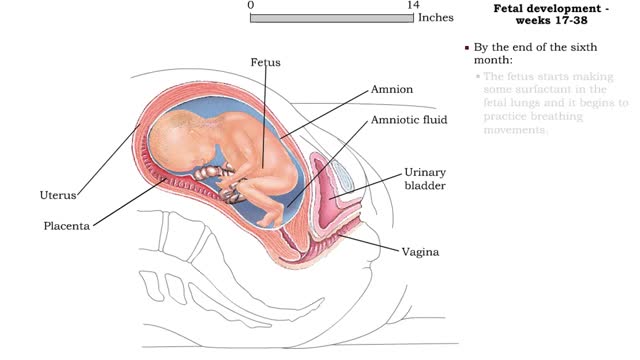
Weeks 9-12 • Fetal development during the third month includes: • A large head, about 1/2 the length of the fetus. • Visible eyes and ears. • A detectable heartbeat. • Kidneys that form urine. • Gender identification. • Weak, undetectable body movements. • By the e...
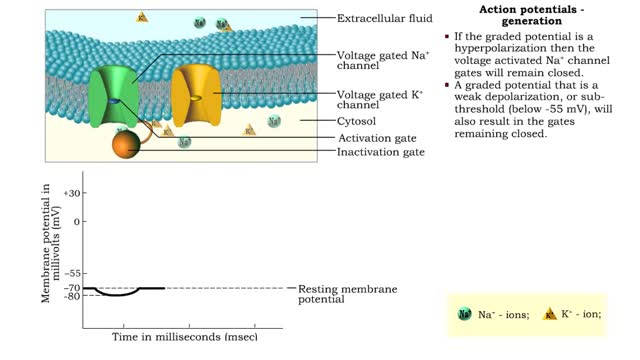
Action potentials - electrical characteristics and generation
By: HWC, Views: 10853
• An action potential is the nervous impulse or signal for long distance communication. Each action potential is generated at the cell's trigger zone. • Action potentials are considered an all-or-nothing phenomena because they are either generated or not. • The generation of an action...
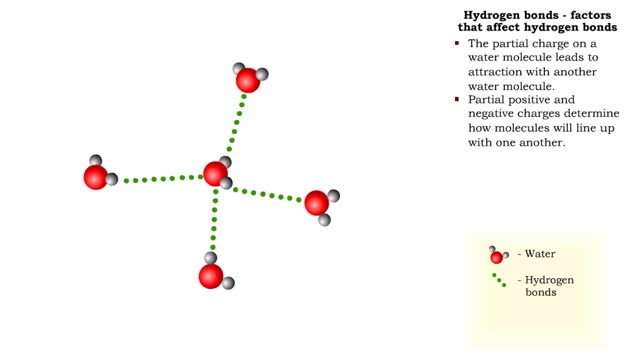
Hydrogen bonds - role in the body
By: HWC, Views: 11334
A hydrogen bond is the electromagnetic attraction between polar molecules in which hydrogen is bound to a larger atom, such as oxygen or nitrogen. This is not a sharing of electrons, as in a covalent bond. Instead, this is an attraction between the positive and negative poles of charged atoms. ...
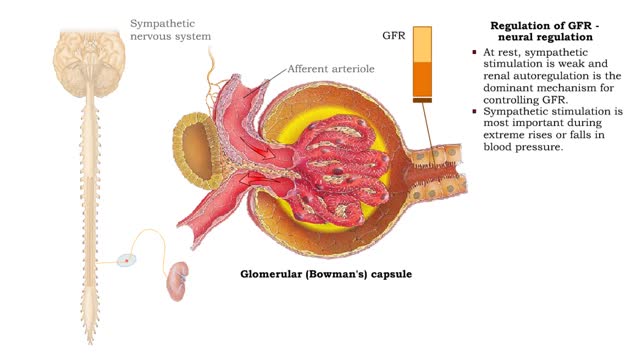
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via tubuloglomerular feedback, neural & hormonal regulation
By: HWC, Views: 12089
• When blood pressure is above normal, rapid filtrate flow reduces ion retention so filtrate in tubule has more Na+, C1-, and water. • It is believed that vasoconstricting chemicals from the juxtaglomerular cells are released when the macula densa cells detect higher water and ion levels in ...
Advertisement